add all llamacpypy
This commit is contained in:
parent
eb3d30e53d
commit
092393781f
9 changed files with 1208 additions and 240 deletions
134
.gitignore
vendored
134
.gitignore
vendored
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,133 @@
|
|||
# Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
*.py[cod]
|
||||
*$py.class
|
||||
|
||||
# C extensions
|
||||
*.so
|
||||
|
||||
# Distribution / packaging
|
||||
.Python
|
||||
build/
|
||||
develop-eggs/
|
||||
dist/
|
||||
downloads/
|
||||
eggs/
|
||||
.eggs/
|
||||
lib/
|
||||
lib64/
|
||||
parts/
|
||||
sdist/
|
||||
var/
|
||||
wheels/
|
||||
pip-wheel-metadata/
|
||||
share/python-wheels/
|
||||
*.egg-info/
|
||||
.installed.cfg
|
||||
*.egg
|
||||
MANIFEST
|
||||
|
||||
# PyInstaller
|
||||
# Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
|
||||
# before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
|
||||
*.manifest
|
||||
*.spec
|
||||
|
||||
# Installer logs
|
||||
pip-log.txt
|
||||
pip-delete-this-directory.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Unit test / coverage reports
|
||||
htmlcov/
|
||||
.tox/
|
||||
.nox/
|
||||
.coverage
|
||||
.coverage.*
|
||||
.cache
|
||||
nosetests.xml
|
||||
coverage.xml
|
||||
*.cover
|
||||
*.py,cover
|
||||
.hypothesis/
|
||||
.pytest_cache/
|
||||
|
||||
# Translations
|
||||
*.mo
|
||||
*.pot
|
||||
|
||||
# Django stuff:
|
||||
*.log
|
||||
local_settings.py
|
||||
db.sqlite3
|
||||
db.sqlite3-journal
|
||||
|
||||
# Flask stuff:
|
||||
instance/
|
||||
.webassets-cache
|
||||
|
||||
# Scrapy stuff:
|
||||
.scrapy
|
||||
|
||||
# Sphinx documentation
|
||||
docs/_build/
|
||||
|
||||
# PyBuilder
|
||||
target/
|
||||
|
||||
# Jupyter Notebook
|
||||
.ipynb_checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
# IPython
|
||||
profile_default/
|
||||
ipython_config.py
|
||||
|
||||
# pyenv
|
||||
.python-version
|
||||
|
||||
# pipenv
|
||||
# According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
|
||||
# However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
|
||||
# having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
|
||||
# install all needed dependencies.
|
||||
#Pipfile.lock
|
||||
|
||||
# PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow
|
||||
__pypackages__/
|
||||
|
||||
# Celery stuff
|
||||
celerybeat-schedule
|
||||
celerybeat.pid
|
||||
|
||||
# SageMath parsed files
|
||||
*.sage.py
|
||||
|
||||
# Environments
|
||||
.env
|
||||
.venv
|
||||
env/
|
||||
venv/
|
||||
ENV/
|
||||
env.bak/
|
||||
venv.bak/
|
||||
|
||||
# Spyder project settings
|
||||
.spyderproject
|
||||
.spyproject
|
||||
|
||||
# Rope project settings
|
||||
.ropeproject
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdocs documentation
|
||||
/site
|
||||
|
||||
# mypy
|
||||
.mypy_cache/
|
||||
.dmypy.json
|
||||
dmypy.json
|
||||
|
||||
# Pyre type checker
|
||||
.pyre/
|
||||
|
||||
*.o
|
||||
*.a
|
||||
.cache/
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,10 +148,6 @@ models/*
|
|||
|
||||
/main
|
||||
/quantize
|
||||
/result
|
||||
|
||||
arm_neon.h
|
||||
compile_commands.json
|
||||
|
||||
.envrc
|
||||
.direnv/
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -129,3 +129,11 @@ target_include_directories(ggml PUBLIC .)
|
|||
target_link_libraries(quantize PRIVATE ggml)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(llama PRIVATE ggml)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(ggml PRIVATE Threads::Threads)
|
||||
|
||||
add_subdirectory(extern/pybind11)
|
||||
pybind11_add_module(_core src/inference.cpp src/inference.h utils.cpp utils.h ggml.c ggml.h)
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(_core PUBLIC ${LLAMA_EXTRA_FLAGS})
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(_core PRIVATE VERSION_INFO=${PROJECT_VERSION})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(_core PRIVATE ggml)
|
||||
|
||||
install(TARGETS _core DESTINATION llamacpypy)
|
||||
281
README.md
281
README.md
|
|
@ -1,254 +1,63 @@
|
|||
# llama.cpp
|
||||
# llamacpypy
|
||||
llamacpp but wrapped in python
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/actions)
|
||||
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
|
||||
This allows serving llama using libraries such as fastAPI using the optimized and in particular quantized models of the [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) ecosystem instead of using torch directly. This should decrease ressource consumption over plain torch.
|
||||
|
||||
Inference of [LLaMA](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971) model in pure C/C++
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
**Hot topics:**
|
||||
Atm this is all very raw so it will require some work on the users part.
|
||||
|
||||
- RMSNorm implementation / fixes: https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/issues/173
|
||||
- Cache input prompts for faster initialization: https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/issues/64
|
||||
- Create a `llama.cpp` logo: https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/issues/105
|
||||
|
||||
## Description
|
||||
|
||||
The main goal is to run the model using 4-bit quantization on a MacBook
|
||||
|
||||
- Plain C/C++ implementation without dependencies
|
||||
- Apple silicon first-class citizen - optimized via ARM NEON
|
||||
- AVX2 support for x86 architectures
|
||||
- Mixed F16 / F32 precision
|
||||
- 4-bit quantization support
|
||||
- Runs on the CPU
|
||||
|
||||
This was [hacked in an evening](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/issues/33#issuecomment-1465108022) - I have no idea if it works correctly.
|
||||
Please do not make conclusions about the models based on the results from this implementation.
|
||||
For all I know, it can be completely wrong. This project is for educational purposes.
|
||||
New features will probably be added mostly through community contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported platforms:
|
||||
|
||||
- [X] Mac OS
|
||||
- [X] Linux
|
||||
- [X] Windows (via CMake)
|
||||
- [X] Docker
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a typical run using LLaMA-7B:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
make -j && ./main -m ./models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
|
||||
I llama.cpp build info:
|
||||
I UNAME_S: Darwin
|
||||
I UNAME_P: arm
|
||||
I UNAME_M: arm64
|
||||
I CFLAGS: -I. -O3 -DNDEBUG -std=c11 -fPIC -pthread -DGGML_USE_ACCELERATE
|
||||
I CXXFLAGS: -I. -I./examples -O3 -DNDEBUG -std=c++11 -fPIC -pthread
|
||||
I LDFLAGS: -framework Accelerate
|
||||
I CC: Apple clang version 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
|
||||
I CXX: Apple clang version 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
|
||||
|
||||
make: Nothing to be done for `default'.
|
||||
main: seed = 1678486056
|
||||
llama_model_load: loading model from './models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin' - please wait ...
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_vocab = 32000
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_ctx = 512
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_embd = 4096
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_mult = 256
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_head = 32
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_layer = 32
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_rot = 128
|
||||
llama_model_load: f16 = 2
|
||||
llama_model_load: n_ff = 11008
|
||||
llama_model_load: ggml ctx size = 4529.34 MB
|
||||
llama_model_load: memory_size = 512.00 MB, n_mem = 16384
|
||||
llama_model_load: .................................... done
|
||||
llama_model_load: model size = 4017.27 MB / num tensors = 291
|
||||
|
||||
main: prompt: 'Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:'
|
||||
main: number of tokens in prompt = 15
|
||||
1 -> ''
|
||||
8893 -> 'Build'
|
||||
292 -> 'ing'
|
||||
263 -> ' a'
|
||||
4700 -> ' website'
|
||||
508 -> ' can'
|
||||
367 -> ' be'
|
||||
2309 -> ' done'
|
||||
297 -> ' in'
|
||||
29871 -> ' '
|
||||
29896 -> '1'
|
||||
29900 -> '0'
|
||||
2560 -> ' simple'
|
||||
6576 -> ' steps'
|
||||
29901 -> ':'
|
||||
|
||||
sampling parameters: temp = 0.800000, top_k = 40, top_p = 0.950000
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:
|
||||
1) Select a domain name and web hosting plan
|
||||
2) Complete a sitemap
|
||||
3) List your products
|
||||
4) Write product descriptions
|
||||
5) Create a user account
|
||||
6) Build the template
|
||||
7) Start building the website
|
||||
8) Advertise the website
|
||||
9) Provide email support
|
||||
10) Submit the website to search engines
|
||||
A website is a collection of web pages that are formatted with HTML. HTML is the code that defines what the website looks like and how it behaves.
|
||||
The HTML code is formatted into a template or a format. Once this is done, it is displayed on the user's browser.
|
||||
The web pages are stored in a web server. The web server is also called a host. When the website is accessed, it is retrieved from the server and displayed on the user's computer.
|
||||
A website is known as a website when it is hosted. This means that it is displayed on a host. The host is usually a web server.
|
||||
A website can be displayed on different browsers. The browsers are basically the software that renders the website on the user's screen.
|
||||
A website can also be viewed on different devices such as desktops, tablets and smartphones.
|
||||
Hence, to have a website displayed on a browser, the website must be hosted.
|
||||
A domain name is an address of a website. It is the name of the website.
|
||||
The website is known as a website when it is hosted. This means that it is displayed on a host. The host is usually a web server.
|
||||
A website can be displayed on different browsers. The browsers are basically the software that renders the website on the user’s screen.
|
||||
A website can also be viewed on different devices such as desktops, tablets and smartphones. Hence, to have a website displayed on a browser, the website must be hosted.
|
||||
A domain name is an address of a website. It is the name of the website.
|
||||
A website is an address of a website. It is a collection of web pages that are formatted with HTML. HTML is the code that defines what the website looks like and how it behaves.
|
||||
The HTML code is formatted into a template or a format. Once this is done, it is displayed on the user’s browser.
|
||||
A website is known as a website when it is hosted
|
||||
|
||||
main: mem per token = 14434244 bytes
|
||||
main: load time = 1332.48 ms
|
||||
main: sample time = 1081.40 ms
|
||||
main: predict time = 31378.77 ms / 61.41 ms per token
|
||||
main: total time = 34036.74 ms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And here is another demo of running both LLaMA-7B and [whisper.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/whisper.cpp) on a single M1 Pro MacBook:
|
||||
|
||||
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1991296/224442907-7693d4be-acaa-4e01-8b4f-add84093ffff.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the step for the LLaMA-7B model:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# build this repo
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
|
||||
cd llama.cpp
|
||||
make
|
||||
|
||||
# obtain the original LLaMA model weights and place them in ./models
|
||||
ls ./models
|
||||
65B 30B 13B 7B tokenizer_checklist.chk tokenizer.model
|
||||
|
||||
# install Python dependencies
|
||||
python3 -m pip install torch numpy sentencepiece
|
||||
|
||||
# convert the 7B model to ggml FP16 format
|
||||
python3 convert-pth-to-ggml.py models/7B/ 1
|
||||
|
||||
# quantize the model to 4-bits
|
||||
./quantize.sh 7B
|
||||
|
||||
# run the inference
|
||||
./main -m ./models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -n 128
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When running the larger models, make sure you have enough disk space to store all the intermediate files.
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: add model disk/mem requirements
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive mode
|
||||
|
||||
If you want a more ChatGPT-like experience, you can run in interactive mode by passing `-i` as a parameter.
|
||||
In this mode, you can always interrupt generation by pressing Ctrl+C and enter one or more lines of text which will be converted into tokens and appended to the current context. You can also specify a *reverse prompt* with the parameter `-r "reverse prompt string"`. This will result in user input being prompted whenever the exact tokens of the reverse prompt string are encountered in the generation. A typical use is to use a prompt which makes LLaMa emulate a chat between multiple users, say Alice and Bob, and pass `-r "Alice:"`.
|
||||
|
||||
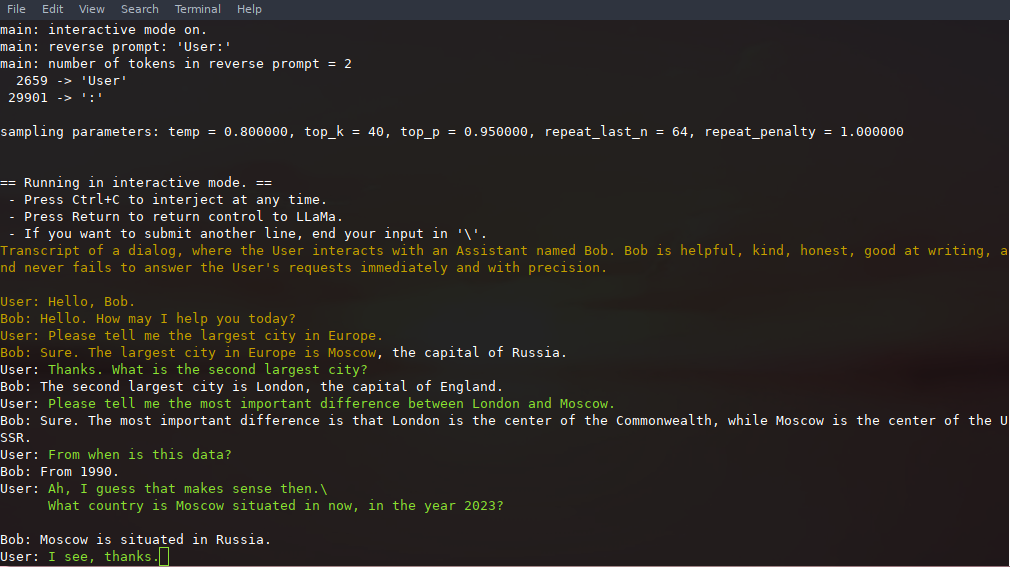
Here is an example few-shot interaction, invoked with the command
|
||||
```
|
||||
./main -m ./models/13B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -n 256 --repeat_penalty 1.0 --color -i -r "User:" \
|
||||
-p \
|
||||
"Transcript of a dialog, where the User interacts with an Assistant named Bob. Bob is helpful, kind, honest, good at writing, and never fails to answer the User's requests immediately and with precision.
|
||||
|
||||
User: Hello, Bob.
|
||||
Bob: Hello. How may I help you today?
|
||||
User: Please tell me the largest city in Europe.
|
||||
Bob: Sure. The largest city in Europe is Moscow, the capital of Russia.
|
||||
User:"
|
||||
### Clone the repo and pull the external repo for pybind11
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Note the use of `--color` to distinguish between user input and generated text.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Android
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily run `llama.cpp` on Android device with [termux](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.termux).
|
||||
First, obtain the [Android NDK](https://developer.android.com/ndk) and then build with CMake:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkdir build-android
|
||||
$ cd build-android
|
||||
$ export NDK=<your_ndk_directory>
|
||||
$ cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=$NDK/build/cmake/android.toolchain.cmake -DANDROID_ABI=arm64-v8a -DANDROID_PLATFORM=android-23 -DCMAKE_C_FLAGS=-march=armv8.4a+dotprod ..
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
```
|
||||
Install [termux](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.termux) on your device and run `termux-setup-storage` to get access to your SD card.
|
||||
Finally, copy the `llama` binary and the model files to your device storage. Here is a demo of an interactive session running on Pixel 5 phone:
|
||||
|
||||
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/271616/225014776-1d567049-ad71-4ef2-b050-55b0b3b9274c.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker
|
||||
|
||||
#### Prerequisites
|
||||
* Docker must be installed and running on your system.
|
||||
* Create a folder to store big models & intermediate files (in ex. im using /llama/models)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Images
|
||||
We have two Docker images available for this project:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full`: This image includes both the main executable file and the tools to convert LLaMA models into ggml and convert into 4-bit quantization.
|
||||
2. `ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:light`: This image only includes the main executable file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to download the models, convert them to ggml and optimize them is with the --all-in-one command which includes the full docker image.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -v /llama/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full --all-in-one "/models/" 7B
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/seemanne/llamacpypy.git
|
||||
cd llamacpypy
|
||||
git submodule update --init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On complete, you are ready to play!
|
||||
### Set up your venv and install the requirements as always
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -v /llama/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full --run -m /models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
|
||||
If you have poetry, there are artifacts in the pyproject file that should allow you to do `poetry install` to set up venv, however it wont install the project itself. This can be done by using `poetry shell` and then calling `pip install ./` as below.
|
||||
|
||||
If anyone want to fix the build process to make it less cumbersome, I would be very happy.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have another setup just pip install the reqs in your virtual env of choice and then continue as described below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Run makefile
|
||||
|
||||
This isn't actually required, but it will give compile errors if something is wrong.
|
||||
```
|
||||
make -j
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or with light image:
|
||||
### Install the module using pip
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -v /llama/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:light -m /models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install ./
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Limitations
|
||||
# Usage
|
||||
|
||||
- We don't know yet how much the quantization affects the quality of the generated text
|
||||
- Probably the token sampling can be improved
|
||||
- The Accelerate framework is actually currently unused since I found that for tensor shapes typical for the Decoder,
|
||||
there is no benefit compared to the ARM_NEON intrinsics implementation. Of course, it's possible that I simply don't
|
||||
know how to utilize it properly. But in any case, you can even disable it with `LLAMA_NO_ACCELERATE=1 make` and the
|
||||
performance will be the same, since no BLAS calls are invoked by the current implementation
|
||||
Initialize the model instance:
|
||||
```
|
||||
from llamacpypy import Llama
|
||||
|
||||
### Contributing
|
||||
llama = Llama('models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin', warm_start=False)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Load your model into memory:
|
||||
```
|
||||
llama.load_model()
|
||||
```
|
||||
Generate from a given prompt:
|
||||
```
|
||||
var = llama.generate("This is the weather report, we are reporting a clown fiesta happening at backer street. The clowns ")
|
||||
print(var)
|
||||
>>> This is the weather report, we are reporting a clown fiesta happening at backer street. The clowns 1st of July parade was going to be in their own neighborhood but they just couldn't contain themselves;
|
||||
They decided it would look better and probably have more fun if all went into one area which meant that the whole town had to shut down for a little while as all roads were blocked. At least traffic wasn’t too bad today because most of people are out shopping, but I did see some shoppers in their car driving away from Backer street with “clowns” on wheels outside their windows…
|
||||
The kids lined up along the route and waited for the parade to pass by
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Contributors can open PRs
|
||||
- Collaborators can push to branches in the `llama.cpp` repo and merge PRs into the `master` branch
|
||||
- Collaborators will be invited based on contributions
|
||||
- Any help with managing issues and PRs is very appreciated!
|
||||
- Make sure to read this: [Inference at the edge](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/discussions/205)
|
||||
# Implementation details
|
||||
|
||||
### Coding guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
- Avoid adding third-party dependencies, extra files, extra headers, etc.
|
||||
- Always consider cross-compatibility with other operating systems and architectures
|
||||
- Avoid fancy looking modern STL constructs, use basic `for` loops, avoid templates, keep it simple
|
||||
- There are no strict rules for the code style, but try to follow the patterns in the code (indentation, spaces, etc.). Vertical alignment makes things more readable and easier to batch edit
|
||||
- Clean-up any trailing whitespaces, use 4 spaces indentation, brackets on same line, `void * ptr`, `int & a`
|
||||
- See [good first issues](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) for tasks suitable for first contributions
|
||||
This python module is mainly a wrapper around the `llama` class in `src/inference.cpp`. As such, any changes should be done in there.
|
||||
As the llamacpp code is mostly contained in `main.cpp` which doesn't expose a good api, this repo will have to be manually patched on a need-be basis. Changes to `ggml` should not be a problem. Fixing the api on the main repo would allow this to be set up as a downstream fork rather than the weird sidekick repo it currently is.
|
||||
33
pyproject.toml
Normal file
33
pyproject.toml
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
|||
[project]
|
||||
name = "llamacpypy"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
description = ""
|
||||
authors = [{name = "Emanuel Seemann", email = "github@emanuelseemann.ch"}]
|
||||
readme = "README.md"
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.poetry]
|
||||
name = "llamacpypy"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
description = ""
|
||||
authors = ["Emanuel Seemann <github@emanuelseemann.ch>"]
|
||||
readme = "README.md"
|
||||
packages = [{include = "./src"}]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.poetry.dependencies]
|
||||
python = "^3.9"
|
||||
pybind11 = "^2.10.4"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[build-system]
|
||||
requires = ["scikit-build-core>=0.2.1", "pybind11"]
|
||||
build-backend = "scikit_build_core.build"
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.scikit-build]
|
||||
wheel.expand-macos-universal-tags = true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.cibuildwheel]
|
||||
test-command = "pytest {project}/tests"
|
||||
test-extras = ["test"]
|
||||
test-skip = ["*universal2:arm64"]
|
||||
build-verbosity = 1
|
||||
1
requirements.txt
Normal file
1
requirements.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
|||
pybind11==2.10.4
|
||||
818
src/inference.cpp
Normal file
818
src/inference.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,818 @@
|
|||
#include "inference.h"
|
||||
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace py = pybind11;
|
||||
|
||||
PYBIND11_MODULE(_core, m) {
|
||||
py::class_<llama>(m, "LlamaModel")
|
||||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>())
|
||||
.def("set_params", &llama::set_params, "Set the parameters of the model",
|
||||
py::arg("n_threads") = 4,
|
||||
py::arg("n_predict") = 128,
|
||||
py::arg("repeat_last_n") = 64,
|
||||
py::arg("n_ctx") = 512,
|
||||
|
||||
py::arg("top_k") = 40,
|
||||
py::arg("top_p") = 1.0f,
|
||||
py::arg("temp") = 0.70f,
|
||||
py::arg("repeat_penalty") = 1.30f,
|
||||
py::arg("n_batch")= 8
|
||||
)
|
||||
.def("load_model", &llama::load_model, "Loads the model binary into memory")
|
||||
.def("generate", &llama::generate), "Generate text with the current model";
|
||||
}
|
||||
bool llama_eval(
|
||||
const llama_model & model,
|
||||
const int n_threads,
|
||||
const int n_past,
|
||||
const std::vector<gpt_vocab::id> & embd_inp,
|
||||
std::vector<float> & embd_w,
|
||||
size_t & mem_per_token) {
|
||||
const int N = embd_inp.size();
|
||||
|
||||
const auto & hparams = model.hparams;
|
||||
|
||||
const int n_embd = hparams.n_embd;
|
||||
const int n_layer = hparams.n_layer;
|
||||
const int n_ctx = hparams.n_ctx;
|
||||
const int n_head = hparams.n_head;
|
||||
const int n_vocab = hparams.n_vocab;
|
||||
const int n_rot = hparams.n_embd/hparams.n_head;
|
||||
|
||||
const int d_key = n_embd/n_head;
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: check if this size scales with n_ctx linearly and remove constant. somehow I feel it wasn't the case
|
||||
// static size_t buf_size = hparams.n_ctx*1024*1024;
|
||||
static size_t buf_size = 512u*1024*1024;
|
||||
static void * buf = malloc(buf_size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (mem_per_token > 0 && mem_per_token*N > buf_size) {
|
||||
const size_t buf_size_new = 1.1*(mem_per_token*N); // add 10% to account for ggml object overhead
|
||||
//fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: reallocating buffer from %zu to %zu bytes\n", __func__, buf_size, buf_size_new);
|
||||
|
||||
// reallocate
|
||||
buf_size = buf_size_new;
|
||||
buf = realloc(buf, buf_size);
|
||||
if (buf == nullptr) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: failed to allocate %zu bytes\n", __func__, buf_size);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_init_params params = {
|
||||
/*.mem_size =*/ buf_size,
|
||||
/*.mem_buffer =*/ buf,
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_context * ctx0 = ggml_init(params);
|
||||
ggml_cgraph gf = {};
|
||||
gf.n_threads = n_threads;
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * embd = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx0, GGML_TYPE_I32, N);
|
||||
memcpy(embd->data, embd_inp.data(), N*ggml_element_size(embd));
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * inpL = ggml_get_rows(ctx0, model.tok_embeddings, embd);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int il = 0; il < n_layer; ++il) {
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * inpSA = inpL;
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * cur;
|
||||
|
||||
// norm
|
||||
{
|
||||
cur = ggml_rms_norm(ctx0, inpL);
|
||||
|
||||
// cur = attention_norm*cur
|
||||
cur = ggml_mul(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_repeat(ctx0, model.layers[il].attention_norm, cur),
|
||||
cur);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// self-attention
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * Qcur = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0, model.layers[il].wq, cur);
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * Kcur = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0, model.layers[il].wk, cur);
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * Vcur = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0, model.layers[il].wv, cur);
|
||||
|
||||
// store key and value to memory
|
||||
if (N >= 1) {
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * k = ggml_view_1d(ctx0, model.memory_k, N*n_embd, (ggml_element_size(model.memory_k)*n_embd)*(il*n_ctx + n_past));
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * v = ggml_view_1d(ctx0, model.memory_v, N*n_embd, (ggml_element_size(model.memory_v)*n_embd)*(il*n_ctx + n_past));
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_build_forward_expand(&gf, ggml_cpy(ctx0, Kcur, k));
|
||||
ggml_build_forward_expand(&gf, ggml_cpy(ctx0, Vcur, v));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Q = Qcur.contiguous().view(n_embd/n_head, n_head, N).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * Q =
|
||||
ggml_permute(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_rope(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_cpy(ctx0,
|
||||
Qcur,
|
||||
ggml_new_tensor_3d(ctx0, GGML_TYPE_F32, n_embd/n_head, n_head, N)),
|
||||
n_past, n_rot, 0),
|
||||
0, 2, 1, 3);
|
||||
|
||||
// K = Kmem.view(n_embd/n_head, n_head, n_past + N).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * K =
|
||||
ggml_permute(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_rope(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_reshape_3d(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_view_1d(ctx0, model.memory_k, (n_past + N)*n_embd, il*n_ctx*ggml_element_size(model.memory_k)*n_embd),
|
||||
n_embd/n_head, n_head, n_past + N),
|
||||
n_past, n_rot, 1),
|
||||
0, 2, 1, 3);
|
||||
|
||||
// K * Q
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * KQ = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0, K, Q);
|
||||
|
||||
// KQ_scaled = KQ / sqrt(n_embd/n_head)
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * KQ_scaled =
|
||||
ggml_scale(ctx0,
|
||||
KQ,
|
||||
ggml_new_f32(ctx0, 1.0f/sqrt(float(n_embd)/n_head))
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
// KQ_masked = mask_past(KQ_scaled)
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * KQ_masked = ggml_diag_mask_inf(ctx0, KQ_scaled, n_past);
|
||||
|
||||
// KQ = soft_max(KQ_masked)
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * KQ_soft_max = ggml_soft_max(ctx0, KQ_masked);
|
||||
|
||||
// V_trans = Vmem.view(n_embd/n_head, n_head, n_past + N).permute(1, 2, 0, 3).contiguous()
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * V_trans =
|
||||
ggml_permute(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_reshape_3d(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_view_1d(ctx0, model.memory_v, (n_past + N)*n_embd, il*n_ctx*ggml_element_size(model.memory_v)*n_embd),
|
||||
n_embd/n_head, n_head, n_past + N),
|
||||
1, 2, 0, 3);
|
||||
|
||||
// KQV = transpose(V) * KQ_soft_max
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * KQV = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0, V_trans, KQ_soft_max);
|
||||
|
||||
// KQV_merged = KQV.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * KQV_merged = ggml_permute(ctx0, KQV, 0, 2, 1, 3);
|
||||
|
||||
// cur = KQV_merged.contiguous().view(n_embd, N)
|
||||
cur = ggml_cpy(ctx0,
|
||||
KQV_merged,
|
||||
ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx0, GGML_TYPE_F32, n_embd, N));
|
||||
|
||||
// projection (no bias)
|
||||
cur = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0,
|
||||
model.layers[il].wo,
|
||||
cur);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * inpFF = ggml_add(ctx0, cur, inpSA);
|
||||
|
||||
// feed-forward network
|
||||
{
|
||||
// norm
|
||||
{
|
||||
cur = ggml_rms_norm(ctx0, inpFF);
|
||||
|
||||
// cur = ffn_norm*cur
|
||||
cur = ggml_mul(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_repeat(ctx0, model.layers[il].ffn_norm, cur),
|
||||
cur);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * tmp = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0,
|
||||
model.layers[il].w3,
|
||||
cur);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
cur = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0,
|
||||
model.layers[il].w1,
|
||||
cur);
|
||||
|
||||
// SILU activation
|
||||
cur = ggml_silu(ctx0, cur);
|
||||
|
||||
cur = ggml_mul(ctx0, cur, tmp);
|
||||
|
||||
cur = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0,
|
||||
model.layers[il].w2,
|
||||
cur);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cur = ggml_add(ctx0, cur, inpFF);
|
||||
|
||||
// input for next layer
|
||||
inpL = cur;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// norm
|
||||
{
|
||||
inpL = ggml_rms_norm(ctx0, inpL);
|
||||
|
||||
// inpL = norm*inpL
|
||||
inpL = ggml_mul(ctx0,
|
||||
ggml_repeat(ctx0, model.norm, inpL),
|
||||
inpL);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lm_head
|
||||
{
|
||||
inpL = ggml_mul_mat(ctx0, model.output, inpL);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// logits -> probs
|
||||
//inpL = ggml_soft_max(ctx0, inpL);
|
||||
|
||||
// run the computation
|
||||
ggml_build_forward_expand(&gf, inpL);
|
||||
ggml_graph_compute (ctx0, &gf);
|
||||
|
||||
//if (n_past%100 == 0) {
|
||||
// ggml_graph_print (&gf);
|
||||
// ggml_graph_dump_dot(&gf, NULL, "gpt-2.dot");
|
||||
//}
|
||||
|
||||
//embd_w.resize(n_vocab*N);
|
||||
//memcpy(embd_w.data(), ggml_get_data(inpL), sizeof(float)*n_vocab*N);
|
||||
|
||||
// return result for just the last token
|
||||
embd_w.resize(n_vocab);
|
||||
memcpy(embd_w.data(), (float *) ggml_get_data(inpL) + (n_vocab*(N-1)), sizeof(float)*n_vocab);
|
||||
|
||||
if (mem_per_token == 0) {
|
||||
mem_per_token = ggml_used_mem(ctx0)/N;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//fprintf(stderr, "used_mem = %zu\n", ggml_used_mem(ctx0));
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_free(ctx0);
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
bool llama::load_model(){
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: loading model from '%s' - please wait ...\n", __func__, params.model.c_str());
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<char> f_buf(1024*1024);
|
||||
|
||||
auto fin = std::ifstream(params.model, std::ios::binary);
|
||||
fin.rdbuf()->pubsetbuf(f_buf.data(), f_buf.size());
|
||||
if (!fin) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: failed to open '%s'\n", __func__, params.model.c_str());
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// verify magic
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint32_t magic;
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &magic, sizeof(magic));
|
||||
if (magic != 0x67676d6c) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: invalid model file '%s' (bad magic)\n", __func__, params.model.c_str());
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int n_ff = 0;
|
||||
int n_parts = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// load hparams
|
||||
{
|
||||
auto & hparams = model.hparams;
|
||||
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &hparams.n_vocab, sizeof(hparams.n_vocab));
|
||||
//fin.read((char *) &hparams.n_ctx, sizeof(hparams.n_ctx));
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &hparams.n_embd, sizeof(hparams.n_embd));
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &hparams.n_mult, sizeof(hparams.n_mult));
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &hparams.n_head, sizeof(hparams.n_head));
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &hparams.n_layer, sizeof(hparams.n_layer));
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &hparams.n_rot, sizeof(hparams.n_rot));
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &hparams.f16, sizeof(hparams.f16));
|
||||
|
||||
hparams.n_ctx = params.n_ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
n_ff = ((2*(4*hparams.n_embd)/3 + hparams.n_mult - 1)/hparams.n_mult)*hparams.n_mult;
|
||||
n_parts = LLAMA_N_PARTS.at(hparams.n_embd);
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_vocab = %d\n", __func__, hparams.n_vocab);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_ctx = %d\n", __func__, hparams.n_ctx);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_embd = %d\n", __func__, hparams.n_embd);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_mult = %d\n", __func__, hparams.n_mult);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_head = %d\n", __func__, hparams.n_head);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_layer = %d\n", __func__, hparams.n_layer);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_rot = %d\n", __func__, hparams.n_rot);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: f16 = %d\n", __func__, hparams.f16);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_ff = %d\n", __func__, n_ff);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: n_parts = %d\n", __func__, n_parts);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// load vocab
|
||||
{
|
||||
const int32_t n_vocab = model.hparams.n_vocab;
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_vocab != model.hparams.n_vocab) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: invalid model file '%s' (bad vocab size %d != %d)\n",
|
||||
__func__, params.model.c_str(), n_vocab, model.hparams.n_vocab);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::string word;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n_vocab; i++) {
|
||||
uint32_t len;
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &len, sizeof(len));
|
||||
|
||||
word.resize(len);
|
||||
fin.read((char *) word.data(), len);
|
||||
|
||||
vocab.token_to_id[word] = i;
|
||||
vocab.id_to_token[i] = word;
|
||||
|
||||
//if (i < 30000) {
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "%s: vocab[%d] = '%s'\n", __func__, i, word.c_str());
|
||||
//}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// for the big tensors, we have the option to store the data in 16-bit floats or quantized
|
||||
// in order to save memory and also to speed up the computation
|
||||
ggml_type wtype = GGML_TYPE_COUNT;
|
||||
switch (model.hparams.f16) {
|
||||
case 0: wtype = GGML_TYPE_F32; break;
|
||||
case 1: wtype = GGML_TYPE_F16; break;
|
||||
case 2: wtype = GGML_TYPE_Q4_0; break;
|
||||
case 3: wtype = GGML_TYPE_Q4_1; break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: invalid model file '%s' (bad f16 value %d)\n",
|
||||
__func__, params.model.c_str(), model.hparams.f16);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const ggml_type wtype2 = GGML_TYPE_F32;
|
||||
|
||||
auto & ctx = model.ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t ctx_size = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
const auto & hparams = model.hparams;
|
||||
|
||||
const int n_embd = hparams.n_embd;
|
||||
const int n_layer = hparams.n_layer;
|
||||
const int n_ctx = hparams.n_ctx;
|
||||
const int n_vocab = hparams.n_vocab;
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_embd*n_vocab*ggml_type_sizef(wtype); // tok_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(GGML_TYPE_F32); // norm
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_embd*n_vocab*ggml_type_sizef(wtype); // output
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(GGML_TYPE_F32)); // attention_norm
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_embd*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(wtype)); // wq
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_embd*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(wtype)); // wk
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_embd*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(wtype)); // wv
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_embd*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(wtype)); // wo
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(GGML_TYPE_F32)); // ffn_norm
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_ff*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(wtype)); // w1
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_ff*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(wtype)); // w2
|
||||
ctx_size += n_layer*(n_ff*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(wtype)); // w3
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += n_ctx*n_layer*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(GGML_TYPE_F32); // memory_k
|
||||
ctx_size += n_ctx*n_layer*n_embd*ggml_type_sizef(GGML_TYPE_F32); // memory_v
|
||||
|
||||
ctx_size += (5 + 10*n_layer)*256; // object overhead
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: ggml ctx size = %6.2f MB\n", __func__, ctx_size/(1024.0*1024.0));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// create the ggml context
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct ggml_init_params params = {
|
||||
/*.mem_size =*/ ctx_size,
|
||||
/*.mem_buffer =*/ NULL,
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
model.ctx = ggml_init(params);
|
||||
if (!model.ctx) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: ggml_init() failed\n", __func__);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// prepare memory for the weights
|
||||
{
|
||||
const auto & hparams = model.hparams;
|
||||
|
||||
const int n_embd = hparams.n_embd;
|
||||
const int n_layer = hparams.n_layer;
|
||||
const int n_ctx = hparams.n_ctx;
|
||||
const int n_vocab = hparams.n_vocab;
|
||||
|
||||
model.layers.resize(n_layer);
|
||||
|
||||
model.tok_embeddings = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_vocab);
|
||||
|
||||
model.norm = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_F32, n_embd);
|
||||
model.output = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_vocab);
|
||||
|
||||
// map by name
|
||||
model.tensors["tok_embeddings.weight"] = model.tok_embeddings;
|
||||
|
||||
model.tensors["norm.weight"] = model.norm;
|
||||
model.tensors["output.weight"] = model.output;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n_layer; ++i) {
|
||||
auto & layer = model.layers[i];
|
||||
|
||||
layer.attention_norm = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_F32, n_embd);
|
||||
|
||||
layer.wq = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_embd);
|
||||
layer.wk = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_embd);
|
||||
layer.wv = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_embd);
|
||||
layer.wo = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_embd);
|
||||
|
||||
layer.ffn_norm = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_F32, n_embd);
|
||||
|
||||
layer.w1 = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_ff);
|
||||
layer.w2 = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_ff, n_embd);
|
||||
layer.w3 = ggml_new_tensor_2d(ctx, wtype, n_embd, n_ff);
|
||||
|
||||
// map by name
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".attention_norm.weight"] = layer.attention_norm;
|
||||
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".attention.wq.weight"] = layer.wq;
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".attention.wk.weight"] = layer.wk;
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".attention.wv.weight"] = layer.wv;
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".attention.wo.weight"] = layer.wo;
|
||||
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".ffn_norm.weight"] = layer.ffn_norm;
|
||||
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".feed_forward.w1.weight"] = layer.w1;
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".feed_forward.w2.weight"] = layer.w2;
|
||||
model.tensors["layers." + std::to_string(i) + ".feed_forward.w3.weight"] = layer.w3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// key + value memory
|
||||
{
|
||||
const auto & hparams = model.hparams;
|
||||
|
||||
const int n_embd = hparams.n_embd;
|
||||
const int n_layer = hparams.n_layer;
|
||||
const int n_ctx = hparams.n_ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
const int n_mem = n_layer*n_ctx;
|
||||
const int n_elements = n_embd*n_mem;
|
||||
|
||||
model.memory_k = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_F32, n_elements);
|
||||
model.memory_v = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx, GGML_TYPE_F32, n_elements);
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t memory_size = ggml_nbytes(model.memory_k) + ggml_nbytes(model.memory_v);
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: memory_size = %8.2f MB, n_mem = %d\n", __func__, memory_size/1024.0/1024.0, n_mem);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t file_offset = fin.tellg();
|
||||
|
||||
fin.close();
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> tmp;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n_parts; ++i) {
|
||||
const int part_id = i;
|
||||
//const int part_id = n_parts - i - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
std::string fname_part = params.model;
|
||||
if (i > 0) {
|
||||
fname_part += "." + std::to_string(i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: loading model part %d/%d from '%s'\n", __func__, i+1, n_parts, fname_part.c_str());
|
||||
|
||||
fin = std::ifstream(fname_part, std::ios::binary);
|
||||
fin.rdbuf()->pubsetbuf(f_buf.data(), f_buf.size());
|
||||
fin.seekg(file_offset);
|
||||
|
||||
// load weights
|
||||
{
|
||||
int n_tensors = 0;
|
||||
size_t total_size = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: ", __func__);
|
||||
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
int32_t n_dims;
|
||||
int32_t length;
|
||||
int32_t ftype;
|
||||
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&n_dims), sizeof(n_dims));
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&length), sizeof(length));
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&ftype), sizeof(ftype));
|
||||
|
||||
if (fin.eof()) {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t nelements = 1;
|
||||
int32_t ne[2] = { 1, 1 };
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n_dims; ++i) {
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&ne[i]), sizeof(ne[i]));
|
||||
nelements *= ne[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::string name(length, 0);
|
||||
fin.read(&name[0], length);
|
||||
|
||||
if (model.tensors.find(name.data()) == model.tensors.end()) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: unknown tensor '%s' in model file\n", __func__, name.data());
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// split_type = 0: split by columns
|
||||
// split_type = 1: split by rows
|
||||
int split_type = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// split_type = 0:
|
||||
// regex:
|
||||
// - tok_embeddings.*
|
||||
// - layers.*.attention.wo.weight
|
||||
// - layers.*.feed_forward.w2.weight
|
||||
|
||||
// split_type = 1:
|
||||
// regex:
|
||||
// - output.*
|
||||
// - layers.*.attention.wq.weight
|
||||
// - layers.*.attention.wk.weight
|
||||
// - layers.*.attention.wv.weight
|
||||
// - layers.*.feed_forward.w1.weight
|
||||
// - layers.*.feed_forward.w3.weight
|
||||
if (name.find("tok_embeddings") != std::string::npos) {
|
||||
split_type = 0;
|
||||
} else if (name.find("layers") != std::string::npos) {
|
||||
if (name.find("attention.wo.weight") != std::string::npos) {
|
||||
split_type = 0;
|
||||
} else if (name.find("feed_forward.w2.weight") != std::string::npos) {
|
||||
split_type = 0;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
split_type = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (name.find("output") != std::string::npos) {
|
||||
split_type = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto tensor = model.tensors[name.data()];
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_dims == 1) {
|
||||
if (ggml_nelements(tensor) != nelements) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: tensor '%s' has wrong size in model file\n", __func__, name.data());
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (ggml_nelements(tensor)/n_parts != nelements) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: tensor '%s' has wrong size in model file\n", __func__, name.data());
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_dims == 1) {
|
||||
if (tensor->ne[0] != ne[0] || tensor->ne[1] != ne[1]) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: tensor '%s' has wrong shape in model file: got [%d, %d], expected [%d, %d]\n",
|
||||
__func__, name.data(), tensor->ne[0], tensor->ne[1], ne[0], ne[1]);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (split_type == 0) {
|
||||
if (tensor->ne[0]/n_parts != ne[0] || tensor->ne[1] != ne[1]) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: tensor '%s' has wrong shape in model file: got [%d, %d], expected [%d, %d]\n",
|
||||
__func__, name.data(), tensor->ne[0]/n_parts, tensor->ne[1], ne[0], ne[1]);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (tensor->ne[0] != ne[0] || tensor->ne[1]/n_parts != ne[1]) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: tensor '%s' has wrong shape in model file: got [%d, %d], expected [%d, %d]\n",
|
||||
__func__, name.data(), tensor->ne[0], tensor->ne[1]/n_parts, ne[0], ne[1]);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (0) {
|
||||
static const char * ftype_str[] = { "f32", "f16", "q4_0", "q4_1", };
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%24s - [%5d, %5d], type = %6s, split = %d\n", name.data(), ne[0], ne[1], ftype_str[ftype], split_type);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
size_t bpe = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
switch (ftype) {
|
||||
case 0: bpe = ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_F32); break;
|
||||
case 1: bpe = ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_F16); break;
|
||||
case 2: bpe = ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_Q4_0); assert(ne[0] % 64 == 0); break;
|
||||
case 3: bpe = ggml_type_size(GGML_TYPE_Q4_1); assert(ne[0] % 64 == 0); break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: unknown ftype %d in model file\n", __func__, ftype);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_dims == 1 || n_parts == 1) {
|
||||
if ((nelements*bpe)/ggml_blck_size(tensor->type) != ggml_nbytes(tensor)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: tensor '%s' has wrong size in model file: got %zu, expected %zu\n",
|
||||
__func__, name.data(), ggml_nbytes(tensor), nelements*bpe);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (part_id == 0) {
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(tensor->data), ggml_nbytes(tensor));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fin.seekg(ggml_nbytes(tensor), std::ios::cur);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
total_size += ggml_nbytes(tensor);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if ((nelements*bpe)/ggml_blck_size(tensor->type) != ggml_nbytes(tensor)/n_parts) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: tensor '%s' has wrong size in model file: got %zu, expected %zu\n",
|
||||
__func__, name.data(), ggml_nbytes(tensor)/n_parts, nelements*bpe);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (split_type == 0) {
|
||||
const int np0 = ne[0];
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t row_size = (tensor->ne[0]/ggml_blck_size(tensor->type))*ggml_type_size(tensor->type);
|
||||
assert(row_size == tensor->nb[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < ne[1]; ++i1) {
|
||||
const size_t offset_row = i1*row_size;
|
||||
const size_t offset = offset_row + ((part_id*np0)/ggml_blck_size(tensor->type))*ggml_type_size(tensor->type);
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(tensor->data) + offset, row_size/n_parts);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
const int np1 = ne[1];
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t row_size = (tensor->ne[0]/ggml_blck_size(tensor->type))*ggml_type_size(tensor->type);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < ne[1]; ++i1) {
|
||||
const size_t offset_row = (i1 + part_id*np1)*row_size;
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(tensor->data) + offset_row, row_size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
total_size += ggml_nbytes(tensor)/n_parts;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//fprintf(stderr, "%42s - [%5d, %5d], type = %6s, %6.2f MB\n", name.data(), ne[0], ne[1], ftype == 0 ? "float" : "f16", ggml_nbytes(tensor)/1024.0/1024.0);
|
||||
if (++n_tensors % 8 == 0) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, ".");
|
||||
fflush(stderr);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " done\n");
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: model size = %8.2f MB / num tensors = %d\n", __func__, total_size/1024.0/1024.0, n_tensors);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fin.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool llama::set_params(
|
||||
int32_t n_threads,
|
||||
int32_t n_predict,
|
||||
int32_t repeat_last_n,
|
||||
int32_t n_ctx,
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t top_k,
|
||||
float top_p,
|
||||
float temp,
|
||||
float repeat_penalty,
|
||||
int32_t n_batch
|
||||
){
|
||||
params.n_threads = n_threads;
|
||||
params.n_predict = n_predict;
|
||||
params.repeat_last_n = repeat_last_n;
|
||||
params.n_ctx = n_ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
params.top_k = top_k;
|
||||
params.top_p = top_p;
|
||||
params.temp = temp;
|
||||
params.repeat_penalty = repeat_penalty;
|
||||
params.n_batch = n_batch;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
std::string llama::generate(const std::string & prompt){
|
||||
|
||||
std::string ret_string;
|
||||
std::mt19937 rng(params.seed);
|
||||
int n_past = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int64_t t_sample_us = 0;
|
||||
int64_t t_predict_us = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<float> logits;
|
||||
|
||||
// tokenize the prompt
|
||||
std::vector<gpt_vocab::id> embd_inp = ::llama_tokenize(vocab, prompt, true);
|
||||
|
||||
params.n_predict = std::min(params.n_predict, model.hparams.n_ctx - (int) embd_inp.size());
|
||||
|
||||
// tokenize the reverse prompt
|
||||
std::vector<gpt_vocab::id> antiprompt_inp = ::llama_tokenize(vocab, params.antiprompt, false);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<gpt_vocab::id> embd;
|
||||
|
||||
// determine the required inference memory per token:
|
||||
size_t mem_per_token = 0;
|
||||
llama_eval(model, params.n_threads, 0, { 0, 1, 2, 3 }, logits, mem_per_token);
|
||||
|
||||
int last_n_size = params.repeat_last_n;
|
||||
std::vector<gpt_vocab::id> last_n_tokens(last_n_size);
|
||||
std::fill(last_n_tokens.begin(), last_n_tokens.end(), 0);
|
||||
|
||||
int remaining_tokens = params.n_predict;
|
||||
int input_consumed = 0;
|
||||
bool input_noecho = false;
|
||||
|
||||
while (remaining_tokens > 0) {
|
||||
// predict
|
||||
if (embd.size() > 0) {
|
||||
const int64_t t_start_us = ggml_time_us();
|
||||
|
||||
if (!llama_eval(model, params.n_threads, n_past, embd, logits, mem_per_token)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to predict\n");
|
||||
std::string error_str = "error";
|
||||
return error_str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
t_predict_us += ggml_time_us() - t_start_us;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n_past += embd.size();
|
||||
embd.clear();
|
||||
|
||||
if (embd_inp.size() <= input_consumed) {
|
||||
// out of user input, sample next token
|
||||
const float top_k = params.top_k;
|
||||
const float top_p = params.top_p;
|
||||
const float temp = params.temp;
|
||||
const float repeat_penalty = params.repeat_penalty;
|
||||
|
||||
const int n_vocab = model.hparams.n_vocab;
|
||||
|
||||
gpt_vocab::id id = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
const int64_t t_start_sample_us = ggml_time_us();
|
||||
|
||||
id = llama_sample_top_p_top_k(vocab, logits.data() + (logits.size() - n_vocab), last_n_tokens, repeat_penalty, top_k, top_p, temp, rng);
|
||||
|
||||
last_n_tokens.erase(last_n_tokens.begin());
|
||||
last_n_tokens.push_back(id);
|
||||
|
||||
t_sample_us += ggml_time_us() - t_start_sample_us;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// add it to the context
|
||||
embd.push_back(id);
|
||||
|
||||
// echo this to console
|
||||
input_noecho = false;
|
||||
|
||||
// decrement remaining sampling budget
|
||||
--remaining_tokens;
|
||||
}else {
|
||||
// some user input remains from prompt or interaction, forward it to processing
|
||||
while (embd_inp.size() > input_consumed) {
|
||||
embd.push_back(embd_inp[input_consumed]);
|
||||
last_n_tokens.erase(last_n_tokens.begin());
|
||||
last_n_tokens.push_back(embd_inp[input_consumed]);
|
||||
++input_consumed;
|
||||
if (embd.size() > params.n_batch) {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// reset color to default if we there is no pending user input
|
||||
if (!input_noecho && params.use_color && embd_inp.size() == input_consumed) {
|
||||
printf(ANSI_COLOR_RESET);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (auto id : embd) {
|
||||
ret_string.append(vocab.id_to_token[id].c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (embd.back() == 2) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " [end of text]\n");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ret_string;
|
||||
}
|
||||
109
src/inference.h
Normal file
109
src/inference.h
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
|||
#include "utils.h"
|
||||
#include "ggml.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <cassert>
|
||||
#include <cmath>
|
||||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#include <cstring>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
#include <map>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined (__unix__) || (defined (__APPLE__) && defined (__MACH__))
|
||||
#include <signal.h>
|
||||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||||
#elif defined (_WIN32)
|
||||
#include <signal.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#define ANSI_COLOR_RED "\x1b[31m"
|
||||
#define ANSI_COLOR_GREEN "\x1b[32m"
|
||||
#define ANSI_COLOR_YELLOW "\x1b[33m"
|
||||
#define ANSI_COLOR_BLUE "\x1b[34m"
|
||||
#define ANSI_COLOR_MAGENTA "\x1b[35m"
|
||||
#define ANSI_COLOR_CYAN "\x1b[36m"
|
||||
#define ANSI_COLOR_RESET "\x1b[0m"
|
||||
#define ANSI_BOLD "\x1b[1m"
|
||||
|
||||
// determine number of model parts based on the dimension
|
||||
static const std::map<int, int> LLAMA_N_PARTS = {
|
||||
{ 4096, 1 },
|
||||
{ 5120, 2 },
|
||||
{ 6656, 4 },
|
||||
{ 8192, 8 },
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// default hparams (LLaMA 7B)
|
||||
struct llama_hparams {
|
||||
int32_t n_vocab = 32000;
|
||||
int32_t n_ctx = 512; // this is provided as user input?
|
||||
int32_t n_embd = 4096;
|
||||
int32_t n_mult = 256;
|
||||
int32_t n_head = 32;
|
||||
int32_t n_layer = 32;
|
||||
int32_t n_rot = 64;
|
||||
int32_t f16 = 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct llama_layer {
|
||||
// normalization
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * attention_norm;
|
||||
|
||||
// attention
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * wq;
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * wk;
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * wv;
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * wo;
|
||||
|
||||
// normalization
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * ffn_norm;
|
||||
|
||||
// ff
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * w1;
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * w2;
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * w3;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct llama_model {
|
||||
llama_hparams hparams;
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * tok_embeddings;
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * norm;
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * output;
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<llama_layer> layers;
|
||||
|
||||
// key + value memory
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * memory_k;
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * memory_v;
|
||||
|
||||
//
|
||||
struct ggml_context * ctx;
|
||||
std::map<std::string, struct ggml_tensor *> tensors;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct llama {
|
||||
llama(const std::string & fname_){
|
||||
params.model = fname_;
|
||||
};
|
||||
bool set_params(
|
||||
int32_t n_threads = std::min(4, (int32_t) std::thread::hardware_concurrency()),
|
||||
int32_t n_predict = 128,
|
||||
int32_t repeat_last_n = 64,
|
||||
int32_t n_ctx = 512,
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t top_k = 40,
|
||||
float top_p = 1.0f,
|
||||
float temp = 0.70f,
|
||||
float repeat_penalty = 1.30f,
|
||||
int32_t n_batch= 8
|
||||
);
|
||||
bool load_model();
|
||||
std::string generate(const std::string & prompt);
|
||||
|
||||
gpt_params params;
|
||||
llama_model model;
|
||||
gpt_vocab vocab;
|
||||
};
|
||||
4
src/llamacpypy/__init__.py
Normal file
4
src/llamacpypy/__init__.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
|||
from ._core import LlamaModel
|
||||
from .llama import Llama
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [LlamaModel, Llama]
|
||||
60
src/llamacpypy/llama.py
Normal file
60
src/llamacpypy/llama.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
|||
from ._core import LlamaModel
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_PARAMS = {
|
||||
|
||||
"n_predict" : 128,
|
||||
"repeat_last_n" : 64,
|
||||
"n_ctx" : 512,
|
||||
|
||||
"top_k" : 40,
|
||||
"top_p" : 1.0,
|
||||
"temp" : 0.7,
|
||||
"repeat_penalty" : 1.3,
|
||||
|
||||
"n_batch" : 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Llama():
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, model_name: str, model_params_dict=None, warm_start=True) -> None:
|
||||
|
||||
self.model_name = model_name
|
||||
self.model = LlamaModel(model_name)
|
||||
if model_params_dict:
|
||||
self.set_params(model_params_dict)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.set_params(DEFAULT_PARAMS)
|
||||
if warm_start:
|
||||
self.load_model()
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(self, prompt: str) -> str:
|
||||
|
||||
return self.model.generate(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
def set_params(self, model_param_dict):
|
||||
|
||||
_typecheck_model_params(model_param_dict)
|
||||
self.model.set_params(**model_param_dict)
|
||||
|
||||
def load_model(self):
|
||||
|
||||
ret = self.model.load_model()
|
||||
if not ret:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Model {self.model_name} did not load properly. Is the filepath correct?")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _typecheck_model_params(model_params_dict):
|
||||
|
||||
floats = ['top_p', 'temp', 'repeat_penalty']
|
||||
ints = ['n_threads', 'n_predict', 'repeat_last_n', 'n_ctx', 'top_k', 'n_batch']
|
||||
for key in model_params_dict:
|
||||
|
||||
if key in floats:
|
||||
if not isinstance(model_params_dict[key], float):
|
||||
raise TypeError(f"Model parameter {key} must be a float, was given a {type(model_params_dict[key])}")
|
||||
if key in ints:
|
||||
if not isinstance(model_params_dict[key], int):
|
||||
raise TypeError(f"Model parameter {key} must be an int, was given a {type(model_params_dict[key])}")
|
||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue