Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp into jon/tall-and-skinny-matmul
This commit is contained in:
commit
0a320ed274
39 changed files with 5697 additions and 1914 deletions
19
.github/workflows/build.yml
vendored
19
.github/workflows/build.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -8,17 +8,19 @@ on:
|
|||
required: true
|
||||
type: boolean
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- master
|
||||
paths: ['.github/workflows/**', '**/CMakeLists.txt', '**/Makefile', '**/*.h', '**/*.c', '**/*.cpp']
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
types: [opened, synchronize, edited, reopened, review_requested, ready_for_review]
|
||||
types: [opened, synchronize, reopened]
|
||||
paths: ['**/CMakeLists.txt', '**/Makefile', '**/*.h', '**/*.c', '**/*.cpp']
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
BRANCH_NAME: ${{ github.head_ref || github.ref_name }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
ubuntu-latest-make:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
ubuntu-focal-make:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-20.04
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Clone
|
||||
|
|
@ -29,12 +31,12 @@ jobs:
|
|||
id: depends
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install build-essential
|
||||
sudo apt-get install build-essential gcc-8
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build
|
||||
id: make_build
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
make
|
||||
CC=gcc-8 make
|
||||
|
||||
ubuntu-latest-cmake:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
|
@ -73,7 +75,6 @@ jobs:
|
|||
matrix:
|
||||
sanitizer: [ADDRESS, THREAD, UNDEFINED]
|
||||
build_type: [Debug, Release]
|
||||
accelerate: [ON, OFF]
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Clone
|
||||
|
|
@ -91,7 +92,7 @@ jobs:
|
|||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
cd build
|
||||
cmake .. -DLLAMA_SANITIZE_${{ matrix.sanitizer }}=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${{ matrix.build_type }} -DLLAMA_ACCELERATE=${{ matrix.accelerate }}
|
||||
cmake .. -DLLAMA_SANITIZE_${{ matrix.sanitizer }}=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=${{ matrix.build_type }}
|
||||
cmake --build . --config ${{ matrix.build_type }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test
|
||||
|
|
@ -156,7 +157,7 @@ jobs:
|
|||
- build: 'avx'
|
||||
defines: '-DLLAMA_AVX2=OFF'
|
||||
- build: 'avx512'
|
||||
defines: '-DLLAMA_AVX512=ON'
|
||||
defines: '-DLLAMA_AVX512=ON -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON'
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Clone
|
||||
|
|
@ -215,7 +216,7 @@ jobs:
|
|||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
needs:
|
||||
- ubuntu-latest-make
|
||||
- ubuntu-focal-make
|
||||
- ubuntu-latest-cmake
|
||||
- macOS-latest-make
|
||||
- macOS-latest-cmake
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
2
.github/workflows/docker.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/docker.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -18,6 +18,8 @@ on:
|
|||
jobs:
|
||||
push_to_registry:
|
||||
name: Push Docker image to Docker Hub
|
||||
if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
env:
|
||||
COMMIT_SHA: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
16
.gitignore
vendored
16
.gitignore
vendored
|
|
@ -1,11 +1,15 @@
|
|||
*.o
|
||||
*.a
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.build/
|
||||
.cache/
|
||||
.direnv/
|
||||
.envrc
|
||||
.swiftpm
|
||||
.venv
|
||||
.vs/
|
||||
.vscode/
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
|
||||
.build/
|
||||
build/
|
||||
build-em/
|
||||
build-debug/
|
||||
|
|
@ -24,17 +28,15 @@ models/*
|
|||
/perplexity
|
||||
/embedding
|
||||
/benchmark-q4_0-matmult
|
||||
/vdot
|
||||
/Pipfile
|
||||
|
||||
arm_neon.h
|
||||
compile_commands.json
|
||||
|
||||
.envrc
|
||||
.direnv/
|
||||
|
||||
.venv
|
||||
__pycache__
|
||||
.swiftpm
|
||||
|
||||
zig-out/
|
||||
zig-cache/
|
||||
|
||||
ppl-*.txt
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -55,6 +55,8 @@ option(LLAMA_SANITIZE_UNDEFINED "llama: enable undefined sanitizer"
|
|||
option(LLAMA_AVX "llama: enable AVX" ON)
|
||||
option(LLAMA_AVX2 "llama: enable AVX2" ON)
|
||||
option(LLAMA_AVX512 "llama: enable AVX512" OFF)
|
||||
option(LLAMA_AVX512_VBMI "llama: enable AVX512-VBMI" OFF)
|
||||
option(LLAMA_AVX512_VNNI "llama: enable AVX512-VNNI" OFF)
|
||||
option(LLAMA_FMA "llama: enable FMA" ON)
|
||||
# in MSVC F16C is implied with AVX2/AVX512
|
||||
if (NOT MSVC)
|
||||
|
|
@ -64,6 +66,7 @@ endif()
|
|||
# 3rd party libs
|
||||
option(LLAMA_ACCELERATE "llama: enable Accelerate framework" ON)
|
||||
option(LLAMA_OPENBLAS "llama: use OpenBLAS" OFF)
|
||||
option(LLAMA_CUBLAS "llama: use cuBLAS" OFF)
|
||||
|
||||
option(LLAMA_BUILD_TESTS "llama: build tests" ${LLAMA_STANDALONE})
|
||||
option(LLAMA_BUILD_EXAMPLES "llama: build examples" ${LLAMA_STANDALONE})
|
||||
|
|
@ -107,6 +110,7 @@ if (APPLE AND LLAMA_ACCELERATE)
|
|||
message(WARNING "Accelerate framework not found")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
if (LLAMA_OPENBLAS)
|
||||
if (LLAMA_STATIC)
|
||||
set(BLA_STATIC ON)
|
||||
|
|
@ -140,6 +144,30 @@ if (LLAMA_OPENBLAS)
|
|||
endif()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
if (LLAMA_CUBLAS)
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.17)
|
||||
|
||||
find_package(CUDAToolkit)
|
||||
if (CUDAToolkit_FOUND)
|
||||
message(STATUS "cuBLAS found")
|
||||
|
||||
enable_language(CUDA)
|
||||
|
||||
set(GGML_CUDA_SOURCES ggml-cuda.cu ggml-cuda.h)
|
||||
|
||||
add_compile_definitions(GGML_USE_CUBLAS)
|
||||
|
||||
if (LLAMA_STATIC)
|
||||
set(LLAMA_EXTRA_LIBS ${LLAMA_EXTRA_LIBS} CUDA::cudart_static CUDA::cublas_static CUDA::cublasLt_static)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
set(LLAMA_EXTRA_LIBS ${LLAMA_EXTRA_LIBS} CUDA::cudart CUDA::cublas CUDA::cublasLt)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
else()
|
||||
message(WARNING "cuBLAS not found")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
if (LLAMA_ALL_WARNINGS)
|
||||
if (NOT MSVC)
|
||||
set(c_flags
|
||||
|
|
@ -151,7 +179,6 @@ if (LLAMA_ALL_WARNINGS)
|
|||
-Wshadow
|
||||
-Wstrict-prototypes
|
||||
-Wpointer-arith
|
||||
-Wno-unused-function
|
||||
)
|
||||
set(cxx_flags
|
||||
-Wall
|
||||
|
|
@ -174,6 +201,10 @@ endif()
|
|||
|
||||
if (MSVC)
|
||||
add_compile_definitions(_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS)
|
||||
|
||||
if (BUILD_SHARED_LIBS)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_WINDOWS_EXPORT_ALL_SYMBOLS ON)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
if (LLAMA_LTO)
|
||||
|
|
@ -219,11 +250,26 @@ elseif (${CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR} MATCHES "^(x86_64|i686|AMD64)$")
|
|||
message(STATUS "x86 detected")
|
||||
if (MSVC)
|
||||
if (LLAMA_AVX512)
|
||||
add_compile_options(/arch:AVX512)
|
||||
add_compile_options($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:C>:/arch:AVX512>)
|
||||
add_compile_options($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>:/arch:AVX512>)
|
||||
# MSVC has no compile-time flags enabling specific
|
||||
# AVX512 extensions, neither it defines the
|
||||
# macros corresponding to the extensions.
|
||||
# Do it manually.
|
||||
if (LLAMA_AVX512_VBMI)
|
||||
add_compile_definitions($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:C>:__AVX512VBMI__>)
|
||||
add_compile_definitions($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>:__AVX512VBMI__>)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
if (LLAMA_AVX512_VNNI)
|
||||
add_compile_definitions($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:C>:__AVX512VNNI__>)
|
||||
add_compile_definitions($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>:__AVX512VNNI__>)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
elseif (LLAMA_AVX2)
|
||||
add_compile_options(/arch:AVX2)
|
||||
add_compile_options($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:C>:/arch:AVX2>)
|
||||
add_compile_options($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>:/arch:AVX2>)
|
||||
elseif (LLAMA_AVX)
|
||||
add_compile_options(/arch:AVX)
|
||||
add_compile_options($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:C>:/arch:AVX>)
|
||||
add_compile_options($<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>:/arch:AVX>)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
else()
|
||||
if (LLAMA_F16C)
|
||||
|
|
@ -240,9 +286,13 @@ elseif (${CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR} MATCHES "^(x86_64|i686|AMD64)$")
|
|||
endif()
|
||||
if (LLAMA_AVX512)
|
||||
add_compile_options(-mavx512f)
|
||||
# add_compile_options(-mavx512cd)
|
||||
# add_compile_options(-mavx512dq)
|
||||
# add_compile_options(-mavx512bw)
|
||||
add_compile_options(-mavx512bw)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
if (LLAMA_AVX512_VBMI)
|
||||
add_compile_options(-mavx512vbmi)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
if (LLAMA_AVX512_VNNI)
|
||||
add_compile_options(-mavx512vnni)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
else()
|
||||
|
|
@ -256,11 +306,13 @@ endif()
|
|||
|
||||
add_library(ggml OBJECT
|
||||
ggml.c
|
||||
ggml.h)
|
||||
ggml.h
|
||||
${GGML_CUDA_SOURCES})
|
||||
|
||||
target_include_directories(ggml PUBLIC .)
|
||||
target_compile_features(ggml PUBLIC c_std_11) # don't bump
|
||||
target_link_libraries(ggml PRIVATE Threads::Threads ${LLAMA_EXTRA_LIBS})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(ggml PUBLIC Threads::Threads ${LLAMA_EXTRA_LIBS})
|
||||
|
||||
if (BUILD_SHARED_LIBS)
|
||||
set_target_properties(ggml PROPERTIES POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE ON)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
|
@ -273,11 +325,20 @@ add_library(llama
|
|||
target_include_directories(llama PUBLIC .)
|
||||
target_compile_features(llama PUBLIC cxx_std_11) # don't bump
|
||||
target_link_libraries(llama PRIVATE ggml ${LLAMA_EXTRA_LIBS})
|
||||
|
||||
if (BUILD_SHARED_LIBS)
|
||||
set_target_properties(llama PROPERTIES POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE ON)
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(llama PRIVATE LLAMA_SHARED LLAMA_BUILD)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
if (GGML_CUDA_SOURCES)
|
||||
message(STATUS "GGML CUDA sources found, configuring CUDA architecture")
|
||||
set_property(TARGET ggml PROPERTY CUDA_ARCHITECTURES OFF)
|
||||
set_property(TARGET ggml PROPERTY CUDA_SELECT_NVCC_ARCH_FLAGS "Auto")
|
||||
set_property(TARGET llama PROPERTY CUDA_ARCHITECTURES OFF)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# programs, examples and tests
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
|
@ -289,4 +350,5 @@ endif ()
|
|||
|
||||
if (LLAMA_BUILD_EXAMPLES)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(examples)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(pocs)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
47
Makefile
47
Makefile
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,6 @@
|
|||
# Define the default target now so that it is always the first target
|
||||
default: main quantize quantize-stats perplexity embedding vdot
|
||||
|
||||
ifndef UNAME_S
|
||||
UNAME_S := $(shell uname -s)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,7 +39,7 @@ CXXFLAGS = -I. -I./examples -O3 -DNDEBUG -std=c++11 -fPIC
|
|||
LDFLAGS =
|
||||
|
||||
# warnings
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -Wcast-qual -Wdouble-promotion -Wshadow -Wstrict-prototypes -Wpointer-arith -Wno-unused-function
|
||||
CFLAGS += -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -Wcast-qual -Wdouble-promotion -Wshadow -Wstrict-prototypes -Wpointer-arith
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -Wcast-qual -Wno-unused-function -Wno-multichar
|
||||
|
||||
# OS specific
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,13 +74,17 @@ endif
|
|||
# feel free to update the Makefile for your architecture and send a pull request or issue
|
||||
ifeq ($(UNAME_M),$(filter $(UNAME_M),x86_64 i686))
|
||||
# Use all CPU extensions that are available:
|
||||
CFLAGS += -march=native -mtune=native
|
||||
CFLAGS += -march=native -mtune=native
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -march=native -mtune=native
|
||||
|
||||
# Usage AVX-only
|
||||
#CFLAGS += -mfma -mf16c -mavx
|
||||
#CXXFLAGS += -mfma -mf16c -mavx
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifneq ($(filter ppc64%,$(UNAME_M)),)
|
||||
POWER9_M := $(shell grep "POWER9" /proc/cpuinfo)
|
||||
ifneq (,$(findstring POWER9,$(POWER9_M)))
|
||||
CFLAGS += -mcpu=power9
|
||||
CFLAGS += -mcpu=power9
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -mcpu=power9
|
||||
endif
|
||||
# Require c++23's std::byteswap for big-endian support.
|
||||
|
|
@ -97,12 +104,25 @@ ifdef LLAMA_OPENBLAS
|
|||
CFLAGS += -DGGML_USE_OPENBLAS -I/usr/local/include/openblas
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lopenblas
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifdef LLAMA_CUBLAS
|
||||
CFLAGS += -DGGML_USE_CUBLAS -I/usr/local/cuda/include
|
||||
LDFLAGS += -lcublas -lculibos -lcudart -lcublasLt -lpthread -ldl -lrt -L/usr/local/cuda/lib64
|
||||
OBJS += ggml-cuda.o
|
||||
NVCC = nvcc
|
||||
NVCCFLAGS = --forward-unknown-to-host-compiler -arch=native
|
||||
ggml-cuda.o: ggml-cuda.cu ggml-cuda.h
|
||||
$(NVCC) $(NVCCFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) -Wno-pedantic -c $< -o $@
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifdef LLAMA_GPROF
|
||||
CFLAGS += -pg
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -pg
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifdef LLAMA_PERF
|
||||
CFLAGS += -DGGML_PERF
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -DGGML_PERF
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifneq ($(filter aarch64%,$(UNAME_M)),)
|
||||
CFLAGS += -mcpu=native
|
||||
CFLAGS += -mcpu=native
|
||||
CXXFLAGS += -mcpu=native
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifneq ($(filter armv6%,$(UNAME_M)),)
|
||||
|
|
@ -133,8 +153,6 @@ $(info I CC: $(CCV))
|
|||
$(info I CXX: $(CXXV))
|
||||
$(info )
|
||||
|
||||
default: main quantize perplexity embedding
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Build library
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
|
@ -151,32 +169,35 @@ common.o: examples/common.cpp examples/common.h
|
|||
clean:
|
||||
rm -vf *.o main quantize quantize-stats perplexity embedding benchmark-q4_0-matmult
|
||||
|
||||
main: examples/main/main.cpp ggml.o llama.o common.o
|
||||
main: examples/main/main.cpp ggml.o llama.o common.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
@echo
|
||||
@echo '==== Run ./main -h for help. ===='
|
||||
@echo
|
||||
|
||||
quantize: examples/quantize/quantize.cpp ggml.o llama.o
|
||||
quantize: examples/quantize/quantize.cpp ggml.o llama.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
quantize-stats: examples/quantize-stats/quantize-stats.cpp ggml.o llama.o
|
||||
quantize-stats: examples/quantize-stats/quantize-stats.cpp ggml.o llama.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
perplexity: examples/perplexity/perplexity.cpp ggml.o llama.o common.o
|
||||
perplexity: examples/perplexity/perplexity.cpp ggml.o llama.o common.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
embedding: examples/embedding/embedding.cpp ggml.o llama.o common.o
|
||||
embedding: examples/embedding/embedding.cpp ggml.o llama.o common.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
libllama.so: llama.o ggml.o
|
||||
vdot: pocs/vdot/vdot.cpp ggml.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o $@ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
libllama.so: llama.o ggml.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) -shared -fPIC -o $@ $^ $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Tests
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
benchmark: examples/benchmark/benchmark-q4_0-matmult.c ggml.o llama.o common.o
|
||||
benchmark: examples/benchmark/benchmark-q4_0-matmult.c ggml.o llama.o common.o $(OBJS)
|
||||
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o benchmark-q4_0-matmult $(LDFLAGS)
|
||||
./benchmark-q4_0-matmult
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
86
README.md
86
README.md
|
|
@ -7,14 +7,19 @@
|
|||
|
||||
Inference of [LLaMA](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971) model in pure C/C++
|
||||
|
||||
**Warnings**
|
||||
|
||||
- `Q4_2` and `Q4_3` are still in development. Do not expect any kind of backward compatibility until they are finalized
|
||||
|
||||
**Hot topics:**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Added LoRA support](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/820)
|
||||
- [Add GPU support to ggml](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/discussions/915)
|
||||
- [Roadmap Apr 2023](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/discussions/784)
|
||||
|
||||
## Description
|
||||
|
||||
The main goal is to run the model using 4-bit quantization on a MacBook
|
||||
The main goal of llama.cpp is to run the llama model using 4-bit quantization on a MacBook.
|
||||
|
||||
- Plain C/C++ implementation without dependencies
|
||||
- Apple silicon first-class citizen - optimized via ARM NEON and Accelerate framework
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,6 +55,7 @@ New features will probably be added mostly through community contributions.
|
|||
- Python: [abetlen/llama-cpp-python](https://github.com/abetlen/llama-cpp-python)
|
||||
- Go: [go-skynet/go-llama.cpp](https://github.com/go-skynet/go-llama.cpp)
|
||||
- Node.js: [hlhr202/llama-node](https://github.com/hlhr202/llama-node)
|
||||
- Ruby: [yoshoku/llama_cpp.rb](https://github.com/yoshoku/llama_cpp.rb)
|
||||
|
||||
**UI:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,7 +156,7 @@ https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1991296/224442907-7693d4be-acaa-4e01-8
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the step for the LLaMA-7B model.
|
||||
Here are the steps for the LLaMA-7B model.
|
||||
|
||||
### Get the Code
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -208,8 +214,7 @@ When running the larger models, make sure you have enough disk space to store al
|
|||
|
||||
### Memory/Disk Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
As the models are currently fully loaded into memory, you will need adequate disk space to save them
|
||||
and sufficient RAM to load them. At the moment, memory and disk requirements are the same.
|
||||
As the models are currently fully loaded into memory, you will need adequate disk space to save them and sufficient RAM to load them. At the moment, memory and disk requirements are the same.
|
||||
|
||||
| model | original size | quantized size (4-bit) |
|
||||
|-------|---------------|------------------------|
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,22 +226,22 @@ and sufficient RAM to load them. At the moment, memory and disk requirements are
|
|||
### Interactive mode
|
||||
|
||||
If you want a more ChatGPT-like experience, you can run in interactive mode by passing `-i` as a parameter.
|
||||
In this mode, you can always interrupt generation by pressing Ctrl+C and enter one or more lines of text which will be converted into tokens and appended to the current context. You can also specify a *reverse prompt* with the parameter `-r "reverse prompt string"`. This will result in user input being prompted whenever the exact tokens of the reverse prompt string are encountered in the generation. A typical use is to use a prompt which makes LLaMa emulate a chat between multiple users, say Alice and Bob, and pass `-r "Alice:"`.
|
||||
In this mode, you can always interrupt generation by pressing Ctrl+C and entering one or more lines of text, which will be converted into tokens and appended to the current context. You can also specify a *reverse prompt* with the parameter `-r "reverse prompt string"`. This will result in user input being prompted whenever the exact tokens of the reverse prompt string are encountered in the generation. A typical use is to use a prompt that makes LLaMa emulate a chat between multiple users, say Alice and Bob, and pass `-r "Alice:"`.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example few-shot interaction, invoked with the command
|
||||
Here is an example of a few-shot interaction, invoked with the command
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# default arguments using 7B model
|
||||
# default arguments using a 7B model
|
||||
./examples/chat.sh
|
||||
|
||||
# advanced chat with 13B model
|
||||
# advanced chat with a 13B model
|
||||
./examples/chat-13B.sh
|
||||
|
||||
# custom arguments using 13B model
|
||||
# custom arguments using a 13B model
|
||||
./main -m ./models/13B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -n 256 --repeat_penalty 1.0 --color -i -r "User:" -f prompts/chat-with-bob.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note the use of `--color` to distinguish between user input and generated text.
|
||||
Note the use of `--color` to distinguish between user input and generated text. Other parameters are explained in more detail in the [README](examples/main/README.md) for the `main` example program.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -270,22 +275,23 @@ cadaver, cauliflower, cabbage (vegetable), catalpa (tree) and Cailleach.
|
|||
|
||||
### Using [GPT4All](https://github.com/nomic-ai/gpt4all)
|
||||
|
||||
- Obtain the `gpt4all-lora-quantized.bin` model
|
||||
- Obtain the `tokenizer.model` file from LLaMA model and put it to `models`
|
||||
- Obtain the `added_tokens.json` file from Alpaca model and put it to `models`
|
||||
- Obtain the `gpt4all-lora-quantized.bin` file from GPT4All model and put it to `models/gpt4all-7B`
|
||||
- It is distributed in the old `ggml` format which is now obsoleted
|
||||
- You have to convert it to the new format using [./convert-gpt4all-to-ggml.py](./convert-gpt4all-to-ggml.py). You may also need to
|
||||
convert the model from the old format to the new format with [./migrate-ggml-2023-03-30-pr613.py](./migrate-ggml-2023-03-30-pr613.py):
|
||||
- You have to convert it to the new format using `convert.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 convert-gpt4all-to-ggml.py models/gpt4all-7B/gpt4all-lora-quantized.bin ./models/tokenizer.model
|
||||
python3 migrate-ggml-2023-03-30-pr613.py models/gpt4all-7B/gpt4all-lora-quantized.bin models/gpt4all-7B/gpt4all-lora-quantized-new.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 convert.py models/gpt4all-7B/gpt4all-lora-quantized.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- You can now use the newly generated `gpt4all-lora-quantized-new.bin` model in exactly the same way as all other models
|
||||
- The original model is saved in the same folder with a suffix `.orig`
|
||||
- You can now use the newly generated `models/gpt4all-7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin` model in exactly the same way as all other models
|
||||
|
||||
- The newer GPT4All-J model is not yet supported!
|
||||
|
||||
### Obtaining and verifying the Facebook LLaMA original model and Stanford Alpaca model data
|
||||
|
||||
- **Under no circumstances share IPFS, magnet links, or any other links to model downloads anywhere in this respository, including in issues, discussions or pull requests. They will be immediately deleted.**
|
||||
- **Under no circumstances should IPFS, magnet links, or any other links to model downloads be shared anywhere in this repository, including in issues, discussions, or pull requests. They will be immediately deleted.**
|
||||
- The LLaMA models are officially distributed by Facebook and will **never** be provided through this repository.
|
||||
- Refer to [Facebook's LLaMA repository](https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama/pull/73/files) if you need to request access to the model data.
|
||||
- Please verify the [sha256 checksums](SHA256SUMS) of all downloaded model files to confirm that you have the correct model data files before creating an issue relating to your model files.
|
||||
|
|
@ -297,29 +303,27 @@ convert the model from the old format to the new format with [./migrate-ggml-202
|
|||
|
||||
`shasum -a 256 --ignore-missing -c SHA256SUMS` on macOS
|
||||
|
||||
- If your issue is with model generation quality then please at least scan the following links and papers to understand the limitations of LLaMA models. This is especially important when choosing an appropriate model size and appreciating both the significant and subtle differences between LLaMA models and ChatGPT:
|
||||
- LLaMA:
|
||||
- [Introducing LLaMA: A foundational, 65-billion-parameter large language model](https://ai.facebook.com/blog/large-language-model-llama-meta-ai/)
|
||||
- [LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971)
|
||||
- GPT-3
|
||||
- [Language Models are Few-Shot Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.14165)
|
||||
- GPT-3.5 / InstructGPT / ChatGPT:
|
||||
- [Aligning language models to follow instructions](https://openai.com/research/instruction-following)
|
||||
- [Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02155)
|
||||
- If your issue is with model generation quality, then please at least scan the following links and papers to understand the limitations of LLaMA models. This is especially important when choosing an appropriate model size and appreciating both the significant and subtle differences between LLaMA models and ChatGPT:
|
||||
- LLaMA:
|
||||
- [Introducing LLaMA: A foundational, 65-billion-parameter large language model](https://ai.facebook.com/blog/large-language-model-llama-meta-ai/)
|
||||
- [LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971)
|
||||
- GPT-3
|
||||
- [Language Models are Few-Shot Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.14165)
|
||||
- GPT-3.5 / InstructGPT / ChatGPT:
|
||||
- [Aligning language models to follow instructions](https://openai.com/research/instruction-following)
|
||||
- [Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02155)
|
||||
|
||||
### Perplexity (Measuring model quality)
|
||||
### Perplexity (measuring model quality)
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the `perplexity` example to measure perplexity over the given prompt. For more background,
|
||||
see https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perplexity. However, in general, lower perplexity is better for LLMs.
|
||||
You can use the `perplexity` example to measure perplexity over the given prompt. For more background, see [https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perplexity](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perplexity). However, in general, lower perplexity is better for LLMs.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Latest measurements
|
||||
|
||||
The latest perplexity scores for the various model sizes and quantizations are being tracked in [discussion #406](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/discussions/406). `llama.cpp` is measuring very well
|
||||
compared to the baseline implementations. Quantization has a small negative impact to quality, but, as you can see, running
|
||||
The latest perplexity scores for the various model sizes and quantizations are being tracked in [discussion #406](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/discussions/406). `llama.cpp` is measuring very well compared to the baseline implementations. Quantization has a small negative impact on quality, but, as you can see, running
|
||||
13B at q4_0 beats the 7B f16 model by a significant amount.
|
||||
|
||||
All measurements are done against wikitext2 test dataset (https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/wikitext-2), with default options (512 length context).
|
||||
Note that the changing the context length will have a significant impact on perplexity (longer context = better perplexity).
|
||||
All measurements are done against the wikitext2 test dataset (https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/wikitext-2), with default options (512 length context).
|
||||
Note that changing the context length will have a significant impact on perplexity (longer context = better perplexity).
|
||||
```
|
||||
Perplexity - model options
|
||||
5.5985 - 13B, q4_0
|
||||
|
|
@ -361,7 +365,7 @@ https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/271616/225014776-1d567049-ad71-4ef2-b0
|
|||
|
||||
#### Prerequisites
|
||||
* Docker must be installed and running on your system.
|
||||
* Create a folder to store big models & intermediate files (in ex. im using /llama/models)
|
||||
* Create a folder to store big models & intermediate files (ex. /llama/models)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Images
|
||||
We have two Docker images available for this project:
|
||||
|
|
@ -375,17 +379,17 @@ The easiest way to download the models, convert them to ggml and optimize them i
|
|||
|
||||
Replace `/path/to/models` below with the actual path where you downloaded the models.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -v /path/to/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full --all-in-one "/models/" 7B
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On complete, you are ready to play!
|
||||
On completion, you are ready to play!
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -v /path/to/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full --run -m /models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or with light image:
|
||||
or with a light image:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -v /path/to/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:light -m /models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
|
||||
|
|
@ -406,7 +410,7 @@ docker run -v /path/to/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:light -m /mode
|
|||
- Always consider cross-compatibility with other operating systems and architectures
|
||||
- Avoid fancy looking modern STL constructs, use basic `for` loops, avoid templates, keep it simple
|
||||
- There are no strict rules for the code style, but try to follow the patterns in the code (indentation, spaces, etc.). Vertical alignment makes things more readable and easier to batch edit
|
||||
- Clean-up any trailing whitespaces, use 4 spaces indentation, brackets on same line, `void * ptr`, `int & a`
|
||||
- Clean-up any trailing whitespaces, use 4 spaces for indentation, brackets on the same line, `void * ptr`, `int & a`
|
||||
- See [good first issues](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) for tasks suitable for first contributions
|
||||
|
||||
### Docs
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
20
SHA256SUMS
20
SHA256SUMS
|
|
@ -1,12 +1,27 @@
|
|||
700df0d3013b703a806d2ae7f1bfb8e59814e3d06ae78be0c66368a50059f33d models/7B/consolidated.00.pth
|
||||
666a4bb533b303bdaf89e1b6a3b6f93535d868de31d903afdc20983dc526c847 models/7B/ggml-model-f16.bin
|
||||
99aeb35f26b577fa2732716cca4d8b5ada39a78ea9b2dca2651fc632b5d101b6 models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin
|
||||
cc061458339a3eb8bcecbf0a825e9924fb7d1a8150f63cd5d091caa99215aafe models/7B/ggml-model-q4_1.bin
|
||||
25b050337a87344da687a7f2adddc03bd99b7f6c140450e836649f3585fb6496 models/7B/ggml-model-q4_2.bin
|
||||
3429bf198ec771886cf81a574df45245f3ebf04f0ce0956b73ef5d0ab01ff48b models/7B/ggml-model-q4_3.bin
|
||||
7e89e242ddc0dd6f060b43ca219ce8b3e8f08959a72cb3c0855df8bb04d46265 models/7B/params.json
|
||||
745bf4e29a4dd6f411e72976d92b452da1b49168a4f41c951cfcc8051823cf08 models/13B/consolidated.00.pth
|
||||
d5ccbcc465c71c0de439a5aeffebe8344c68a519bce70bc7f9f92654ee567085 models/13B/consolidated.01.pth
|
||||
2b206e9b21fb1076f11cafc624e2af97c9e48ea09312a0962153acc20d45f808 models/13B/ggml-model-f16.bin
|
||||
eecb575d325d935157761172e2bf05984dad216eb2b06777b73463cf9b818bab models/13B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin
|
||||
d9581b5b88e5622532fe897c9f9b0e67a317d22dd27a6f90fa4ab8c6d23ccdbb models/13B/ggml-model-q4_1.bin
|
||||
75a218a47df03f5f96354656329864613abcb67779412b9bc2282b28c1c3cbaa models/13B/ggml-model-q4_2.bin
|
||||
4208cdec9788ffa48dc1a17af2c36a0299f5bf3eb0e2b87889dda7fad591fca3 models/13B/ggml-model-q4_3.bin
|
||||
4ab77bec4d4405ccb66a97b282574c89a94417e3c32e5f68f37e2876fc21322f models/13B/params.json
|
||||
e23294a58552d8cdec5b7e8abb87993b97ea6eced4178ff2697c02472539d067 models/30B/consolidated.00.pth
|
||||
4e077b7136c7ae2302e954860cf64930458d3076fcde9443f4d0e939e95903ff models/30B/consolidated.01.pth
|
||||
24a87f01028cbd3a12de551dcedb712346c0b5cbdeff1454e0ddf2df9b675378 models/30B/consolidated.02.pth
|
||||
1adfcef71420886119544949767f6a56cb6339b4d5fcde755d80fe68b49de93b models/30B/consolidated.03.pth
|
||||
7e1b524061a9f4b27c22a12d6d2a5bf13b8ebbea73e99f218809351ed9cf7d37 models/30B/ggml-model-f16.bin
|
||||
517b9e525742c42b5478a6280a4b41ec66f46298c57aba7f0453d491682fe42d models/30B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin
|
||||
7b75ac615fa369ee593493a7e6ef87542bf0350255db928b22c5a24f6d598bcd models/30B/ggml-model-q4_1.bin
|
||||
aadbc9cf806313a55be570f62884eed289d30c313fac3b7838717e01bd553204 models/30B/ggml-model-q4_2.bin
|
||||
a6188660199dbcb8d5658abe7d89169869e50423494385830d9e6b330ea7fc33 models/30B/ggml-model-q4_3.bin
|
||||
2c07118ea98d69dbe7810d88520e30288fa994751b337f8fca02b171955f44cb models/30B/params.json
|
||||
135c563f6b3938114458183afb01adc9a63bef3d8ff7cccc3977e5d3664ecafe models/65B/consolidated.00.pth
|
||||
9a600b37b19d38c7e43809485f70d17d1dc12206c07efa83bc72bb498a568bde models/65B/consolidated.01.pth
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,5 +31,10 @@ e7babf7c5606f165a3756f527cb0fedc4f83e67ef1290391e52fb1cce5f26770 models/65B/con
|
|||
a287c0dfe49081626567c7fe87f74cce5831f58e459b427b5e05567641f47b78 models/65B/consolidated.05.pth
|
||||
72b4eba67a1a3b18cb67a85b70f8f1640caae9b40033ea943fb166bd80a7b36b models/65B/consolidated.06.pth
|
||||
d27f5b0677d7ff129ceacd73fd461c4d06910ad7787cf217b249948c3f3bc638 models/65B/consolidated.07.pth
|
||||
60758f2384d74e423dffddfd020ffed9d3bb186ebc54506f9c4a787d0f5367b0 models/65B/ggml-model-f16.bin
|
||||
01672072136f8be6ca9d7cebe5f86ed316e8b85851b9fe3de951809233cea4f2 models/65B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin
|
||||
4743a28aac3e5f32a6e838a815f51d3779de44fbbe251d745251e66c23c5950f models/65B/ggml-model-q4_1.bin
|
||||
1b6f6588d0e2ecfe6c4d849088e48e5e3083466b962daa32e3261363e21fc5e9 models/65B/ggml-model-q4_2.bin
|
||||
305e91a4608b4f627b9b8ad5b4af75187d2684254bfd76dcb9db571618ef293c models/65B/ggml-model-q4_3.bin
|
||||
999ed1659b469ccc2a941714c0a9656fa571d17c9f7c8c7589817ca90edef51b models/65B/params.json
|
||||
9e556afd44213b6bd1be2b850ebbbd98f5481437a8021afaf58ee7fb1818d347 models/tokenizer.model
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
129
convert-lora-to-ggml.py
Normal file
129
convert-lora-to-ggml.py
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
|||
import json
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import struct
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, Sequence, TextIO
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from convert import DATA_TYPE_TO_FTYPE, NUMPY_TYPE_TO_DATA_TYPE, DataType
|
||||
|
||||
HF_SUBLAYER_TO_GGML = {
|
||||
"self_attn.q_proj": "attention.wq",
|
||||
"self_attn.k_proj": "attention.wk",
|
||||
"self_attn.v_proj": "attention.wv",
|
||||
"self_attn.o_proj": "attention.wo",
|
||||
"mlp.gate_proj": "feed_forward.w1",
|
||||
"mlp.down_proj": "feed_forward.w2",
|
||||
"mlp.up_proj": "feed_forward.w3",
|
||||
"input_layernorm": "attention_norm",
|
||||
"post_attention_layernorm": "ffn_norm",
|
||||
# "norm": "norm",
|
||||
# "embed_tokens": "tok_embeddings",
|
||||
# "lm_head": "output",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def translate_tensor_name(t: str) -> str:
|
||||
match = re.match(r".*layers\.(\d+)\.(\w+\.\w+)\.lora_(A|B)\.weight", t)
|
||||
if match:
|
||||
nn = match.group(1)
|
||||
sub_layer = match.group(2)
|
||||
lora_type = match.group(3)
|
||||
|
||||
sub_layer_renamed = HF_SUBLAYER_TO_GGML.get(sub_layer)
|
||||
if sub_layer_renamed is None:
|
||||
print(f"Error: unrecognized sub-layer {sub_layer} in tensor {t}")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
output_string = (
|
||||
f"layers.{nn}.{HF_SUBLAYER_TO_GGML[sub_layer]}.weight.lora{lora_type}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return output_string
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(f"Error: unrecognized tensor {t}")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def write_file_header(fout: TextIO, params: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
|
||||
fout.write(b"ggla"[::-1]) # magic (ggml lora)
|
||||
fout.write(struct.pack("i", 1)) # file version
|
||||
fout.write(struct.pack("i", params["r"]))
|
||||
# https://opendelta.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/deltas.html says that `lora_alpha` is an int
|
||||
# but some models ship a float value instead
|
||||
# let's convert to int, but fail if lossless conversion is not possible
|
||||
assert int(params["lora_alpha"]) == params["lora_alpha"], "cannot convert float to int losslessly"
|
||||
fout.write(struct.pack("i", int(params["lora_alpha"])))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def write_tensor_header(
|
||||
self, name: str, shape: Sequence[int], data_type: DataType
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
sname = name.encode("utf-8")
|
||||
fout.write(
|
||||
struct.pack(
|
||||
"iii",
|
||||
len(shape),
|
||||
len(sname),
|
||||
DATA_TYPE_TO_FTYPE[NUMPY_TYPE_TO_DATA_TYPE[data_type]],
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
fout.write(struct.pack("i" * len(shape), *shape[::-1]))
|
||||
fout.write(sname)
|
||||
fout.seek((fout.tell() + 31) & -32)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
|
||||
print(f"Usage: python {sys.argv[0]} <path>")
|
||||
print(
|
||||
"Path must contain HuggingFace PEFT LoRA files 'adapter_config.json' and 'adapter_model.bin'"
|
||||
)
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
input_json = os.path.join(sys.argv[1], "adapter_config.json")
|
||||
input_model = os.path.join(sys.argv[1], "adapter_model.bin")
|
||||
output_path = os.path.join(sys.argv[1], "ggml-adapter-model.bin")
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.load(input_model, map_location="cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
with open(input_json, "r") as f:
|
||||
params = json.load(f)
|
||||
|
||||
if params["peft_type"] != "LORA":
|
||||
print(f"Error: unsupported adapter type {params['peft_type']}, expected LORA")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
if params["fan_in_fan_out"] is True:
|
||||
print("Error: param fan_in_fan_out is not supported")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
if params["bias"] is not None and params["bias"] != "none":
|
||||
print("Error: param bias is not supported")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: these seem to be layers that have been trained but without lora.
|
||||
# doesn't seem widely used but eventually should be supported
|
||||
if params["modules_to_save"] is not None and len(params["modules_to_save"]) > 0:
|
||||
print("Error: param modules_to_save is not supported")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
with open(output_path, "wb") as fout:
|
||||
fout.truncate()
|
||||
|
||||
write_file_header(fout, params)
|
||||
for k, v in model.items():
|
||||
if k.endswith("lora_A.weight"):
|
||||
if v.dtype != torch.float16 and v.dtype != torch.float32:
|
||||
v = v.float()
|
||||
v = v.T
|
||||
else:
|
||||
v = v.float()
|
||||
|
||||
t = v.numpy()
|
||||
tname = translate_tensor_name(k)
|
||||
print(f"{k} => {tname} {t.shape} {t.dtype} {t.nbytes/1024/1024:.2f}MB")
|
||||
write_tensor_header(fout, tname, t.shape, t.dtype)
|
||||
t.tofile(fout)
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Converted {input_json} and {input_model} to {output_path}")
|
||||
14
convert.py
14
convert.py
|
|
@ -735,7 +735,7 @@ def lazy_load_safetensors_file(fp: IO[bytes], path: Path) -> ModelPlus:
|
|||
header: Dict[str, Dict[str, Any]] = json.loads(fp.read(header_size))
|
||||
# Use mmap for the actual data to avoid race conditions with the file offset.
|
||||
mapped = memoryview(mmap.mmap(fp.fileno(), 0, access=mmap.ACCESS_READ))
|
||||
byte_buf = mapped[fp.tell():]
|
||||
byte_buf = mapped[8 + header_size:]
|
||||
|
||||
def convert(info: Dict[str, Any]) -> LazyTensor:
|
||||
data_type = SAFETENSORS_DATA_TYPES[info['dtype']]
|
||||
|
|
@ -761,7 +761,7 @@ def must_read(fp: IO[bytes], length: int) -> bytes:
|
|||
return ret
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def lazy_load_ggml_file(fp: IO[bytes], path: Path) -> ModelPlus:
|
||||
def lazy_load_ggml_file(fp: io.BufferedReader, path: Path) -> ModelPlus:
|
||||
magic = must_read(fp, 4)[::-1]
|
||||
if magic in (b'ggmf', b'ggjt'):
|
||||
version, = struct.unpack("i", must_read(fp, 4))
|
||||
|
|
@ -795,7 +795,9 @@ def lazy_load_ggml_file(fp: IO[bytes], path: Path) -> ModelPlus:
|
|||
|
||||
model: LazyModel = {}
|
||||
# Use mmap for the actual data to avoid race conditions with the file offset.
|
||||
off = fp.raw.tell()
|
||||
mapped = memoryview(mmap.mmap(fp.fileno(), 0, access=mmap.ACCESS_READ))
|
||||
fp.raw.seek(off) # needed on Windows
|
||||
|
||||
def read_tensor() -> None: # this is a function so that variables captured in `load` don't change
|
||||
shape_len, name_len, ftype = struct.unpack("iii", must_read(fp, 12))
|
||||
|
|
@ -949,8 +951,9 @@ class OutputFile:
|
|||
|
||||
ndarrays = bounded_parallel_map(do_item, model.items(), concurrency=8)
|
||||
for i, ((name, lazy_tensor), ndarray) in enumerate(zip(model.items(), ndarrays)):
|
||||
size = ' x '.join(map(str, lazy_tensor.shape))
|
||||
print(f"[{i+1}/{len(model)}] Writing tensor {name}, size {size}...")
|
||||
size = ' x '.join(f"{dim:6d}" for dim in lazy_tensor.shape)
|
||||
padi = len(str(len(model)))
|
||||
print(f"[{i+1:{padi}d}/{len(model)}] Writing tensor {name:38s} | size {size:16} | type {lazy_tensor.data_type}")
|
||||
of.write_tensor_header(name, lazy_tensor.shape, lazy_tensor.data_type)
|
||||
ndarray.tofile(of.fout)
|
||||
of.fout.close()
|
||||
|
|
@ -1082,6 +1085,7 @@ def default_outfile(model_paths: List[Path], params: Params) -> Path:
|
|||
namestr = {
|
||||
GGMLFileType.AllF32: "f32",
|
||||
GGMLFileType.MostlyF16: "f16",
|
||||
GGMLFileType.MostlyQ4_0: "q4_0",
|
||||
GGMLFileType.MostlyQ4_1: "q4_1",
|
||||
GGMLFileType.PerLayerIsQ4_1: "q4_1",
|
||||
}[params.file_type]
|
||||
|
|
@ -1105,7 +1109,7 @@ def main(args_in: Optional[List[str]] = None) -> None:
|
|||
parser.add_argument("--dump", action="store_true", help="don't convert, just show what's in the model")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--dump-single", action="store_true", help="don't convert, just show what's in a single model file")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--vocab-only", action="store_true", help="extract only the vocab")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--outtype", choices=["f32", "f16", "q4_1"], help="output format (default: based on input)")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--outtype", choices=["f32", "f16", "q4_1", "q4_0"], help="output format (default: based on input)")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--vocab-dir", type=Path, help="directory containing tokenizer.model, if separate from model file")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--outfile", type=Path, help="path to write to; default: based on input")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("model", type=Path, help="directory containing model file, or model file itself (*.pth, *.pt, *.bin)")
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -34,5 +34,6 @@ else()
|
|||
add_subdirectory(quantize-stats)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(perplexity)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(embedding)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(save-load-state)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(benchmark)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,4 +7,13 @@
|
|||
cd `dirname $0`
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
|
||||
./main -m ./models/ggml-alpaca-7b-q4.bin --color -f ./prompts/alpaca.txt --ctx_size 2048 -n -1 -ins -b 256 --top_k 10000 --temp 0.2 --repeat_penalty 1 -t 7
|
||||
./main -m ./models/ggml-alpaca-7b-q4.bin \
|
||||
--color \
|
||||
-f ./prompts/alpaca.txt \
|
||||
--ctx_size 2048 \
|
||||
-n -1 \
|
||||
-ins -b 256 \
|
||||
--top_k 10000 \
|
||||
--temp 0.2 \
|
||||
--repeat_penalty 1.1 \
|
||||
-t 7
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -139,14 +139,25 @@ bool gpt_params_parse(int argc, char ** argv, gpt_params & params) {
|
|||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params.model = argv[i];
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--lora") {
|
||||
if (++i >= argc) {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params.lora_adapter = argv[i];
|
||||
params.use_mmap = false;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--lora-base") {
|
||||
if (++i >= argc) {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params.lora_base = argv[i];
|
||||
} else if (arg == "-i" || arg == "--interactive") {
|
||||
params.interactive = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--embedding") {
|
||||
params.embedding = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--interactive-start") {
|
||||
params.interactive = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--interactive-first") {
|
||||
params.interactive_start = true;
|
||||
params.interactive_first = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "-ins" || arg == "--instruct") {
|
||||
params.instruct = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--color") {
|
||||
|
|
@ -242,6 +253,8 @@ void gpt_print_usage(int /*argc*/, char ** argv, const gpt_params & params) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " --mtest compute maximum memory usage\n");
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " --verbose-prompt print prompt before generation\n");
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " --lora FNAME apply LoRA adapter (implies --no-mmap)\n");
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " --lora-base FNAME optional model to use as a base for the layers modified by the LoRA adapter\n");
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " -m FNAME, --model FNAME\n");
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " model path (default: %s)\n", params.model.c_str());
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ struct gpt_params {
|
|||
int32_t repeat_last_n = 64; // last n tokens to penalize
|
||||
int32_t n_parts = -1; // amount of model parts (-1 = determine from model dimensions)
|
||||
int32_t n_ctx = 512; // context size
|
||||
int32_t n_batch = 8; // batch size for prompt processing
|
||||
int32_t n_batch = 512; // batch size for prompt processing (must be >=32 to use BLAS)
|
||||
int32_t n_keep = 0; // number of tokens to keep from initial prompt
|
||||
|
||||
// sampling parameters
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,18 +31,19 @@ struct gpt_params {
|
|||
|
||||
std::string model = "models/lamma-7B/ggml-model.bin"; // model path
|
||||
std::string prompt = "";
|
||||
std::string input_prefix = ""; // string to prefix user inputs with
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
std::string input_prefix = ""; // string to prefix user inputs with
|
||||
std::vector<std::string> antiprompt; // string upon seeing which more user input is prompted
|
||||
|
||||
std::string lora_adapter = ""; // lora adapter path
|
||||
std::string lora_base = ""; // base model path for the lora adapter
|
||||
|
||||
bool memory_f16 = true; // use f16 instead of f32 for memory kv
|
||||
bool random_prompt = false; // do not randomize prompt if none provided
|
||||
bool use_color = false; // use color to distinguish generations and inputs
|
||||
bool interactive = false; // interactive mode
|
||||
|
||||
bool embedding = false; // get only sentence embedding
|
||||
bool interactive_start = false; // wait for user input immediately
|
||||
bool interactive_first = false; // wait for user input immediately
|
||||
|
||||
bool instruct = false; // instruction mode (used for Alpaca models)
|
||||
bool ignore_eos = false; // do not stop generating after eos
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
|
|||
#include "common.h"
|
||||
#include "llama.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <ctime>
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
||||
gpt_params params;
|
||||
params.model = "models/llama-7B/ggml-model.bin";
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,191 @@
|
|||
# main
|
||||
# llama.cpp/example/main
|
||||
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
This example program allows you to use various LLaMA language models in an easy and efficient way. It is specifically designed to work with the [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) project, which provides a plain C/C++ implementation with optional 4-bit quantization support for faster, lower memory inference, and is optimized for desktop CPUs. This program can be used to perform various inference tasks with LLaMA models, including generating text based on user-provided prompts and chat-like interactions with reverse prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of Contents
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Quick Start](#quick-start)
|
||||
2. [Common Options](#common-options)
|
||||
3. [Input Prompts](#input-prompts)
|
||||
4. [Interaction](#interaction)
|
||||
5. [Context Management](#context-management)
|
||||
6. [Generation Flags](#generation-flags)
|
||||
7. [Performance Tuning and Memory Options](#performance-tuning-and-memory-options)
|
||||
8. [Additional Options](#additional-options)
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Start
|
||||
|
||||
To get started right away, run the following command, making sure to use the correct path for the model you have:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./main -m models/7B/ggml-model.bin --prompt "Once upon a time"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following command generates "infinite" text from a starting prompt (you can use `Ctrl-C` to stop it):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./main -m models/7B/ggml-model.bin --ignore-eos --n_predict -1 --keep -1 --prompt "Once upon a time"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For an interactive experience, try this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./main -m models/7B/ggml-model.bin -n -1 --color -r "User:" --in-prefix " " --prompt $'User: Hi\nAI: Hello. I am an AI chatbot. Would you like to talk?\nUser: Sure!\nAI: What would you like to talk about?\nUser:'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the newline characters in the prompt string above only work on Linux. On Windows, you will have to use the ``--file`` option (see below) to load a multi-line prompt from file instead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Options
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we cover the most commonly used options for running the `main` program with the LLaMA models:
|
||||
|
||||
- `-m FNAME, --model FNAME`: Specify the path to the LLaMA model file (e.g., `models/7B/ggml-model.bin`).
|
||||
- `-i, --interactive`: Run the program in interactive mode, allowing you to provide input directly and receive real-time responses.
|
||||
- `-ins, --instruct`: Run the program in instruction mode, which is particularly useful when working with Alpaca models.
|
||||
- `-t N, --threads N`: Set the number of threads to use during computation. It is recommended to set this to the number of physical cores your CPU has.
|
||||
- `-n N, --n_predict N`: Set the number of tokens to predict when generating text. Adjusting this value can influence the length of the generated text.
|
||||
- `-c N, --ctx_size N`: Set the size of the prompt context. The default is 512, but LLaMA models were built with a context of 2048, which will provide better results for longer input/inference.
|
||||
|
||||
## Input Prompts
|
||||
|
||||
The `main` program provides several ways to interact with the LLaMA models using input prompts:
|
||||
|
||||
- `--prompt PROMPT`: Provide a prompt directly as a command-line option.
|
||||
- `--file FNAME`: Provide a file containing a prompt or multiple prompts.
|
||||
- `--interactive-first`: Run the program in interactive mode and wait for input right away. (More on this below.)
|
||||
- `--random-prompt`: Start with a randomized prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
## Interaction
|
||||
|
||||
The `main` program offers a seamless way to interact with LLaMA models, allowing users to engage in real-time conversations or provide instructions for specific tasks. The interactive mode can be triggered using various options, including `--interactive`, `--interactive-first`, and `--instruct`.
|
||||
|
||||
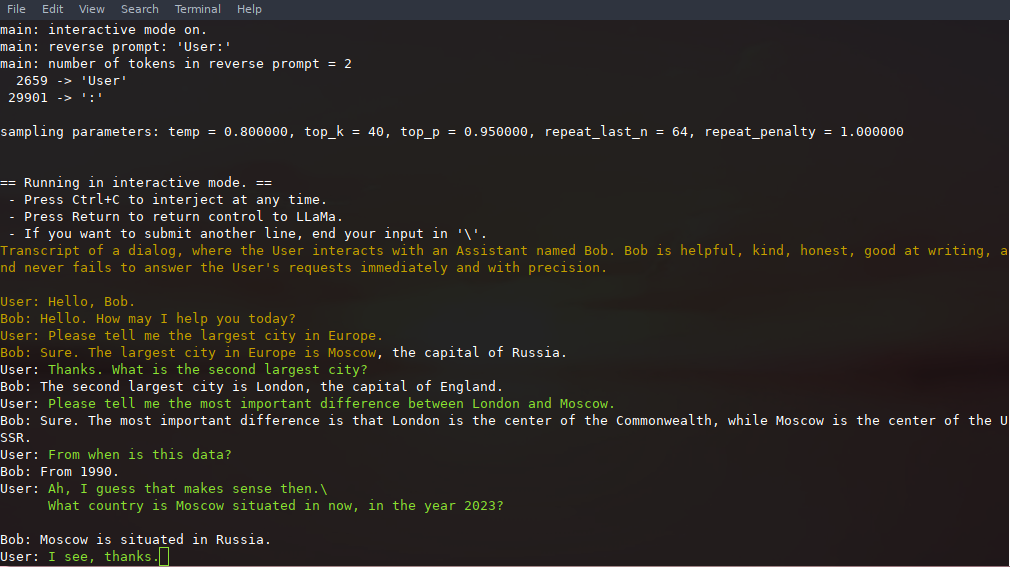
In interactive mode, users can participate in text generation by injecting their input during the process. Users can press `Ctrl+C` at any time to interject and type their input, followed by pressing `Return` to submit it to the LLaMA model. To submit additional lines without finalizing input, users can end the current line with a backslash (`\`) and continue typing.
|
||||
|
||||
### Interaction Options
|
||||
|
||||
- `-i, --interactive`: Run the program in interactive mode, allowing users to engage in real-time conversations or provide specific instructions to the model.
|
||||
- `--interactive-first`: Run the program in interactive mode and immediately wait for user input before starting the text generation.
|
||||
- `-ins, --instruct`: Run the program in instruction mode, which is specifically designed to work with Alpaca models that excel in completing tasks based on user instructions.
|
||||
- `--color`: Enable colorized output to differentiate visually distinguishing between prompts, user input, and generated text.
|
||||
|
||||
By understanding and utilizing these interaction options, you can create engaging and dynamic experiences with the LLaMA models, tailoring the text generation process to your specific needs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reverse Prompts
|
||||
|
||||
Reverse prompts are a powerful way to create a chat-like experience with a LLaMA model by pausing the text generation when specific text strings are encountered:
|
||||
|
||||
- `-r PROMPT, --reverse-prompt PROMPT`: Specify one or multiple reverse prompts to pause text generation and switch to interactive mode. For example, `-r "User:"` can be used to jump back into the conversation whenever it's the user's turn to speak. This helps create a more interactive and conversational experience. However, the reverse prompt doesn't work when it ends with a space.
|
||||
|
||||
To overcome this limitation, you can use the `--in-prefix` flag to add a space or any other characters after the reverse prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
### In-Prefix
|
||||
|
||||
The `--in-prefix` flag is used to add a prefix to your input, primarily, this is used to insert a space after the reverse prompt. Here's an example of how to use the `--in-prefix` flag in conjunction with the `--reverse-prompt` flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
./main -r "User:" --in-prefix " "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Instruction Mode
|
||||
|
||||
Instruction mode is particularly useful when working with Alpaca models, which are designed to follow user instructions for specific tasks:
|
||||
|
||||
- `-ins, --instruct`: Enable instruction mode to leverage the capabilities of Alpaca models in completing tasks based on user-provided instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
Technical detail: the user's input is internally prefixed with the reverse prompt (or ``### Instruction:`` as the default), and followed by ``### Response:`` (except if you just press Return without any input, to keep generating a longer response).
|
||||
|
||||
By understanding and utilizing these interaction options, you can create engaging and dynamic experiences with the LLaMA models, tailoring the text generation process to your specific needs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Context Management
|
||||
|
||||
During text generation, LLaMA models have a limited context size, which means they can only consider a certain number of tokens from the input and generated text. When the context fills up, the model resets internally, potentially losing some information from the beginning of the conversation or instructions. Context management options help maintain continuity and coherence in these situations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Context Size
|
||||
|
||||
The `--ctx_size` option allows you to set the size of the prompt context used by the LLaMA models during text generation. A larger context size helps the model to better comprehend and generate responses for longer input or conversations.
|
||||
|
||||
- `-c N, --ctx_size N`: Set the size of the prompt context (default: 512). The LLaMA models were built with a context of 2048, which will yield the best results on longer input/inference. However, increasing the context size beyond 2048 may lead to unpredictable results.
|
||||
|
||||
### Keep Prompt
|
||||
|
||||
The `--keep` option allows users to retain the original prompt when the model runs out of context, ensuring a connection to the initial instruction or conversation topic is maintained.
|
||||
|
||||
- `--keep N`: Specify the number of tokens from the initial prompt to retain when the model resets its internal context. By default, this value is set to 0 (meaning no tokens are kept). Use `-1` to retain all tokens from the initial prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
By utilizing context management options like `--ctx_size` and `--keep`, you can maintain a more coherent and consistent interaction with the LLaMA models, ensuring that the generated text remains relevant to the original prompt or conversation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Generation Flags
|
||||
|
||||
The following options are related to controlling the text generation process, influencing the diversity, creativity, and quality of the generated text. Understanding these options will help you fine-tune the output according to your needs:
|
||||
|
||||
### Number of Tokens to Predict
|
||||
|
||||
- `-n N, --n_predict N`: Set the number of tokens to predict when generating text (default: 128, -1 = infinity).
|
||||
|
||||
The `--n_predict` option controls the number of tokens the model generates in response to the input prompt. By adjusting this value, you can influence the length of the generated text. A higher value will result in longer text, while a lower value will produce shorter text. A value of -1 will cause text to be generated without limit.
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to note that the generated text may be shorter than the specified number of tokens if an End-of-Sequence (EOS) token or a reverse prompt is encountered. In interactive mode text generation will pause and control will be returned to the user. In non-interactive mode, the program will end. In both cases, the text generation may stop before reaching the specified `n_predict` value. If you want the model to keep going without ever producing End-of-Sequence on its own, you can use the ``--ignore-eos`` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
### RNG Seed
|
||||
|
||||
- `-s SEED, --seed SEED`: Set the random number generator (RNG) seed (default: -1).
|
||||
|
||||
The RNG seed is used to initialize the random number generator that influences the text generation process. By setting a specific seed value, you can obtain consistent and reproducible results across multiple runs with the same input and settings. This can be helpful for testing, debugging, or comparing the effects of different options on the generated text to see when they diverge. If the seed is set to a value less than or equal to 0, a random seed will be used, which will result in different outputs on each run.
|
||||
|
||||
### Temperature
|
||||
|
||||
- `--temp N`: Adjust the randomness of the generated text (default: 0.8).
|
||||
|
||||
Temperature is a hyperparameter that controls the randomness of the generated text. It affects the probability distribution of the model's output tokens. A higher temperature (e.g., 1.5) makes the output more random and creative, while a lower temperature (e.g., 0.5) makes the output more focused, deterministic, and conservative. The default value is 0.8, which provides a balance between randomness and determinism. At the extreme, a temperature of 0 will always pick the most likely next token, leading to identical outputs in each run.
|
||||
|
||||
Example usage: `--temp 0.8`
|
||||
|
||||
### Repeat Penalty
|
||||
|
||||
- `--repeat_penalty N`: Control the repetition of token sequences in the generated text (default: 1.1).
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat penalty is a hyperparameter used to penalize the repetition of token sequences during text generation. It helps prevent the model from generating repetitive or monotonous text. A higher value (e.g., 1.5) will penalize repetitions more strongly, while a lower value (e.g., 0.9) will be more lenient. The default value is 1.1.
|
||||
|
||||
Example usage: `--repeat_penalty 1.1`
|
||||
|
||||
### Top-K Sampling
|
||||
|
||||
- `--top_k N`: Limit the next token selection to the K most probable tokens (default: 40).
|
||||
|
||||
Top-k sampling is a text generation method that selects the next token only from the top k most likely tokens predicted by the model. It helps reduce the risk of generating low-probability or nonsensical tokens, but it may also limit the diversity of the output. A higher value for top_k (e.g., 100) will consider more tokens and lead to more diverse text, while a lower value (e.g., 10) will focus on the most probable tokens and generate more conservative text. The default value is 40.
|
||||
|
||||
Example usage: `--top_k 40`
|
||||
|
||||
### Top-P Sampling
|
||||
|
||||
- `--top_p N`: Limit the next token selection to a subset of tokens with a cumulative probability above a threshold P (default: 0.9).
|
||||
|
||||
Top-p sampling, also known as nucleus sampling, is another text generation method that selects the next token from a subset of tokens that together have a cumulative probability of at least p. This method provides a balance between diversity and quality by considering both the probabilities of tokens and the number of tokens to sample from. A higher value for top_p (e.g., 0.95) will lead to more diverse text, while a lower value (e.g., 0.5) will generate more focused and conservative text. The default value is 0.9.
|
||||
|
||||
Example usage: `--top_p 0.9`
|
||||
|
||||
By adjusting these options, you can control the diversity, quality, and creativity of the generated text to better suit your needs. You can experiment with different combinations of values to find the best settings for your specific use case.
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance Tuning and Memory Options
|
||||
|
||||
These options help improve the performance and memory usage of the LLaMA models:
|
||||
|
||||
- `-t N, --threads N`: Set the number of threads to use during computation. Using the correct number of threads can greatly improve performance. It is recommended to set this value to the number of CPU cores.
|
||||
- `--mlock`: Lock the model in memory, preventing it from being swapped out when mmaped. This can improve performance.
|
||||
- `--no-mmap`: Do not memory-map the model. This results in a slower load time but may reduce pageouts if you're not using `mlock`.
|
||||
- `--memory_f32`: Use 32 bit floats instead of 16 bit floats for memory key+value, allowing higher quality inference at the cost of memory.
|
||||
- `-b N, --batch_size N`: Set the batch size for prompt processing (default: 512). This large batch size benefits users who have BLAS installed and enabled it during the build. If you don't have BLAS enabled ("BLAS=0"), you can use a smaller number, such as 8, to see the prompt progress as it's evaluated in some situations.
|
||||
|
||||
For information about 4-bit quantization, which can significantly improve performance and reduce memory usage, please refer to llama.cpp's primary [README](../../README.md#prepare-data--run).
|
||||
|
||||
By understanding and using these performance tuning settings, you can optimize the LLaMA model's behavior to achieve the best performance for your specific needs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional Options
|
||||
|
||||
These options provide extra functionality and customization when running the LLaMA models:
|
||||
|
||||
- `-h, --help`: Display a help message showing all available options and their default values. This is particularly useful for checking the latest options and default values, as they can change frequently, and the information in this document may become outdated.
|
||||
- `--verbose-prompt`: Print the prompt before generating text.
|
||||
- `--mtest`: Test the model's functionality by running a series of tests to ensure it's working properly.
|
||||
- `--lora FNAME`: Apply a LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) adapter to the model (implies --no-mmap). This allows you to adapt the pretrained model to specific tasks or domains.
|
||||
- `--lora-base FNAME`: Optional model to use as a base for the layers modified by the LoRA adapter. This flag is used in conjunction with the `--lora` flag, and specifies the base model for the adaptation.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,6 +11,7 @@
|
|||
#include <cmath>
|
||||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#include <cstring>
|
||||
#include <ctime>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
|
|
@ -24,6 +25,7 @@
|
|||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
static console_state con_st;
|
||||
static llama_context ** g_ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
static bool is_interacting = false;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,6 +37,7 @@ void sigint_handler(int signo) {
|
|||
if (!is_interacting) {
|
||||
is_interacting=true;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
llama_print_timings(*g_ctx);
|
||||
_exit(130);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,6 +96,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
//bool is_prime(int n) {)";
|
||||
|
||||
llama_context * ctx;
|
||||
g_ctx = &ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
// load the model
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
|
@ -113,6 +117,17 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!params.lora_adapter.empty()) {
|
||||
int err = llama_apply_lora_from_file(ctx,
|
||||
params.lora_adapter.c_str(),
|
||||
params.lora_base.empty() ? NULL : params.lora_base.c_str(),
|
||||
params.n_threads);
|
||||
if (err != 0) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: error: failed to apply lora adapter\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// print system information
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
|
||||
|
|
@ -163,12 +178,12 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
|
||||
// in instruct mode, we inject a prefix and a suffix to each input by the user
|
||||
if (params.instruct) {
|
||||
params.interactive_start = true;
|
||||
params.interactive_first = true;
|
||||
params.antiprompt.push_back("### Instruction:\n\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// enable interactive mode if reverse prompt or interactive start is specified
|
||||
if (params.antiprompt.size() != 0 || params.interactive_start) {
|
||||
if (params.antiprompt.size() != 0 || params.interactive_first) {
|
||||
params.interactive = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -231,7 +246,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
#endif
|
||||
" - Press Return to return control to LLaMa.\n"
|
||||
" - If you want to submit another line, end your input in '\\'.\n\n");
|
||||
is_interacting = params.interactive_start;
|
||||
is_interacting = params.interactive_first;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool is_antiprompt = false;
|
||||
|
|
@ -252,7 +267,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
// infinite text generation via context swapping
|
||||
// if we run out of context:
|
||||
// - take the n_keep first tokens from the original prompt (via n_past)
|
||||
// - take half of the last (n_ctx - n_keep) tokens and recompute the logits in a batch
|
||||
// - take half of the last (n_ctx - n_keep) tokens and recompute the logits in batches
|
||||
if (n_past + (int) embd.size() > n_ctx) {
|
||||
const int n_left = n_past - params.n_keep;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -270,13 +285,21 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
//printf("\n---\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (llama_eval(ctx, embd.data(), embd.size(), n_past, params.n_threads)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s : failed to eval\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
// evaluate tokens in batches
|
||||
// embd is typically prepared beforehand to fit within a batch, but not always
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < (int) embd.size(); i += params.n_batch) {
|
||||
int n_eval = (int) embd.size() - i;
|
||||
if (n_eval > params.n_batch) {
|
||||
n_eval = params.n_batch;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (llama_eval(ctx, &embd[i], n_eval, n_past, params.n_threads)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s : failed to eval\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
n_past += n_eval;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n_past += embd.size();
|
||||
embd.clear();
|
||||
|
||||
if ((int) embd_inp.size() <= n_consumed && !is_interacting) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
|
|||
#include "llama.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <cmath>
|
||||
#include <ctime>
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<float> softmax(const std::vector<float>& logits) {
|
||||
std::vector<float> probs(logits.size());
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,7 +53,13 @@ void perplexity(llama_context * ctx, const gpt_params & params) {
|
|||
auto end_t = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
if (i == 0) {
|
||||
const float seconds = std::chrono::duration<float>(end_t - start_t).count();
|
||||
printf("%.2f seconds per pass - ETA %.2f hours\n", seconds, (seconds * seq_count) / (60.0*60.0));
|
||||
printf("%.2f seconds per pass - ETA ", seconds);
|
||||
int total_seconds = (int)(seconds * seq_count);
|
||||
if (total_seconds >= 60*60) {
|
||||
printf("%d hours ", total_seconds / (60*60));
|
||||
total_seconds = total_seconds % (60*60);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("%d minutes\n", total_seconds / 60);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// We get the logits for all the tokens in the context window (params.n_ctx)
|
||||
// from llama_eval above. Now, based on https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perplexity,
|
||||
|
|
@ -133,6 +140,17 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!params.lora_adapter.empty()) {
|
||||
int err = llama_apply_lora_from_file(ctx,
|
||||
params.lora_adapter.c_str(),
|
||||
params.lora_base.empty() ? NULL : params.lora_base.c_str(),
|
||||
params.n_threads);
|
||||
if (err != 0) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: error: failed to apply lora adapter\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// print system information
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,6 +15,8 @@
|
|||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <unordered_map>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <thread>
|
||||
#include <mutex>
|
||||
|
||||
struct quantize_stats_params {
|
||||
std::string model = "models/7B/ggml-model-f16.bin";
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,7 +29,6 @@ struct quantize_stats_params {
|
|||
std::vector<enum ggml_type> include_types;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const int64_t SCRATCH_ELEMENTS = 32*32;
|
||||
const size_t HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS = 150;
|
||||
const double HISTOGRAM_RANGE = 0.03;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,6 +91,13 @@ void update_error_stats(int64_t nelements, const float * input, const float * ou
|
|||
stats.num_samples += nelements;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void combine_error_stats(error_stats & into, const error_stats & from) {
|
||||
into.num_samples += from.num_samples;
|
||||
into.total_error += from.total_error;
|
||||
if (from.max_error > into.max_error) into.max_error = from.max_error;
|
||||
for (size_t i=0; i<HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS; ++i) into.error_histogram[i] += from.error_histogram[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
double find_quantile(const error_stats & stats, double quantile) {
|
||||
double sum = std::accumulate(std::begin(stats.error_histogram), std::end(stats.error_histogram), 0.0);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -130,6 +138,36 @@ static bool tensor_is_contiguous(const struct ggml_tensor * tensor) {
|
|||
tensor->nb[3] == tensor->nb[2]*tensor->ne[2];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void test_roundtrip_on_chunk(
|
||||
const ggml_tensor * layer,
|
||||
int64_t offset,
|
||||
int64_t chunk_size,
|
||||
const quantize_fns_t & qfns,
|
||||
bool use_reference,
|
||||
float * input_scratch,
|
||||
char * quantized_scratch,
|
||||
float * output_scratch,
|
||||
error_stats & stats) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (layer->type == GGML_TYPE_F16) {
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < chunk_size; i++) {
|
||||
input_scratch[i] = ggml_get_f32_1d(layer, i + offset);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
input_scratch = ggml_get_data_f32(layer) + offset;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (use_reference) {
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q_reference(input_scratch, quantized_scratch, chunk_size);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(input_scratch, quantized_scratch, chunk_size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
qfns.dequantize_row_q(quantized_scratch, output_scratch, chunk_size);
|
||||
|
||||
update_error_stats(chunk_size, input_scratch, output_scratch, stats);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Run quantization function for a single layer and update error stats
|
||||
void test_roundtrip_on_layer(
|
||||
std::string & name,
|
||||
|
|
@ -137,40 +175,61 @@ void test_roundtrip_on_layer(
|
|||
const quantize_fns_t & qfns,
|
||||
bool use_reference,
|
||||
const ggml_tensor * layer,
|
||||
float * input_scratch,
|
||||
char *quantized_scratch,
|
||||
float * output_scratch,
|
||||
error_stats & total_error) {
|
||||
std::vector<float> & input_scratch,
|
||||
std::vector<char> & quantized_scratch,
|
||||
std::vector<float> & output_scratch,
|
||||
error_stats & total_error,
|
||||
int max_thread = 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
assert(tensor_is_contiguous(layer));
|
||||
error_stats layer_error {};
|
||||
int64_t nelements = ggml_nelements(layer);
|
||||
uint64_t nelements = ggml_nelements(layer);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int64_t offset = 0; offset < nelements; offset += SCRATCH_ELEMENTS) {
|
||||
int64_t chunk_size = std::min(SCRATCH_ELEMENTS, nelements - offset);
|
||||
|
||||
if (layer->type == GGML_TYPE_F16) {
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < chunk_size; i++) {
|
||||
input_scratch[i] = ggml_get_f32_1d(layer, i + offset);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
input_scratch = ggml_get_data_f32(layer) + offset;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (use_reference) {
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q_reference(input_scratch, quantized_scratch, chunk_size);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(input_scratch, quantized_scratch, chunk_size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
qfns.dequantize_row_q(quantized_scratch, output_scratch, chunk_size);
|
||||
|
||||
update_error_stats(chunk_size, input_scratch, output_scratch, total_error);
|
||||
if (print_layer_stats) {
|
||||
update_error_stats(chunk_size, input_scratch, output_scratch, layer_error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
float* input_scratch_ptr = nullptr;
|
||||
if (layer->type == GGML_TYPE_F16) {
|
||||
if (input_scratch.size() < nelements) input_scratch.resize(nelements);
|
||||
input_scratch_ptr = input_scratch.data();
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (quantized_scratch.size() < 4*nelements) quantized_scratch.resize(4*nelements);
|
||||
if (output_scratch.size() < nelements) output_scratch.resize(nelements);
|
||||
|
||||
if (max_thread < 1) max_thread = std::thread::hardware_concurrency();
|
||||
int chunk_size = 32*512;
|
||||
int num_chunks = (nelements + chunk_size - 1)/chunk_size;
|
||||
|
||||
if (num_chunks < 2 || max_thread < 2) {
|
||||
test_roundtrip_on_chunk(layer, 0, nelements, qfns, use_reference, input_scratch_ptr, quantized_scratch.data(),
|
||||
output_scratch.data(), print_layer_stats ? layer_error : total_error);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
auto & stats = print_layer_stats ? layer_error : total_error;
|
||||
std::mutex mutex;
|
||||
uint64_t counter = 0;
|
||||
auto compute = [&mutex, &counter, &stats, &qfns, nelements, layer, use_reference, input_scratch_ptr,
|
||||
&quantized_scratch, &output_scratch, chunk_size] () {
|
||||
error_stats local_stats {};
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex);
|
||||
uint64_t offset = counter; counter += chunk_size;
|
||||
if (offset >= nelements) {
|
||||
combine_error_stats(stats, local_stats);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
lock.unlock();
|
||||
uint64_t chunk = offset + chunk_size < nelements ? chunk_size : nelements - offset;
|
||||
test_roundtrip_on_chunk(layer, offset, chunk, qfns, use_reference, input_scratch_ptr + offset,
|
||||
quantized_scratch.data() + 4*offset, output_scratch.data() + offset, local_stats);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
int nthread = std::min(num_chunks, max_thread);
|
||||
std::vector<std::thread> workers(nthread-1);
|
||||
for (auto& w : workers) w = std::thread(compute);
|
||||
compute();
|
||||
for (auto& w : workers) w.join();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (print_layer_stats) {
|
||||
print_error_stats(name, layer_error, false);
|
||||
combine_error_stats(total_error, layer_error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,6 +240,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
|
||||
// read command line
|
||||
|
||||
int max_thread = 0;
|
||||
bool invalid_param = false;
|
||||
std::string arg;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,7 +281,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int j;
|
||||
for (j = 0; j < GGML_TYPE_COUNT && strcmp(argv[i], ggml_type_name((ggml_type) i)) != 0; j++) {
|
||||
for (j = 0; j < GGML_TYPE_COUNT && strcmp(argv[i], ggml_type_name((ggml_type) j)) != 0; j++) {
|
||||
// find match
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (j < GGML_TYPE_COUNT) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -230,6 +290,12 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
fprintf(stderr, "error: %s not in list of types\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (arg == "-n" || arg == "--num-threads") {
|
||||
if (++i >= argc) {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
max_thread = atoi(argv[i]);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "error: unknown argument: %s\n", arg.c_str());
|
||||
quantize_stats_print_usage(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
|
@ -295,9 +361,9 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
printf("testing %d layers with max size %" PRId64 "\n", included_layers, max_nelements);
|
||||
// allocate scratch space
|
||||
std::vector<float> input_scratch(SCRATCH_ELEMENTS);
|
||||
std::vector<char> quantized_scratch(SCRATCH_ELEMENTS*4);
|
||||
std::vector<float> output_scratch(SCRATCH_ELEMENTS);
|
||||
std::vector<float> input_scratch;
|
||||
std::vector<char> quantized_scratch;
|
||||
std::vector<float> output_scratch;
|
||||
|
||||
// loop throught quantization types
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < GGML_TYPE_COUNT; i++) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -328,10 +394,11 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
qfns,
|
||||
params.reference,
|
||||
kv_tensor.second,
|
||||
input_scratch.data(),
|
||||
quantized_scratch.data(),
|
||||
output_scratch.data(),
|
||||
global_stats
|
||||
input_scratch,
|
||||
quantized_scratch,
|
||||
output_scratch,
|
||||
global_stats,
|
||||
max_thread
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,10 +10,13 @@
|
|||
int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
||||
ggml_time_init();
|
||||
|
||||
if (argc != 4) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s model-f32.bin model-quant.bin type\n", argv[0]);
|
||||
if (argc < 4) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s model-f32.bin model-quant.bin type [nthread]\n", argv[0]);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " type = %d - q4_0\n", LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_0);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " type = %d - q4_1\n", LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " type = %d - q4_2\n", LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_2);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " type = %d - q4_3\n", LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_3);
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " type = %d - q8_0\n", LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q8_0);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,6 +31,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
const std::string fname_out = argv[2];
|
||||
|
||||
const enum llama_ftype ftype = (enum llama_ftype)atoi(argv[3]);
|
||||
int nthread = argc > 4 ? atoi(argv[4]) : 0;
|
||||
|
||||
const int64_t t_main_start_us = ggml_time_us();
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -37,7 +41,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
{
|
||||
const int64_t t_start_us = ggml_time_us();
|
||||
|
||||
if (llama_model_quantize(fname_inp.c_str(), fname_out.c_str(), ftype)) {
|
||||
if (llama_model_quantize(fname_inp.c_str(), fname_out.c_str(), ftype, nthread)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: failed to quantize model from '%s'\n", __func__, fname_inp.c_str());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
4
examples/save-load-state/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
4
examples/save-load-state/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
|||
set(TARGET save-load-state)
|
||||
add_executable(${TARGET} save-load-state.cpp)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(${TARGET} PRIVATE common llama ${CMAKE_THREAD_LIBS_INIT})
|
||||
target_compile_features(${TARGET} PRIVATE cxx_std_11)
|
||||
128
examples/save-load-state/save-load-state.cpp
Normal file
128
examples/save-load-state/save-load-state.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
|
|||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#include <chrono>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "common.h"
|
||||
#include "llama.h"
|
||||
#include "llama.cpp"
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
||||
gpt_params params;
|
||||
params.model = "models/llama-7B/ggml-model.bin";
|
||||
params.seed = 42;
|
||||
params.n_threads = 4;
|
||||
params.repeat_last_n = 64;
|
||||
params.prompt = "The quick brown fox";
|
||||
|
||||
if (gpt_params_parse(argc, argv, params) == false) {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto lparams = llama_context_default_params();
|
||||
|
||||
lparams.n_ctx = params.n_ctx;
|
||||
lparams.n_parts = params.n_parts;
|
||||
lparams.seed = params.seed;
|
||||
lparams.f16_kv = params.memory_f16;
|
||||
lparams.use_mmap = params.use_mmap;
|
||||
lparams.use_mlock = params.use_mlock;
|
||||
|
||||
auto n_past = 0;
|
||||
auto last_n_tokens_data = vector<llama_token>(params.repeat_last_n, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
// init
|
||||
auto ctx = llama_init_from_file(params.model.c_str(), lparams);
|
||||
auto tokens = vector<llama_token>(params.n_ctx);
|
||||
auto n_prompt_tokens = llama_tokenize(ctx, params.prompt.c_str(), tokens.data(), tokens.size(), true);
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_prompt_tokens < 1) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s : failed to tokenize prompt\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// evaluate prompt
|
||||
|
||||
llama_eval(ctx, tokens.data(), n_prompt_tokens, n_past, params.n_threads);
|
||||
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data.insert(last_n_tokens_data.end(), tokens.data(), tokens.data() + n_prompt_tokens);
|
||||
n_past += n_prompt_tokens;
|
||||
|
||||
// Save state (rng, logits, embedding and kv_cache) to file
|
||||
FILE *fp_write = fopen("dump_state.bin", "wb");
|
||||
auto state_size = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
auto state_mem = new uint8_t[state_size];
|
||||
llama_copy_state_data(ctx, state_mem); // could also copy directly to memory mapped file
|
||||
fwrite(state_mem, 1, state_size, fp_write);
|
||||
fclose(fp_write);
|
||||
|
||||
// save state (last tokens)
|
||||
auto last_n_tokens_data_saved = vector<llama_token>(last_n_tokens_data);
|
||||
auto n_past_saved = n_past;
|
||||
|
||||
// first run
|
||||
printf("\n%s", params.prompt.c_str());
|
||||
for (auto i = 0; i < params.n_predict; i++) {
|
||||
auto next_token = llama_sample_top_p_top_k(
|
||||
ctx,
|
||||
&last_n_tokens_data.back() - params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
40,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.1);
|
||||
auto next_token_str = llama_token_to_str(ctx, next_token);
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data.push_back(next_token);
|
||||
printf("%s", next_token_str);
|
||||
if (llama_eval(ctx, &next_token, 1, n_past, params.n_threads)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s : failed to evaluate\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
n_past += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n\n");
|
||||
|
||||
// free old model
|
||||
llama_free(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// load new model
|
||||
|
||||
auto ctx2 = llama_init_from_file(params.model.c_str(), lparams);
|
||||
|
||||
// Load state (rng, logits, embedding and kv_cache) from file
|
||||
FILE *fp_read = fopen("dump_state.bin", "rb");
|
||||
auto state_size2 = llama_get_state_size(ctx2);
|
||||
if (state_size != state_size2) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s : failed to validate state size\n", __func__);
|
||||
}
|
||||
fread(state_mem, 1, state_size, fp_read);
|
||||
llama_set_state_data(ctx2, state_mem); // could also read directly from memory mapped file
|
||||
fclose(fp_read);
|
||||
|
||||
// restore state (last tokens)
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data = last_n_tokens_data_saved;
|
||||
n_past = n_past_saved;
|
||||
|
||||
// second run
|
||||
for (auto i = 0; i < params.n_predict; i++) {
|
||||
auto next_token = llama_sample_top_p_top_k(
|
||||
ctx2,
|
||||
&last_n_tokens_data.back() - params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
40,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.1);
|
||||
auto next_token_str = llama_token_to_str(ctx2, next_token);
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data.push_back(next_token);
|
||||
printf("%s", next_token_str);
|
||||
if (llama_eval(ctx2, &next_token, 1, n_past, params.n_threads)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s : failed to evaluate\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
n_past += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n\n");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,9 +30,9 @@
|
|||
mv bin/* $out/bin/
|
||||
mv $out/bin/main $out/bin/llama
|
||||
|
||||
echo "#!${llama-python}/bin/python" > $out/bin/convert-pth-to-ggml
|
||||
cat ${./convert-pth-to-ggml.py} >> $out/bin/convert-pth-to-ggml
|
||||
chmod +x $out/bin/convert-pth-to-ggml
|
||||
echo "#!${llama-python}/bin/python" > $out/bin/convert.py
|
||||
cat ${./convert.py} >> $out/bin/convert.py
|
||||
chmod +x $out/bin/convert.py
|
||||
'';
|
||||
meta.mainProgram = "llama";
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
256
ggml-cuda.cu
Normal file
256
ggml-cuda.cu
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,256 @@
|
|||
#include <stdint.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <cuda_fp16.h>
|
||||
#include <atomic>
|
||||
#include "ggml-cuda.h"
|
||||
|
||||
typedef uint16_t ggml_fp16_t;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(__half) == sizeof(ggml_fp16_t), "wrong fp16 size");
|
||||
|
||||
#define QK4_0 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_0 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_0;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_0) == sizeof(float) + QK4_0 / 2, "wrong q4_0 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
#define QK4_1 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
float m; // min
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_1 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_1;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_1) == sizeof(float) * 2 + QK4_1 / 2, "wrong q4_1 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
#define QK4_2 16
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
__half d; // delta
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_2 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_2;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_2) == sizeof(ggml_fp16_t) + QK4_2 / 2, "wrong q4_2 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
#define QK4_3 16
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
__half d; // delta
|
||||
__half m; // min
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_3 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_3;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_3) == 2 * sizeof(ggml_fp16_t) + QK4_3 / 2, "wrong q4_3 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
#define QK8_0 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
int8_t qs[QK8_0]; // quants
|
||||
} block_q8_0;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q8_0) == sizeof(float) + QK8_0, "wrong q8_0 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
static __global__ void dequantize_block_q4_0(const void * vx, float * y) {
|
||||
const block_q4_0 * x = (const block_q4_0 *) vx;
|
||||
|
||||
const int i = blockIdx.x;
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = x[i].d;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t * pp = x[i].qs;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK4_0; l += 2) {
|
||||
const uint8_t vi = pp[l/2];
|
||||
|
||||
const int8_t vi0 = vi & 0xf;
|
||||
const int8_t vi1 = vi >> 4;
|
||||
|
||||
const float v0 = (vi0 - 8)*d;
|
||||
const float v1 = (vi1 - 8)*d;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i*QK4_0 + l + 0] = v0;
|
||||
y[i*QK4_0 + l + 1] = v1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static __global__ void dequantize_block_q4_1(const void * vx, float * y) {
|
||||
const block_q4_1 * x = (const block_q4_1 *) vx;
|
||||
|
||||
const int i = blockIdx.x;
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = x[i].d;
|
||||
const float m = x[i].m;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t * pp = x[i].qs;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK4_1; l += 2) {
|
||||
const uint8_t vi = pp[l/2];
|
||||
|
||||
const int8_t vi0 = vi & 0xf;
|
||||
const int8_t vi1 = vi >> 4;
|
||||
|
||||
const float v0 = vi0*d + m;
|
||||
const float v1 = vi1*d + m;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i*QK4_1 + l + 0] = v0;
|
||||
y[i*QK4_1 + l + 1] = v1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static __global__ void dequantize_block_q4_2(const void * vx, float * y) {
|
||||
const block_q4_2 * x = (const block_q4_2 *) vx;
|
||||
|
||||
const int i = blockIdx.x;
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = x[i].d;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t * pp = x[i].qs;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK4_2; l += 2) {
|
||||
const uint8_t vi = pp[l/2];
|
||||
|
||||
const int8_t vi0 = vi & 0xf;
|
||||
const int8_t vi1 = vi >> 4;
|
||||
|
||||
const float v0 = (vi0 - 8)*d;
|
||||
const float v1 = (vi1 - 8)*d;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i*QK4_2 + l + 0] = v0;
|
||||
y[i*QK4_2 + l + 1] = v1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static __global__ void dequantize_block_q4_3(const void * vx, float * y) {
|
||||
const block_q4_3 * x = (const block_q4_3 *) vx;
|
||||
|
||||
const int i = blockIdx.x;
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = x[i].d;
|
||||
const float m = x[i].m;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t * pp = x[i].qs;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK4_3; l += 2) {
|
||||
const uint8_t vi = pp[l/2];
|
||||
|
||||
const int8_t vi0 = vi & 0xf;
|
||||
const int8_t vi1 = vi >> 4;
|
||||
|
||||
const float v0 = vi0*d + m;
|
||||
const float v1 = vi1*d + m;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i*QK4_3 + l + 0] = v0;
|
||||
y[i*QK4_3 + l + 1] = v1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static __global__ void dequantize_block_q8_0(const void * vx, float * y) {
|
||||
const block_q8_0 * x = (const block_q8_0 *) vx;
|
||||
|
||||
const int i = blockIdx.x;
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = x[i].d;
|
||||
|
||||
const int8_t * pp = x[i].qs;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK8_0; l++) {
|
||||
const int8_t vi = pp[l];
|
||||
|
||||
y[i*QK8_0 + l] = vi*d;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_0_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream) {
|
||||
const int nb = k / QK4_0;
|
||||
dequantize_block_q4_0<<<nb, 1, 0, stream>>>(vx, y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_1_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream) {
|
||||
const int nb = k / QK4_1;
|
||||
dequantize_block_q4_1<<<nb, 1, 0, stream>>>(vx, y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_2_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream) {
|
||||
const int nb = k / QK4_2;
|
||||
dequantize_block_q4_2<<<nb, 1, 0, stream>>>(vx, y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_3_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream) {
|
||||
const int nb = k / QK4_3;
|
||||
dequantize_block_q4_3<<<nb, 1, 0, stream>>>(vx, y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q8_0_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream) {
|
||||
const int nb = k / QK8_0;
|
||||
dequantize_block_q8_0<<<nb, 1, 0, stream>>>(vx, y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer pool for cuda
|
||||
#define MAX_CUDA_BUFFERS 16
|
||||
|
||||
struct scoped_spin_lock {
|
||||
std::atomic_flag& lock;
|
||||
scoped_spin_lock(std::atomic_flag& lock) : lock(lock) {
|
||||
while (lock.test_and_set(std::memory_order_acquire)) {
|
||||
; // spin
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
~scoped_spin_lock() {
|
||||
lock.clear(std::memory_order_release);
|
||||
}
|
||||
scoped_spin_lock(const scoped_spin_lock&) = delete;
|
||||
scoped_spin_lock& operator=(const scoped_spin_lock&) = delete;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct cuda_buffer {
|
||||
void * ptr = nullptr;
|
||||
size_t size = 0;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
static cuda_buffer g_cuda_buffer_pool[MAX_CUDA_BUFFERS];
|
||||
static std::atomic_flag g_cuda_pool_lock = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;
|
||||
|
||||
void * ggml_cuda_pool_malloc(size_t size, size_t * actual_size) {
|
||||
scoped_spin_lock lock(g_cuda_pool_lock);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CUDA_BUFFERS; ++i) {
|
||||
cuda_buffer& b = g_cuda_buffer_pool[i];
|
||||
if (b.size >= size && b.ptr != nullptr) {
|
||||
void * ptr = b.ptr;
|
||||
*actual_size = b.size;
|
||||
b.ptr = nullptr;
|
||||
b.size = 0;
|
||||
return ptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
void * ptr;
|
||||
CUDA_CHECK(cudaMalloc((void **) &ptr, size));
|
||||
*actual_size = size;
|
||||
return ptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void ggml_cuda_pool_free(void * ptr, size_t size) {
|
||||
scoped_spin_lock lock(g_cuda_pool_lock);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CUDA_BUFFERS; ++i) {
|
||||
cuda_buffer& b = g_cuda_buffer_pool[i];
|
||||
if (b.ptr == nullptr) {
|
||||
b.ptr = ptr;
|
||||
b.size = size;
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "WARNING: cuda buffer pool full, increase MAX_CUDA_BUFFERS\n");
|
||||
CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(ptr));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cublasHandle_t g_cublasH = NULL;
|
||||
cudaStream_t g_cudaStream = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
void ggml_init_cublas(void) {
|
||||
if (g_cublasH == NULL) {
|
||||
// create cublas handle, bind a stream
|
||||
CUBLAS_CHECK(cublasCreate(&g_cublasH));
|
||||
|
||||
CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamCreateWithFlags(&g_cudaStream, cudaStreamNonBlocking));
|
||||
|
||||
CUBLAS_CHECK(cublasSetStream(g_cublasH, g_cudaStream));
|
||||
|
||||
// configure logging to stdout
|
||||
// CUBLAS_CHECK(cublasLoggerConfigure(1, 1, 0, NULL));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
42
ggml-cuda.h
Normal file
42
ggml-cuda.h
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|||
#include <cublas_v2.h>
|
||||
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
extern "C" {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#define CUDA_CHECK(err) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
cudaError_t err_ = (err); \
|
||||
if (err_ != cudaSuccess) { \
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "CUDA error %d at %s:%d: %s\n", err_, __FILE__, __LINE__, \
|
||||
cudaGetErrorString(err_)); \
|
||||
exit(1); \
|
||||
} \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#define CUBLAS_CHECK(err) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
cublasStatus_t err_ = (err); \
|
||||
if (err_ != CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS) { \
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "cuBLAS error %d at %s:%d\n", err_, __FILE__, __LINE__); \
|
||||
exit(1); \
|
||||
} \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
extern cublasHandle_t g_cublasH;
|
||||
extern cudaStream_t g_cudaStream;
|
||||
|
||||
void ggml_init_cublas(void);
|
||||
void * ggml_cuda_pool_malloc(size_t size, size_t * actual_size);
|
||||
void ggml_cuda_pool_free(void * ptr, size_t size);
|
||||
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_0_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream);
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_1_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream);
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_2_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream);
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q4_3_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream);
|
||||
void dequantize_row_q8_0_cuda(const void * vx, float * y, int k, cudaStream_t stream);
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
650
llama.cpp
650
llama.cpp
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
|
|||
// Defines fileno on msys:
|
||||
#ifndef _GNU_SOURCE
|
||||
#define _GNU_SOURCE
|
||||
#include <cstdint>
|
||||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "llama_util.h"
|
||||
|
|
@ -9,6 +11,7 @@
|
|||
#include "ggml.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <array>
|
||||
#include <ctime>
|
||||
#include <cinttypes>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
#include <random>
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,6 +24,10 @@
|
|||
#include <memory>
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include <initializer_list>
|
||||
#include <thread>
|
||||
#include <atomic>
|
||||
#include <mutex>
|
||||
#include <sstream>
|
||||
|
||||
#define LLAMA_USE_SCRATCH
|
||||
#define LLAMA_MAX_SCRATCH_BUFFERS 16
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,36 +48,52 @@ static const size_t MB = 1024*1024;
|
|||
// TODO: dynamically determine these sizes
|
||||
// needs modifications in ggml
|
||||
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0 = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> & MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0()
|
||||
{
|
||||
static std::map<e_model, size_t> _MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0 = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 1024ull * MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
return _MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1 = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 512ull*MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> & MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1()
|
||||
{
|
||||
static std::map<e_model, size_t> _MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1 = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 1024ull * MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
return _MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 2*n_embd*n_ctx*n_layer*sizeof(float16)
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> MEM_REQ_KV_SELF = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 1026ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 1608ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 3124ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 5120ull*MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> & MEM_REQ_KV_SELF()
|
||||
{
|
||||
static std::map<e_model, size_t> _MEM_REQ_KV_SELF = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 1026ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 1608ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 3124ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 5120ull * MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
return _MEM_REQ_KV_SELF;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// this is mostly needed for temporary mul_mat buffers to dequantize the data
|
||||
// not actually needed if BLAS is disabled
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> MEM_REQ_EVAL = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 768ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 1024ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 1280ull*MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 1536ull*MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
static const std::map<e_model, size_t> & MEM_REQ_EVAL()
|
||||
{
|
||||
static std::map<e_model, size_t> _MEM_REQ_EVAL = {
|
||||
{ MODEL_7B, 768ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 1024ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 1280ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 1536ull * MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
return _MEM_REQ_EVAL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// default hparams (LLaMA 7B)
|
||||
struct llama_hparams {
|
||||
|
|
@ -261,12 +284,12 @@ static size_t checked_div(size_t a, size_t b) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static std::string llama_format_tensor_shape(const std::vector<uint32_t> & ne) {
|
||||
std::string ret = "[" + std::to_string(ne.at(0));
|
||||
char buf[256];
|
||||
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%5u", ne.at(0));
|
||||
for (size_t i = 1; i < ne.size(); i++) {
|
||||
ret += " x " + std::to_string(ne.at(i));
|
||||
snprintf(buf + strlen(buf), sizeof(buf) - strlen(buf), " x %5u", ne.at(i));
|
||||
}
|
||||
ret += "]";
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
return buf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static size_t llama_calc_tensor_size(const std::vector<uint32_t> & ne, enum ggml_type type) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -459,6 +482,9 @@ struct llama_file_loader {
|
|||
case GGML_TYPE_F16:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_0:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_1:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_2:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_3:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q8_0:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default: {
|
||||
throw format("unrecognized tensor type %u\n", shard.type);
|
||||
|
|
@ -531,6 +557,9 @@ struct llama_file_saver {
|
|||
case GGML_TYPE_F16:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_0:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_1:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_2:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_3:
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q8_0:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default: LLAMA_ASSERT(false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -616,6 +645,7 @@ struct llama_model_loader {
|
|||
throw format("llama.cpp: tensor '%s' has wrong shape; expected %s, got %s",
|
||||
name.c_str(), llama_format_tensor_shape(ne).c_str(), llama_format_tensor_shape(lt.ne).c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return get_tensor_for(lt);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -818,6 +848,9 @@ static const char *llama_ftype_name(enum llama_ftype ftype) {
|
|||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1: return "mostly Q4_1";
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1_SOME_F16:
|
||||
return "mostly Q4_1, some F16";
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_2: return "mostly Q4_2";
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_3: return "mostly Q4_3";
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q8_0: return "mostly Q8_0";
|
||||
default: return "unknown, may not work";
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -898,13 +931,13 @@ static void llama_model_load_internal(
|
|||
const size_t mem_required =
|
||||
ctx_size +
|
||||
mmapped_size +
|
||||
MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0.at(model.type) +
|
||||
MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1.at(model.type) +
|
||||
MEM_REQ_EVAL.at (model.type);
|
||||
MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0().at(model.type) +
|
||||
MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1().at(model.type) +
|
||||
MEM_REQ_EVAL().at(model.type);
|
||||
|
||||
// this is the memory required by one llama_state
|
||||
const size_t mem_required_state =
|
||||
scale*MEM_REQ_KV_SELF.at(model.type);
|
||||
scale*MEM_REQ_KV_SELF().at(model.type);
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: mem required = %7.2f MB (+ %7.2f MB per state)\n", __func__,
|
||||
mem_required / 1024.0 / 1024.0, mem_required_state / 1024.0 / 1024.0);
|
||||
|
|
@ -941,8 +974,8 @@ static void llama_model_load_internal(
|
|||
ml->ggml_ctx = ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
model.tok_embeddings = ml->get_tensor("tok_embeddings.weight", {n_embd, n_vocab});
|
||||
model.norm = ml->get_tensor("norm.weight", {n_embd});
|
||||
model.output = ml->get_tensor("output.weight", {n_embd, n_vocab});
|
||||
model.norm = ml->get_tensor("norm.weight", {n_embd});
|
||||
model.output = ml->get_tensor("output.weight", {n_embd, n_vocab});
|
||||
|
||||
model.layers.resize(n_layer);
|
||||
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < n_layer; ++i) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1046,7 +1079,7 @@ static bool llama_eval_internal(
|
|||
// for big prompts, if BLAS is enabled, it is better to use only one thread
|
||||
// otherwise, the threads are spin-lock waiting for the BLAS calls and are degrading the performance
|
||||
ggml_cgraph gf = {};
|
||||
gf.n_threads = N >= 32 && ggml_cpu_has_blas() ? 1 : n_threads;
|
||||
gf.n_threads = N >= 32 && ggml_cpu_has_blas() && !ggml_cpu_has_cublas() ? 1 : n_threads;
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_tensor * embd = ggml_new_tensor_1d(ctx0, GGML_TYPE_I32, N);
|
||||
memcpy(embd->data, tokens, N*ggml_element_size(embd));
|
||||
|
|
@ -1220,9 +1253,11 @@ static bool llama_eval_internal(
|
|||
ggml_build_forward_expand(&gf, inpL);
|
||||
ggml_graph_compute (ctx0, &gf);
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef GGML_PERF
|
||||
// print timing information per ggml operation (for debugging purposes)
|
||||
// requires GGML_PERF to be defined
|
||||
//ggml_graph_print(&gf);
|
||||
ggml_graph_print(&gf);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// plot the computation graph in dot format (for debugging purposes)
|
||||
//if (n_past%100 == 0) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1546,14 +1581,21 @@ static llama_vocab::id llama_sample_top_p_top_k(
|
|||
// quantization
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
static void llama_model_quantize_internal(const std::string & fname_inp, const std::string & fname_out, enum llama_ftype ftype) {
|
||||
static void llama_model_quantize_internal(const std::string & fname_inp, const std::string & fname_out, enum llama_ftype ftype, int nthread) {
|
||||
ggml_type quantized_type;
|
||||
switch (ftype) {
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_0: quantized_type = GGML_TYPE_Q4_0; break;
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1: quantized_type = GGML_TYPE_Q4_1; break;
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_2: quantized_type = GGML_TYPE_Q4_2; break;
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_3: quantized_type = GGML_TYPE_Q4_3; break;
|
||||
case LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q8_0: quantized_type = GGML_TYPE_Q8_0; break;
|
||||
default: throw format("invalid output file type %d\n", ftype);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
if (nthread <= 0) {
|
||||
nthread = std::thread::hardware_concurrency();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<llama_model_loader> model_loader(new llama_model_loader(fname_inp.c_str(), /*use_mmap*/ false,
|
||||
/*vocab_only*/ false));
|
||||
llama_file_saver file_saver(fname_out.c_str(), model_loader->file_loaders.at(0).get(), ftype);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1562,6 +1604,9 @@ static void llama_model_quantize_internal(const std::string & fname_inp, const s
|
|||
size_t total_size_new = 0;
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> hist_all(1 << 4, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::thread> workers;
|
||||
std::mutex mutex;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t idx = 0;
|
||||
for (llama_load_tensor & tensor : model_loader->tensors_map.tensors) {
|
||||
llama_buffer read_data;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1569,7 +1614,7 @@ static void llama_model_quantize_internal(const std::string & fname_inp, const s
|
|||
tensor.data = read_data.addr;
|
||||
model_loader->load_data_for(tensor);
|
||||
|
||||
printf("[%zu/%zu] %36s - %s, type = %6s, ",
|
||||
printf("[%4zu/%4zu] %36s - %16s, type = %6s, ",
|
||||
++idx, model_loader->tensors_map.tensors.size(),
|
||||
tensor.name.c_str(), llama_format_tensor_shape(tensor.ne).c_str(),
|
||||
ggml_type_name(tensor.type));
|
||||
|
|
@ -1580,6 +1625,11 @@ static void llama_model_quantize_internal(const std::string & fname_inp, const s
|
|||
// quantize only 2D tensors
|
||||
quantize &= (tensor.ne.size() == 2);
|
||||
|
||||
// uncomment this to keep the output layer in FP16
|
||||
//if (tensor.name == "output.weight") {
|
||||
// quantize = false;
|
||||
//}
|
||||
|
||||
enum ggml_type new_type;
|
||||
void * new_data;
|
||||
size_t new_size;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1615,17 +1665,37 @@ static void llama_model_quantize_internal(const std::string & fname_inp, const s
|
|||
new_data = work.addr;
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> hist_cur(1 << 4, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
switch (new_type) {
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_0:
|
||||
{
|
||||
new_size = ggml_quantize_q4_0(f32_data, new_data, nelements, (int) tensor.ne.at(0), hist_cur.data());
|
||||
} break;
|
||||
case GGML_TYPE_Q4_1:
|
||||
{
|
||||
new_size = ggml_quantize_q4_1(f32_data, new_data, nelements, (int) tensor.ne.at(0), hist_cur.data());
|
||||
} break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(false);
|
||||
int chunk_size = 32 * 512;
|
||||
const int nchunk = (nelements + chunk_size - 1)/chunk_size;
|
||||
const int nthread_use = nthread > 1 ? std::max(1, std::min(nthread, nchunk)) : 1;
|
||||
if (nthread_use < 2) {
|
||||
new_size = ggml_quantize_chunk(new_type, f32_data, new_data, 0, nelements, hist_cur.data());
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
size_t counter = 0;
|
||||
new_size = 0;
|
||||
auto compute = [&mutex, &counter, &hist_cur, &new_size, new_type, f32_data, new_data, nelements, chunk_size] () {
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> local_hist;
|
||||
size_t local_size = 0;
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex);
|
||||
size_t first = counter; counter += chunk_size;
|
||||
if (first >= nelements) {
|
||||
if (!local_hist.empty()) {
|
||||
for (int j=0; j<int(local_hist.size()); ++j) hist_cur[j] += local_hist[j];
|
||||
new_size += local_size;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
lock.unlock();
|
||||
size_t last = std::min(nelements, first + chunk_size);
|
||||
if (local_hist.empty()) local_hist.resize(hist_cur.size(), 0);
|
||||
local_size += ggml_quantize_chunk(new_type, f32_data, new_data, first, last - first, local_hist.data());
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
if (int(workers.size()) < nthread_use - 1) workers.resize(nthread_use - 1);
|
||||
for (int it = 0; it < nthread_use - 1; ++it) workers[it] = std::thread(compute);
|
||||
compute();
|
||||
for (int it = 0; it < nthread_use - 1; ++it) workers[it].join();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
printf("size = %8.2f MB -> %8.2f MB | hist: ", tensor.size/1024.0/1024.0, new_size/1024.0/1024.0);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1724,17 +1794,17 @@ struct llama_context * llama_init_from_file(
|
|||
if (params.logits_all) {
|
||||
ctx->logits.reserve(hparams.n_ctx*hparams.n_vocab);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ctx->logits.reserve(hparams.n_ctx);
|
||||
ctx->logits.reserve(hparams.n_vocab);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (params.embedding){
|
||||
ctx->embedding.resize(hparams.n_embd);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx->buf_compute.resize(MEM_REQ_EVAL.at(ctx->model.type));
|
||||
ctx->buf_compute.resize(MEM_REQ_EVAL().at(ctx->model.type));
|
||||
|
||||
ctx->buf_scratch[0].resize(MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0.at(ctx->model.type));
|
||||
ctx->buf_scratch[1].resize(MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1.at(ctx->model.type));
|
||||
ctx->buf_scratch[0].resize(MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0().at(ctx->model.type));
|
||||
ctx->buf_scratch[1].resize(MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1().at(ctx->model.type));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ctx;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1747,9 +1817,10 @@ void llama_free(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
|||
int llama_model_quantize(
|
||||
const char * fname_inp,
|
||||
const char * fname_out,
|
||||
enum llama_ftype ftype) {
|
||||
enum llama_ftype ftype,
|
||||
int nthread) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
llama_model_quantize_internal(fname_inp, fname_out, ftype);
|
||||
llama_model_quantize_internal(fname_inp, fname_out, ftype, nthread);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
} catch (const std::string & err) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: failed to quantize: %s\n", __func__, err.c_str());
|
||||
|
|
@ -1757,31 +1828,439 @@ int llama_model_quantize(
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the KV cache that will contain the context for the
|
||||
// ongoing prediction with the model.
|
||||
const uint8_t * llama_get_kv_cache(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr;
|
||||
int llama_apply_lora_from_file_internal(struct llama_context * ctx, const char * path_lora, const char * path_base_model, int n_threads) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: applying lora adapter from '%s' - please wait ...\n", __func__, path_lora);
|
||||
|
||||
auto & model = ctx->model;
|
||||
|
||||
const int64_t t_start_lora_us = ggml_time_us();
|
||||
|
||||
auto fin = std::ifstream(path_lora, std::ios::binary);
|
||||
if (!fin) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: failed to open '%s'\n", __func__, path_lora);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// verify magic and version
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint32_t magic;
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &magic, sizeof(magic));
|
||||
if (magic != 'ggla') {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: bad file magic\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
uint32_t format_version;
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &format_version, sizeof(format_version));
|
||||
|
||||
if (format_version != 1) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: unsupported file version\n", __func__ );
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t lora_r;
|
||||
int32_t lora_alpha;
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &lora_r, sizeof(lora_r));
|
||||
fin.read((char *) &lora_alpha, sizeof(lora_alpha));
|
||||
float scaling = (float)lora_alpha / (float)lora_r;
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: r = %d, alpha = %d, scaling = %.2f\n", __func__, lora_r, lora_alpha, scaling);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// create a temporary ggml context to store the lora tensors
|
||||
// todo: calculate size from biggest possible tensor
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> lora_buf(1024ull * 1024ull * 1024ull);
|
||||
struct ggml_init_params params;
|
||||
params.mem_size = lora_buf.size();
|
||||
params.mem_buffer = lora_buf.data();
|
||||
params.no_alloc = false;
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_context * lora_ctx = ggml_init(params);
|
||||
std::unordered_map<std::string, struct ggml_tensor *> lora_tensors;
|
||||
|
||||
// create a name -> tensor map of the model to accelerate lookups
|
||||
std::unordered_map<std::string, struct ggml_tensor*> model_tensors;
|
||||
for (auto & kv: model.tensors_by_name) {
|
||||
model_tensors.insert(kv);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// load base model
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<llama_model_loader> model_loader;
|
||||
ggml_context * base_ctx = NULL;
|
||||
llama_buffer base_buf;
|
||||
if (path_base_model) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: loading base model from '%s'\n", __func__, path_base_model);
|
||||
model_loader.reset(new llama_model_loader(path_base_model, /*use_mmap*/ true, /*vocab_only*/ false));
|
||||
|
||||
size_t ctx_size, mmapped_size;
|
||||
model_loader->calc_sizes(&ctx_size, &mmapped_size);
|
||||
base_buf.resize(ctx_size);
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_init_params base_params;
|
||||
base_params.mem_size = base_buf.size;
|
||||
base_params.mem_buffer = base_buf.addr;
|
||||
base_params.no_alloc = model_loader->use_mmap;
|
||||
|
||||
base_ctx = ggml_init(base_params);
|
||||
|
||||
model_loader->ggml_ctx = base_ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
// maybe this should in llama_model_loader
|
||||
if (model_loader->use_mmap) {
|
||||
model_loader->mapping.reset(new llama_mmap(&model_loader->file_loaders.at(0)->file, /* prefetch */ false));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// read tensors and apply
|
||||
bool warned = false;
|
||||
int n_tensors = 0;
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
int32_t n_dims;
|
||||
int32_t length;
|
||||
int32_t ftype;
|
||||
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&n_dims), sizeof(n_dims));
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&length), sizeof(length));
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&ftype), sizeof(ftype));
|
||||
if (fin.eof()) {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t ne[2] = { 1, 1 };
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n_dims; ++i) {
|
||||
fin.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&ne[i]), sizeof(ne[i]));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::string name(length, 0);
|
||||
fin.read(&name[0], length);
|
||||
|
||||
// check for lora suffix and get the type of tensor
|
||||
const std::string lora_suffix = ".lora";
|
||||
size_t pos = name.rfind(lora_suffix);
|
||||
if (pos == std::string::npos) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: error: '%s' is not a lora tensor\n", __func__, name.c_str());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::string lora_type = name.substr(pos + lora_suffix.length());
|
||||
std::string base_name = name;
|
||||
base_name.erase(pos);
|
||||
// fprintf(stderr, "%s: %s => %s (lora type %s) ", __func__, name.c_str(),base_name.c_str(), lora_type.c_str());
|
||||
|
||||
if (model_tensors.find(base_name.data()) == model_tensors.end()) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: unknown tensor '%s' in lora adapter\n", __func__, name.data());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// create ggml tensor
|
||||
ggml_type wtype;
|
||||
switch (ftype) {
|
||||
case 0: wtype = GGML_TYPE_F32; break;
|
||||
case 1: wtype = GGML_TYPE_F16; break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: invalid tensor data type '%d'\n",
|
||||
__func__, ftype);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
ggml_tensor* lora_tensor;
|
||||
if (n_dims == 2) {
|
||||
lora_tensor = ggml_new_tensor_2d(lora_ctx, wtype, ne[0], ne[1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: unsupported tensor dimension %d\n", __func__, n_dims);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// load tensor data
|
||||
size_t offset = fin.tellg();
|
||||
size_t tensor_data_size = ggml_nbytes(lora_tensor);
|
||||
offset = (offset + 31) & -32;
|
||||
fin.seekg(offset);
|
||||
fin.read((char*)lora_tensor->data, tensor_data_size);
|
||||
|
||||
lora_tensors[name] = lora_tensor;
|
||||
|
||||
// check if we have both A and B tensors and apply
|
||||
if (lora_tensors.find(base_name + ".loraA") != lora_tensors.end() &&
|
||||
lora_tensors.find(base_name + ".loraB") != lora_tensors.end()) {
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_tensor * dest_t = model_tensors[base_name];
|
||||
ggml_tensor * base_t;
|
||||
if (model_loader) {
|
||||
// load from base model
|
||||
if (model_loader->tensors_map.name_to_idx.find(base_name) == model_loader->tensors_map.name_to_idx.end()) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: error: tensor '%s' not found in base model\n", __func__, base_name.c_str());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
size_t idx = model_loader->tensors_map.name_to_idx[base_name];
|
||||
llama_load_tensor & lt = model_loader->tensors_map.tensors[idx];
|
||||
base_t = model_loader->get_tensor(base_name, { (uint32_t)dest_t->ne[0], (uint32_t)dest_t->ne[1] });
|
||||
lt.data = (uint8_t *) lt.ggml_tensor->data;
|
||||
model_loader->load_data_for(lt);
|
||||
lt.ggml_tensor->data = lt.data;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
base_t = dest_t;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (ggml_is_quantized(base_t->type)) {
|
||||
if (!warned) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: warning: using a lora adapter with a quantized model may result in poor quality, "
|
||||
"use a f16 or f32 base model with --lora-base\n", __func__);
|
||||
warned = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_tensor * loraA = lora_tensors[base_name + ".loraA"];
|
||||
ggml_tensor * loraB = lora_tensors[base_name + ".loraB"];
|
||||
|
||||
if (base_t->ne[0] != loraA->ne[1] || base_t->ne[1] != loraB->ne[1]) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: incompatible tensor dimensions (%" PRId64 " and %" PRId64 ");"
|
||||
" are you sure that this adapter is for this model?\n", __func__, base_t->ne[0], loraA->ne[1]);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// w = w + BA*s
|
||||
ggml_tensor * BA = ggml_mul_mat(lora_ctx, loraA, loraB);
|
||||
|
||||
if (scaling != 1.0f) {
|
||||
ggml_tensor * scale_tensor = ggml_new_f32(lora_ctx, scaling);
|
||||
BA = ggml_scale(lora_ctx, BA, scale_tensor);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_tensor * r;
|
||||
if (base_t == dest_t) {
|
||||
r = ggml_add_inplace(lora_ctx, dest_t, BA);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
r = ggml_add(lora_ctx, base_t, BA);
|
||||
r = ggml_cpy(lora_ctx, r, dest_t);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct ggml_cgraph gf = ggml_build_forward(r);
|
||||
gf.n_threads = n_threads;
|
||||
ggml_graph_compute(lora_ctx, &gf);
|
||||
|
||||
// we won't need these tensors again, reset the context to save memory
|
||||
ggml_free(lora_ctx);
|
||||
lora_ctx = ggml_init(params);
|
||||
lora_tensors.clear();
|
||||
|
||||
n_tensors++;
|
||||
if (n_tensors % 4 == 0)
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, ".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: this should be in a destructor, it will leak on failure
|
||||
ggml_free(lora_ctx);
|
||||
if (base_ctx) {
|
||||
ggml_free(base_ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const int64_t t_lora_us = ggml_time_us() - t_start_lora_us;
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, " done (%.2f ms)\n", t_lora_us / 1000.0);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size of the KV cache
|
||||
size_t llama_get_kv_cache_size(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size;
|
||||
int llama_apply_lora_from_file(struct llama_context * ctx, const char * path_lora, const char * path_base_model, int n_threads) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
return llama_apply_lora_from_file_internal(ctx, path_lora, path_base_model, n_threads);
|
||||
} catch (const std::string & err) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s: failed to apply lora adapter: %s\n", __func__, err.c_str());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int llama_get_kv_cache_token_count(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx->model.kv_self.n;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sets the KV cache containing the current context for the model
|
||||
void llama_set_kv_cache(
|
||||
struct llama_context * ctx,
|
||||
const uint8_t * kv_cache,
|
||||
size_t n_size,
|
||||
int n_token_count) {
|
||||
// Make sure we have the same kv cache setup
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size == n_size);
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr, kv_cache, n_size);
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.n = n_token_count;
|
||||
#define LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE 64*1024
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size of the state
|
||||
size_t llama_get_state_size(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
// we don't know size of rng until we actually serialize it. so reserve more than enough memory for its serialized state.
|
||||
// for reference, std::mt19937(1337) serializes to 6701 bytes.
|
||||
const size_t s_rng_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_rng = LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE;
|
||||
const size_t s_logits_capacity = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_logits_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_logits = ctx->logits.capacity() * sizeof(float);
|
||||
const size_t s_embedding_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_embedding = ctx->embedding.size() * sizeof(float);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv_ntok = sizeof(int);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv = ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size;
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t s_total = (
|
||||
+ s_rng_size
|
||||
+ s_rng
|
||||
+ s_logits_capacity
|
||||
+ s_logits_size
|
||||
+ s_logits
|
||||
+ s_embedding_size
|
||||
+ s_embedding
|
||||
+ s_kv_size
|
||||
+ s_kv_ntok
|
||||
+ s_kv
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
return s_total;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copies the state to the specified destination address
|
||||
size_t llama_copy_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, uint8_t * dest) {
|
||||
uint8_t * out = dest;
|
||||
|
||||
// copy rng
|
||||
{
|
||||
std::stringstream rng_ss;
|
||||
rng_ss << ctx->rng;
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t rng_size = rng_ss.str().size();
|
||||
char rng_buf[LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE];
|
||||
|
||||
memset(&rng_buf[0], 0, LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE);
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_buf[0], rng_ss.str().data(), rng_ss.str().size());
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &rng_size, sizeof(rng_size)); out += sizeof(rng_size);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &rng_buf[0], LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE); out += LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy logits
|
||||
{
|
||||
const size_t logits_cap = ctx->logits.capacity();
|
||||
const size_t logits_size = ctx->logits.size();
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &logits_cap, sizeof(logits_cap)); out += sizeof(logits_cap);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &logits_size, sizeof(logits_size)); out += sizeof(logits_size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (logits_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->logits.data(), logits_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
out += logits_cap * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy embeddings
|
||||
{
|
||||
const size_t embedding_size = ctx->embedding.size();
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &embedding_size, sizeof(embedding_size)); out += sizeof(embedding_size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (embedding_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->embedding.data(), embedding_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
out += embedding_size * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy kv cache
|
||||
{
|
||||
const size_t kv_size = ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size;
|
||||
const int kv_ntok = llama_get_kv_cache_token_count(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &kv_size, sizeof(kv_size)); out += sizeof(kv_size);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &kv_ntok, sizeof(kv_ntok)); out += sizeof(kv_ntok);
|
||||
|
||||
if (kv_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr, kv_size); out += kv_size;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t written = out - dest;
|
||||
const size_t expected = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(written == expected);
|
||||
|
||||
return written;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sets the state reading from the specified source address
|
||||
size_t llama_set_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, const uint8_t * src) {
|
||||
const uint8_t * in = src;
|
||||
|
||||
// set rng
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t rng_size;
|
||||
char rng_buf[LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE];
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_size, in, sizeof(rng_size)); in += sizeof(rng_size);
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_buf[0], in, LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE); in += LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE;
|
||||
|
||||
std::stringstream rng_ss;
|
||||
rng_ss.str(std::string(&rng_buf[0], rng_size));
|
||||
rng_ss >> ctx->rng;
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(rng_ss.fail() == false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set logits
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t logits_cap;
|
||||
size_t logits_size;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&logits_cap, in, sizeof(logits_cap)); in += sizeof(logits_cap);
|
||||
memcpy(&logits_size, in, sizeof(logits_size)); in += sizeof(logits_size);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->logits.capacity() == logits_cap);
|
||||
|
||||
if (logits_size) {
|
||||
ctx->logits.resize(logits_size);
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->logits.data(), in, logits_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
in += logits_cap * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set embeddings
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t embedding_size;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&embedding_size, in, sizeof(embedding_size)); in += sizeof(embedding_size);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->embedding.capacity() == embedding_size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (embedding_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->embedding.data(), in, embedding_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
in += embedding_size * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set kv cache
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t kv_size;
|
||||
int kv_ntok;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&kv_size, in, sizeof(kv_size)); in += sizeof(kv_size);
|
||||
memcpy(&kv_ntok, in, sizeof(kv_ntok)); in += sizeof(kv_ntok);
|
||||
|
||||
if (kv_size) {
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size == kv_size);
|
||||
|
||||
void * k_data = ctx->model.kv_self.k->data; // remember data pointers
|
||||
void * v_data = ctx->model.kv_self.v->data; // because their value is stored in buf and overwritten by memcpy
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr, in, kv_size); in += kv_size;
|
||||
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.k->data = k_data; // restore correct data pointers
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.v->data = v_data;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.n = kv_ntok;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t nread = in - src;
|
||||
const size_t expected = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(nread == expected);
|
||||
|
||||
return nread;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int llama_eval(
|
||||
|
|
@ -1914,18 +2393,20 @@ const char * llama_print_system_info(void) {
|
|||
static std::string s;
|
||||
|
||||
s = "";
|
||||
s += "AVX = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "AVX2 = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx2()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "AVX512 = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx512()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "FMA = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_fma()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "NEON = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_neon()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "ARM_FMA = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_arm_fma()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "F16C = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_f16c()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "FP16_VA = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_fp16_va()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "WASM_SIMD = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_wasm_simd()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "BLAS = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_blas()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "SSE3 = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_sse3()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "VSX = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_vsx()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "AVX = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "AVX2 = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx2()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "AVX512 = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx512()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "AVX512_VBMI = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx512_vbmi()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "AVX512_VNNI = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_avx512_vnni()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "FMA = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_fma()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "NEON = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_neon()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "ARM_FMA = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_arm_fma()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "F16C = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_f16c()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "FP16_VA = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_fp16_va()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "WASM_SIMD = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_wasm_simd()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "BLAS = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_blas()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "SSE3 = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_sse3()) + " | ";
|
||||
s += "VSX = " + std::to_string(ggml_cpu_has_vsx()) + " | ";
|
||||
|
||||
return s.c_str();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1934,3 +2415,4 @@ const char * llama_print_system_info(void) {
|
|||
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, struct ggml_tensor *>>& llama_internal_get_tensor_map(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx->model.tensors_by_name;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
41
llama.h
41
llama.h
|
|
@ -72,6 +72,9 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_0 = 2, // except 1d tensors
|
||||
LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1 = 3, // except 1d tensors
|
||||
LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1_SOME_F16 = 4, // tok_embeddings.weight and output.weight are F16
|
||||
LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_2 = 5, // except 1d tensors
|
||||
LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_3 = 6, // except 1d tensors
|
||||
LLAMA_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q8_0 = 7, // except 1d tensors
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_API struct llama_context_params llama_context_default_params();
|
||||
|
|
@ -91,27 +94,39 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
|
||||
// TODO: not great API - very likely to change
|
||||
// Returns 0 on success
|
||||
// nthread - how many threads to use. If <=0, will use std::thread::hardware_concurrency(), else the number given
|
||||
LLAMA_API int llama_model_quantize(
|
||||
const char * fname_inp,
|
||||
const char * fname_out,
|
||||
enum llama_ftype ftype);
|
||||
enum llama_ftype ftype,
|
||||
int nthread);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the KV cache that will contain the context for the
|
||||
// ongoing prediction with the model.
|
||||
LLAMA_API const uint8_t * llama_get_kv_cache(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size of the KV cache
|
||||
LLAMA_API size_t llama_get_kv_cache_size(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
// Apply a LoRA adapter to a loaded model
|
||||
// path_base_model is the path to a higher quality model to use as a base for
|
||||
// the layers modified by the adapter. Can be NULL to use the current loaded model.
|
||||
// The model needs to be reloaded before applying a new adapter, otherwise the adapter
|
||||
// will be applied on top of the previous one
|
||||
// Returns 0 on success
|
||||
LLAMA_API int llama_apply_lora_from_file(
|
||||
struct llama_context * ctx,
|
||||
const char * path_lora,
|
||||
const char * path_base_model,
|
||||
int n_threads);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the number of tokens in the KV cache
|
||||
LLAMA_API int llama_get_kv_cache_token_count(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// Sets the KV cache containing the current context for the model
|
||||
LLAMA_API void llama_set_kv_cache(
|
||||
struct llama_context * ctx,
|
||||
const uint8_t * kv_cache,
|
||||
size_t n_size,
|
||||
int n_token_count);
|
||||
// Returns the size in bytes of the state (rng, logits, embedding and kv_cache)
|
||||
LLAMA_API size_t llama_get_state_size(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// Copies the state to the specified destination address.
|
||||
// Destination needs to have allocated enough memory.
|
||||
// Returns the number of bytes copied
|
||||
LLAMA_API size_t llama_copy_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, uint8_t * dest);
|
||||
|
||||
// Set the state reading from the specified address
|
||||
// Returns the number of bytes read
|
||||
LLAMA_API size_t llama_set_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, const uint8_t * src);
|
||||
|
||||
// Run the llama inference to obtain the logits and probabilities for the next token.
|
||||
// tokens + n_tokens is the provided batch of new tokens to process
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
55
llama_util.h
55
llama_util.h
|
|
@ -21,6 +21,9 @@
|
|||
#if defined(_POSIX_MAPPED_FILES)
|
||||
#include <sys/mman.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#if defined(_POSIX_MEMLOCK_RANGE)
|
||||
#include <sys/resource.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -43,8 +46,12 @@
|
|||
} while (0)
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __GNUC__
|
||||
#ifdef __MINGW32__
|
||||
__attribute__((format(gnu_printf, 1, 2)))
|
||||
#else
|
||||
__attribute__((format(printf, 1, 2)))
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
static std::string format(const char * fmt, ...) {
|
||||
va_list ap, ap2;
|
||||
va_start(ap, fmt);
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,7 +64,7 @@ static std::string format(const char * fmt, ...) {
|
|||
va_end(ap2);
|
||||
va_end(ap);
|
||||
return std::string(buf.data(), size);
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct llama_file {
|
||||
// use FILE * so we don't have to re-open the file to mmap
|
||||
|
|
@ -164,7 +171,7 @@ struct llama_mmap {
|
|||
#ifdef _POSIX_MAPPED_FILES
|
||||
static constexpr bool SUPPORTED = true;
|
||||
|
||||
llama_mmap(struct llama_file * file) {
|
||||
llama_mmap(struct llama_file * file, bool prefetch = true) {
|
||||
size = file->size;
|
||||
int fd = fileno(file->fp);
|
||||
int flags = MAP_SHARED;
|
||||
|
|
@ -172,15 +179,16 @@ struct llama_mmap {
|
|||
flags |= MAP_POPULATE;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
addr = mmap(NULL, file->size, PROT_READ, flags, fd, 0);
|
||||
close(fd);
|
||||
if (addr == MAP_FAILED) {
|
||||
throw format("mmap failed: %s", strerror(errno));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Advise the kernel to preload the mapped memory
|
||||
if (madvise(addr, file->size, MADV_WILLNEED)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "warning: madvise(.., MADV_WILLNEED) failed: %s\n",
|
||||
strerror(errno));
|
||||
if (prefetch) {
|
||||
// Advise the kernel to preload the mapped memory
|
||||
if (madvise(addr, file->size, MADV_WILLNEED)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "warning: madvise(.., MADV_WILLNEED) failed: %s\n",
|
||||
strerror(errno));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -190,14 +198,13 @@ struct llama_mmap {
|
|||
#elif defined(_WIN32)
|
||||
static constexpr bool SUPPORTED = true;
|
||||
|
||||
llama_mmap(struct llama_file * file) {
|
||||
llama_mmap(struct llama_file * file, bool prefetch = true) {
|
||||
size = file->size;
|
||||
|
||||
HANDLE hFile = (HANDLE) _get_osfhandle(_fileno(file->fp));
|
||||
|
||||
HANDLE hMapping = CreateFileMappingA(hFile, NULL, PAGE_READONLY, 0, 0, NULL);
|
||||
DWORD error = GetLastError();
|
||||
CloseHandle(hFile);
|
||||
|
||||
if (hMapping == NULL) {
|
||||
throw format("CreateFileMappingA failed: %s", llama_format_win_err(error).c_str());
|
||||
|
|
@ -212,13 +219,15 @@ struct llama_mmap {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if _WIN32_WINNT >= _WIN32_WINNT_WIN8
|
||||
// Advise the kernel to preload the mapped memory
|
||||
WIN32_MEMORY_RANGE_ENTRY range;
|
||||
range.VirtualAddress = addr;
|
||||
range.NumberOfBytes = (SIZE_T)size;
|
||||
if (!PrefetchVirtualMemory(GetCurrentProcess(), 1, &range, 0)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "warning: PrefetchVirtualMemory failed: %s\n",
|
||||
llama_format_win_err(GetLastError()).c_str());
|
||||
if (prefetch) {
|
||||
// Advise the kernel to preload the mapped memory
|
||||
WIN32_MEMORY_RANGE_ENTRY range;
|
||||
range.VirtualAddress = addr;
|
||||
range.NumberOfBytes = (SIZE_T)size;
|
||||
if (!PrefetchVirtualMemory(GetCurrentProcess(), 1, &range, 0)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "warning: PrefetchVirtualMemory failed: %s\n",
|
||||
llama_format_win_err(GetLastError()).c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#pragma message("warning: You are building for pre-Windows 8; prefetch not supported")
|
||||
|
|
@ -297,8 +306,18 @@ struct llama_mlock {
|
|||
if (!mlock(addr, size)) {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "warning: failed to mlock %zu-byte buffer (after previously locking %zu bytes): %s\n" MLOCK_SUGGESTION,
|
||||
size, this->size, std::strerror(errno));
|
||||
char* errmsg = std::strerror(errno);
|
||||
bool suggest = (errno == ENOMEM);
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if the resource limit is fine after all
|
||||
struct rlimit lock_limit;
|
||||
if (suggest && getrlimit(RLIMIT_MEMLOCK, &lock_limit))
|
||||
suggest = false;
|
||||
if (suggest && (lock_limit.rlim_max > lock_limit.rlim_cur + size))
|
||||
suggest = false;
|
||||
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "warning: failed to mlock %zu-byte buffer (after previously locking %zu bytes): %s\n%s",
|
||||
size, this->size, errmsg, suggest ? MLOCK_SUGGESTION : "");
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
12
pocs/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
12
pocs/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
|||
# dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
find_package(Threads REQUIRED)
|
||||
|
||||
# third-party
|
||||
|
||||
include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR})
|
||||
|
||||
if (EMSCRIPTEN)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
add_subdirectory(vdot)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
9
pocs/vdot/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
9
pocs/vdot/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
|||
set(TARGET vdot)
|
||||
add_executable(${TARGET} vdot.cpp)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(${TARGET} PRIVATE common llama ${CMAKE_THREAD_LIBS_INIT})
|
||||
target_compile_features(${TARGET} PRIVATE cxx_std_11)
|
||||
|
||||
set(TARGET q8dot)
|
||||
add_executable(${TARGET} q8dot.cpp)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(${TARGET} PRIVATE common llama ${CMAKE_THREAD_LIBS_INIT})
|
||||
target_compile_features(${TARGET} PRIVATE cxx_std_11)
|
||||
172
pocs/vdot/q8dot.cpp
Normal file
172
pocs/vdot/q8dot.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,172 @@
|
|||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#include <type_traits>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <random>
|
||||
#include <chrono>
|
||||
#include <cstdlib>
|
||||
#include <cmath>
|
||||
#include <cassert>
|
||||
#include <cstring>
|
||||
#include <array>
|
||||
#include <type_traits>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <ggml.h>
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr int kVecSize = 1 << 16;
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy-pasted from ggml.c
|
||||
#define QK4_0 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_0 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_0;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_0) == sizeof(float) + QK4_0 / 2, "wrong q4_0 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
#define QK4_1 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
float m; // min
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_1 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_1;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_1) == sizeof(float) * 2 + QK4_1 / 2, "wrong q4_1 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy-pasted from ggml.c
|
||||
#define QK8_0 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
float s; // d * sum(qs[i])
|
||||
int8_t qs[QK8_0]; // quants
|
||||
} block_q8_0;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q8_0) == 2*sizeof(float) + QK8_0, "wrong q8_0 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
static_assert(QK4_1 == QK8_0, "QK4_1 and QK8_0 must be the same");
|
||||
static_assert(QK4_0 == QK8_0, "QK4_0 and QK8_0 must be the same");
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
void fillQ4blocks(std::vector<T>& blocks, std::mt19937& rndm) {
|
||||
for (auto& b : blocks) {
|
||||
b.d = 1;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<QK4_1/2; ++i) {
|
||||
uint8_t v1 = rndm() >> 28;
|
||||
uint8_t v2 = rndm() >> 28;
|
||||
b.qs[i] = v1 | (v2 << 4);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void fillQ80blocks(std::vector<block_q8_0>& blocks, std::mt19937& rndm) {
|
||||
for (auto& b : blocks) {
|
||||
b.d = 1;
|
||||
int sum = 0;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<QK8_0; ++i) {
|
||||
b.qs[i] = (rndm() >> 24) - 128;
|
||||
sum += b.qs[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.s = b.d * sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
float simpleDot(const block_q4_0& x, const block_q8_0& y) {
|
||||
int s1 = 0; //, s2 = 0;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<QK4_1/2; i+=2) {
|
||||
int v1 = x.qs[i+0] & 0xf;
|
||||
int v2 = x.qs[i+0] >> 4;
|
||||
int v3 = x.qs[i+1] & 0xf;
|
||||
int v4 = x.qs[i+1] >> 4;
|
||||
int j = 2*i;
|
||||
s1 += v1*y.qs[j] + v2*y.qs[j+1] + v3*y.qs[j+2] + v4*y.qs[j+3];
|
||||
//s2 += y.qs[j] + y.qs[j+1] + y.qs[j+2] + y.qs[j+3];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return y.d * x.d * s1 - 8 * x.d * y.s;
|
||||
//return y.d * x.d * (s1 - 8 * s2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
float simpleDot(const block_q4_1& x, const block_q8_0& y) {
|
||||
int s1 = 0; //, s2 = 0;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<QK4_1/2; i+=2) {
|
||||
int v1 = x.qs[i+0] & 0xf;
|
||||
int v2 = x.qs[i+0] >> 4;
|
||||
int v3 = x.qs[i+1] & 0xf;
|
||||
int v4 = x.qs[i+1] >> 4;
|
||||
int j = 2*i;
|
||||
s1 += v1*y.qs[j] + v2*y.qs[j+1] + v3*y.qs[j+2] + v4*y.qs[j+3];
|
||||
//s2 += y.qs[j] + y.qs[j+1] + y.qs[j+2] + y.qs[j+3];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return y.d * x.d * s1 + y.s * x.m;
|
||||
//return y.d * (x.d * s1 + x.m * s2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct Stat {
|
||||
double sum = 0, sumt = 0, sumt2 = 0, maxt = 0;
|
||||
int nloop = 0;
|
||||
void addResult(double s, double t) {
|
||||
sum += s;
|
||||
sumt += t; sumt2 += t*t; maxt = std::max(maxt, t);
|
||||
++nloop;
|
||||
}
|
||||
void reportResult(const char* title) const {
|
||||
if (nloop < 1) {
|
||||
printf("%s(%s): no result\n",__func__,title);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("============ %s\n",title);
|
||||
printf("<dot> = %g\n",sum/nloop);
|
||||
auto t = sumt/nloop, dt = sumt2/nloop - t*t;
|
||||
if (dt > 0) dt = sqrt(dt);
|
||||
printf("<time> = %g +/- %g us. Max. time = %g us.\n",t,dt,maxt);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
int nloop = argc > 1 ? atoi(argv[1]) : 10;
|
||||
int type = argc > 2 ? atoi(argv[2]) : 1;
|
||||
|
||||
std::mt19937 rndm(1234);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<block_q4_1> x41;
|
||||
std::vector<block_q4_0> x40;
|
||||
std::vector<block_q8_0> y(kVecSize);
|
||||
if (type == 0) x40.resize(kVecSize);
|
||||
else {
|
||||
x41.resize(kVecSize);
|
||||
for (auto& b : x41) b.m = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto ggml_type = type == 0 ? GGML_TYPE_Q4_0 : GGML_TYPE_Q4_1;
|
||||
|
||||
auto funcs = ggml_internal_get_quantize_fn(ggml_type);
|
||||
|
||||
Stat simple, ggml;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int iloop=0; iloop<nloop; ++iloop) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (type == 0) fillQ4blocks(x40, rndm);
|
||||
else fillQ4blocks(x41, rndm);
|
||||
fillQ80blocks(y, rndm);
|
||||
|
||||
auto t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
double s = 0;
|
||||
if (type == 0) for (int i=0; i<kVecSize; ++i) s += simpleDot(x40[i], y[i]);
|
||||
else for (int i=0; i<kVecSize; ++i) s += simpleDot(x41[i], y[i]);
|
||||
auto t2 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
auto t = 1e-3*std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(t2-t1).count();
|
||||
if (iloop > 3) simple.addResult(s, t);
|
||||
|
||||
t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
float fs;
|
||||
if (type == 0) funcs.vec_dot_q(kVecSize * QK4_1, &fs, x40.data(), y.data());
|
||||
else funcs.vec_dot_q(kVecSize * QK4_1, &fs, x41.data(), y.data());
|
||||
t2 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
t = 1e-3*std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(t2-t1).count();
|
||||
if (iloop > 3) ggml.addResult(fs, t);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Report the time (and the average of the dot products so the compiler does not come up with the idea
|
||||
// of optimizing away the function calls after figuring that the result is not used).
|
||||
simple.reportResult("Simple");
|
||||
ggml.reportResult("ggml");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
305
pocs/vdot/vdot.cpp
Normal file
305
pocs/vdot/vdot.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
|
|||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <random>
|
||||
#include <chrono>
|
||||
#include <cstdlib>
|
||||
#include <cmath>
|
||||
#include <cassert>
|
||||
#include <cstring>
|
||||
#include <array>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <ggml.h>
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr int kVecSize = 1 << 18;
|
||||
|
||||
float drawFromGaussianPdf(std::mt19937& rndm) {
|
||||
constexpr double kScale = 1./(1. + std::mt19937::max());
|
||||
constexpr double kTwoPiTimesScale = 6.28318530717958647692*kScale;
|
||||
static float lastX;
|
||||
static bool haveX = false;
|
||||
if (haveX) { haveX = false; return lastX; }
|
||||
auto r = sqrt(-2*log(1 - kScale*rndm()));
|
||||
auto phi = kTwoPiTimesScale * rndm();
|
||||
lastX = r*sin(phi);
|
||||
haveX = true;
|
||||
return r*cos(phi);
|
||||
}
|
||||
void fillRandomGaussianFloats(std::vector<float>& values, std::mt19937& rndm, float mean = 0) {
|
||||
for (auto& v : values) v = mean + drawFromGaussianPdf(rndm);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy-pasted from ggml.c
|
||||
#define QK4_0 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_0 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_0;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_0) == sizeof(float) + QK4_0 / 2, "wrong q4_0 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
#define QK4_1 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
float m; // min
|
||||
uint8_t qs[QK4_1 / 2]; // nibbles / quants
|
||||
} block_q4_1;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q4_1) == sizeof(float) * 2 + QK4_1 / 2, "wrong q4_1 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy-pasted from ggml.c
|
||||
#define QK8_0 32
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float d; // delta
|
||||
int8_t qs[QK8_0]; // quants
|
||||
} block_q8_0;
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(block_q8_0) == sizeof(float) + QK8_0, "wrong q8_0 block size/padding");
|
||||
|
||||
// "Scalar" dot product between the quantized vector x and float vector y
|
||||
inline double dot(int n, const block_q4_0* x, const float* y) {
|
||||
const static float kValues[16] = {-8.f, -7.f, -6.f, -5.f, -4.f, -3.f, -2.f, -1.f, 0.f, 1.f, 2.f, 3.f, 4.f, 5.f, 6.f, 7.f};
|
||||
constexpr uint32_t kMask1 = 0x0f0f0f0f;
|
||||
uint32_t u1, u2;
|
||||
auto q1 = (const uint8_t*)&u1;
|
||||
auto q2 = (const uint8_t*)&u2;
|
||||
double sum = 0;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
|
||||
float d = x->d;
|
||||
auto u = (const uint32_t*)x->qs;
|
||||
float s = 0;
|
||||
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k) {
|
||||
u1 = u[k] & kMask1;
|
||||
u2 = (u[k] >> 4) & kMask1;
|
||||
s += y[0]*kValues[q1[0]] + y[1]*kValues[q2[0]] +
|
||||
y[2]*kValues[q1[1]] + y[3]*kValues[q2[1]] +
|
||||
y[4]*kValues[q1[2]] + y[5]*kValues[q2[2]] +
|
||||
y[6]*kValues[q1[3]] + y[7]*kValues[q2[3]];
|
||||
y += 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sum += s*d;
|
||||
++x;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Alternative version of the above. Faster on my Mac (~45 us vs ~55 us per dot product),
|
||||
// but about the same on X86_64 (Ryzen 7950X CPU).
|
||||
inline double dot3(int n, const block_q4_0* x, const float* y) {
|
||||
const static std::pair<float,float> kValues[256] = {
|
||||
{-8.f, -8.f}, {-7.f, -8.f}, {-6.f, -8.f}, {-5.f, -8.f}, {-4.f, -8.f}, {-3.f, -8.f}, {-2.f, -8.f}, {-1.f, -8.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -8.f}, { 1.f, -8.f}, { 2.f, -8.f}, { 3.f, -8.f}, { 4.f, -8.f}, { 5.f, -8.f}, { 6.f, -8.f}, { 7.f, -8.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, -7.f}, {-7.f, -7.f}, {-6.f, -7.f}, {-5.f, -7.f}, {-4.f, -7.f}, {-3.f, -7.f}, {-2.f, -7.f}, {-1.f, -7.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -7.f}, { 1.f, -7.f}, { 2.f, -7.f}, { 3.f, -7.f}, { 4.f, -7.f}, { 5.f, -7.f}, { 6.f, -7.f}, { 7.f, -7.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, -6.f}, {-7.f, -6.f}, {-6.f, -6.f}, {-5.f, -6.f}, {-4.f, -6.f}, {-3.f, -6.f}, {-2.f, -6.f}, {-1.f, -6.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -6.f}, { 1.f, -6.f}, { 2.f, -6.f}, { 3.f, -6.f}, { 4.f, -6.f}, { 5.f, -6.f}, { 6.f, -6.f}, { 7.f, -6.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, -5.f}, {-7.f, -5.f}, {-6.f, -5.f}, {-5.f, -5.f}, {-4.f, -5.f}, {-3.f, -5.f}, {-2.f, -5.f}, {-1.f, -5.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -5.f}, { 1.f, -5.f}, { 2.f, -5.f}, { 3.f, -5.f}, { 4.f, -5.f}, { 5.f, -5.f}, { 6.f, -5.f}, { 7.f, -5.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, -4.f}, {-7.f, -4.f}, {-6.f, -4.f}, {-5.f, -4.f}, {-4.f, -4.f}, {-3.f, -4.f}, {-2.f, -4.f}, {-1.f, -4.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -4.f}, { 1.f, -4.f}, { 2.f, -4.f}, { 3.f, -4.f}, { 4.f, -4.f}, { 5.f, -4.f}, { 6.f, -4.f}, { 7.f, -4.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, -3.f}, {-7.f, -3.f}, {-6.f, -3.f}, {-5.f, -3.f}, {-4.f, -3.f}, {-3.f, -3.f}, {-2.f, -3.f}, {-1.f, -3.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -3.f}, { 1.f, -3.f}, { 2.f, -3.f}, { 3.f, -3.f}, { 4.f, -3.f}, { 5.f, -3.f}, { 6.f, -3.f}, { 7.f, -3.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, -2.f}, {-7.f, -2.f}, {-6.f, -2.f}, {-5.f, -2.f}, {-4.f, -2.f}, {-3.f, -2.f}, {-2.f, -2.f}, {-1.f, -2.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -2.f}, { 1.f, -2.f}, { 2.f, -2.f}, { 3.f, -2.f}, { 4.f, -2.f}, { 5.f, -2.f}, { 6.f, -2.f}, { 7.f, -2.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, -1.f}, {-7.f, -1.f}, {-6.f, -1.f}, {-5.f, -1.f}, {-4.f, -1.f}, {-3.f, -1.f}, {-2.f, -1.f}, {-1.f, -1.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, -1.f}, { 1.f, -1.f}, { 2.f, -1.f}, { 3.f, -1.f}, { 4.f, -1.f}, { 5.f, -1.f}, { 6.f, -1.f}, { 7.f, -1.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 0.f}, {-7.f, 0.f}, {-6.f, 0.f}, {-5.f, 0.f}, {-4.f, 0.f}, {-3.f, 0.f}, {-2.f, 0.f}, {-1.f, 0.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 0.f}, { 1.f, 0.f}, { 2.f, 0.f}, { 3.f, 0.f}, { 4.f, 0.f}, { 5.f, 0.f}, { 6.f, 0.f}, { 7.f, 0.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 1.f}, {-7.f, 1.f}, {-6.f, 1.f}, {-5.f, 1.f}, {-4.f, 1.f}, {-3.f, 1.f}, {-2.f, 1.f}, {-1.f, 1.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 1.f}, { 1.f, 1.f}, { 2.f, 1.f}, { 3.f, 1.f}, { 4.f, 1.f}, { 5.f, 1.f}, { 6.f, 1.f}, { 7.f, 1.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 2.f}, {-7.f, 2.f}, {-6.f, 2.f}, {-5.f, 2.f}, {-4.f, 2.f}, {-3.f, 2.f}, {-2.f, 2.f}, {-1.f, 2.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 2.f}, { 1.f, 2.f}, { 2.f, 2.f}, { 3.f, 2.f}, { 4.f, 2.f}, { 5.f, 2.f}, { 6.f, 2.f}, { 7.f, 2.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 3.f}, {-7.f, 3.f}, {-6.f, 3.f}, {-5.f, 3.f}, {-4.f, 3.f}, {-3.f, 3.f}, {-2.f, 3.f}, {-1.f, 3.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 3.f}, { 1.f, 3.f}, { 2.f, 3.f}, { 3.f, 3.f}, { 4.f, 3.f}, { 5.f, 3.f}, { 6.f, 3.f}, { 7.f, 3.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 4.f}, {-7.f, 4.f}, {-6.f, 4.f}, {-5.f, 4.f}, {-4.f, 4.f}, {-3.f, 4.f}, {-2.f, 4.f}, {-1.f, 4.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 4.f}, { 1.f, 4.f}, { 2.f, 4.f}, { 3.f, 4.f}, { 4.f, 4.f}, { 5.f, 4.f}, { 6.f, 4.f}, { 7.f, 4.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 5.f}, {-7.f, 5.f}, {-6.f, 5.f}, {-5.f, 5.f}, {-4.f, 5.f}, {-3.f, 5.f}, {-2.f, 5.f}, {-1.f, 5.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 5.f}, { 1.f, 5.f}, { 2.f, 5.f}, { 3.f, 5.f}, { 4.f, 5.f}, { 5.f, 5.f}, { 6.f, 5.f}, { 7.f, 5.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 6.f}, {-7.f, 6.f}, {-6.f, 6.f}, {-5.f, 6.f}, {-4.f, 6.f}, {-3.f, 6.f}, {-2.f, 6.f}, {-1.f, 6.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 6.f}, { 1.f, 6.f}, { 2.f, 6.f}, { 3.f, 6.f}, { 4.f, 6.f}, { 5.f, 6.f}, { 6.f, 6.f}, { 7.f, 6.f},
|
||||
{-8.f, 7.f}, {-7.f, 7.f}, {-6.f, 7.f}, {-5.f, 7.f}, {-4.f, 7.f}, {-3.f, 7.f}, {-2.f, 7.f}, {-1.f, 7.f},
|
||||
{ 0.f, 7.f}, { 1.f, 7.f}, { 2.f, 7.f}, { 3.f, 7.f}, { 4.f, 7.f}, { 5.f, 7.f}, { 6.f, 7.f}, { 7.f, 7.f}
|
||||
};
|
||||
double sum = 0;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
|
||||
float d = x->d;
|
||||
auto q = x->qs;
|
||||
float s = 0;
|
||||
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k) {
|
||||
s += y[0]*kValues[q[0]].first + y[1]*kValues[q[0]].second +
|
||||
y[2]*kValues[q[1]].first + y[3]*kValues[q[1]].second +
|
||||
y[4]*kValues[q[2]].first + y[5]*kValues[q[2]].second +
|
||||
y[6]*kValues[q[3]].first + y[7]*kValues[q[3]].second;
|
||||
y += 8; q += 4;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sum += s*d;
|
||||
++x;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline double dot41(int n, const block_q4_1* x, const float* y) {
|
||||
const static float kValues[16] = {0.f, 1.f, 2.f, 3.f, 4.f, 5.f, 6.f, 7.f, 8.f, 9.f, 10.f, 11.f, 12.f, 13.f, 14.f, 15.f};
|
||||
constexpr uint32_t kMask1 = 0x0f0f0f0f;
|
||||
uint32_t u1, u2;
|
||||
auto q1 = (const uint8_t*)&u1;
|
||||
auto q2 = (const uint8_t*)&u2;
|
||||
double sum = 0;
|
||||
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
|
||||
auto u = (const uint32_t*)x->qs;
|
||||
float s = 0, s1 = 0;
|
||||
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k) {
|
||||
u1 = u[k] & kMask1;
|
||||
u2 = (u[k] >> 4) & kMask1;
|
||||
s += y[0]*kValues[q1[0]] + y[1]*kValues[q2[0]] +
|
||||
y[2]*kValues[q1[1]] + y[3]*kValues[q2[1]] +
|
||||
y[4]*kValues[q1[2]] + y[5]*kValues[q2[2]] +
|
||||
y[6]*kValues[q1[3]] + y[7]*kValues[q2[3]];
|
||||
s1 += y[0] + y[1] + y[2] + y[3] + y[4] + y[5] + y[6] + y[7];
|
||||
y += 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sum += s*x->d + s1*x->m;
|
||||
++x;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy-pasted from ggml.c
|
||||
static void quantize_row_q8_0_reference(const float *x, block_q8_0 *y, int k) {
|
||||
assert(k % QK8_0 == 0);
|
||||
const int nb = k / QK8_0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
float amax = 0.0f; // absolute max
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK8_0; l++) {
|
||||
const float v = x[i*QK8_0 + l];
|
||||
amax = std::max(amax, fabsf(v));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = amax / ((1 << 7) - 1);
|
||||
const float id = d ? 1.0f/d : 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i].d = d;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK8_0; ++l) {
|
||||
const float v = x[i*QK8_0 + l]*id;
|
||||
y[i].qs[l] = roundf(v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy-pasted from ggml.c
|
||||
static void dot_q4_q8(const int n, float* s, const void* vx, const void* vy) {
|
||||
const int nb = n / QK8_0;
|
||||
const block_q4_0* x = (const block_q4_0*)vx;
|
||||
const block_q8_0* y = (const block_q8_0*)vy;
|
||||
float sumf = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
const float d0 = x[i].d;
|
||||
const float d1 = y[i].d;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t * p0 = x[i].qs;
|
||||
const int8_t * p1 = y[i].qs;
|
||||
|
||||
int sumi = 0;
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < QK8_0/2; j++) {
|
||||
const uint8_t v0 = p0[j];
|
||||
|
||||
const int i0 = (int8_t) (v0 & 0xf) - 8;
|
||||
const int i1 = (int8_t) (v0 >> 4) - 8;
|
||||
|
||||
const int i2 = p1[2*j + 0];
|
||||
const int i3 = p1[2*j + 1];
|
||||
|
||||
sumi += i0*i2 + i1*i3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sumf += d0*d1*sumi;
|
||||
}
|
||||
*s = sumf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
|
||||
|
||||
int nloop = argc > 1 ? atoi(argv[1]) : 10;
|
||||
bool scalar = argc > 2 ? atoi(argv[2]) : false;
|
||||
bool useQ4_1 = argc > 3 ? atoi(argv[3]) : false;
|
||||
|
||||
if (scalar && useQ4_1) {
|
||||
printf("It is not possible to use Q4_1 quantization and scalar implementations\n");
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::mt19937 rndm(1234);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<float> x1(kVecSize), y1(kVecSize);
|
||||
int n4 = useQ4_1 ? kVecSize / QK4_1 : kVecSize / QK4_0; n4 = 64*((n4 + 63)/64);
|
||||
int n8 = kVecSize / QK8_0; n8 = 64*((n8 + 63)/64);
|
||||
|
||||
auto funcs = useQ4_1 ? ggml_internal_get_quantize_fn(GGML_TYPE_Q4_1) : ggml_internal_get_quantize_fn(GGML_TYPE_Q4_0);
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<block_q4_0> q40;
|
||||
std::vector<block_q4_1> q41;
|
||||
if (useQ4_1) q41.resize(n4);
|
||||
else q40.resize(n4);
|
||||
std::vector<block_q8_0> q8(n8);
|
||||
std::vector<int64_t> H(16, 0);
|
||||
double sumt = 0, sumt2 = 0, maxt = 0;
|
||||
double sumqt = 0, sumqt2 = 0, maxqt = 0;
|
||||
double sum = 0, sumq = 0, exactSum = 0;
|
||||
for (int iloop=0; iloop<nloop; ++iloop) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill vector x with random numbers
|
||||
fillRandomGaussianFloats(x1, rndm);
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill vector y with random numbers
|
||||
fillRandomGaussianFloats(y1, rndm);
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the exact dot product
|
||||
for (int k=0; k<kVecSize; ++k) exactSum += x1[k]*y1[k];
|
||||
|
||||
// quantize x.
|
||||
// Note, we do not include this in the timing as in practical application
|
||||
// we already have the quantized model weights.
|
||||
if (useQ4_1) {
|
||||
funcs.quantize_row_q(x1.data(), q41.data(), kVecSize);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
funcs.quantize_row_q(x1.data(), q40.data(), kVecSize);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Now measure time the dot product needs using the "scalar" version above
|
||||
auto t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
if (useQ4_1) sum += dot41(kVecSize / QK4_1, q41.data(), y1.data());
|
||||
else sum += dot(kVecSize / QK4_0, q40.data(), y1.data());
|
||||
auto t2 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
auto t = 1e-3*std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(t2-t1).count();
|
||||
sumt += t; sumt2 += t*t; maxt = std::max(maxt, t);
|
||||
|
||||
// And now measure the time needed to quantize y and perform the dot product with the quantized y
|
||||
t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
float result;
|
||||
if (scalar) {
|
||||
quantize_row_q8_0_reference(y1.data(), q8.data(), kVecSize);
|
||||
dot_q4_q8(kVecSize, &result, q40.data(), q8.data());
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
funcs.quantize_row_q_dot(y1.data(), q8.data(), kVecSize);
|
||||
if (useQ4_1) funcs.vec_dot_q(kVecSize, &result, q41.data(), q8.data());
|
||||
else funcs.vec_dot_q(kVecSize, &result, q40.data(), q8.data());
|
||||
}
|
||||
sumq += result;
|
||||
t2 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
|
||||
t = 1e-3*std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(t2-t1).count();
|
||||
sumqt += t; sumqt2 += t*t; maxqt = std::max(maxqt, t);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Report the time (and the average of the dot products so the compiler does not come up with the idea
|
||||
// of optimizing away the function calls after figuring that the result is not used).
|
||||
sum /= nloop; sumq /= nloop;
|
||||
exactSum /= nloop;
|
||||
printf("Exact result: <dot> = %g\n",exactSum);
|
||||
printf("<dot> = %g, %g\n",sum,sumq);
|
||||
sumt /= nloop; sumt2 /= nloop; sumt2 -= sumt*sumt;
|
||||
if (sumt2 > 0) sumt2 = sqrt(sumt2);
|
||||
printf("time = %g +/- %g us. maxt = %g us\n",sumt,sumt2,maxt);
|
||||
sumqt /= nloop; sumqt2 /= nloop; sumqt2 -= sumqt*sumqt;
|
||||
if (sumqt2 > 0) sumqt2 = sqrt(sumqt2);
|
||||
printf("timeq = %g +/- %g us. maxt = %g us\n",sumqt,sumqt2,maxqt);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
6
scripts/sync-ggml.sh
Executable file
6
scripts/sync-ggml.sh
Executable file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
|||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
cp -rpv ../ggml/src/ggml.c ./ggml.c
|
||||
cp -rpv ../ggml/src/ggml-cuda.cu ./ggml-cuda.cu
|
||||
cp -rpv ../ggml/src/ggml-cuda.h ./ggml-cuda.h
|
||||
cp -rpv ../ggml/include/ggml/ggml.h ./ggml.h
|
||||
|
|
@ -6,5 +6,6 @@ function(llama_add_test source)
|
|||
endfunction()
|
||||
|
||||
# llama_add_test(test-double-float.c) # SLOW
|
||||
llama_add_test(test-quantize.c)
|
||||
llama_add_test(test-quantize-fns.cpp)
|
||||
llama_add_test(test-quantize-perf.cpp)
|
||||
llama_add_test(test-tokenizer-0.cpp ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/../models/ggml-vocab.bin)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
154
tests/test-quantize-fns.cpp
Normal file
154
tests/test-quantize-fns.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
|||
// Unit tests for quantization specific functions - quantize, dequantize and dot product
|
||||
|
||||
#include "ggml.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#undef NDEBUG
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
const float MAX_QUANTIZATION_REFERENCE_ERROR = 0.0001;
|
||||
const float MAX_QUANTIZATION_TOTAL_ERROR = 0.002;
|
||||
const float MAX_DOT_PRODUCT_ERROR = 0.02;
|
||||
|
||||
const char* RESULT_STR[] = {"ok", "FAILED"};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate synthetic data
|
||||
void generate_data(float offset, size_t n, float * dst) {
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
dst[i] = 0.1 + 2*cosf(i + offset);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate RMSE between two float arrays
|
||||
float array_rmse(const float * a1, const float * a2, size_t n) {
|
||||
double sum = 0;
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
double diff = a1[i] - a2[i];
|
||||
sum += diff * diff;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sqrtf(sum) / n;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Total quantization error on test data
|
||||
float total_quantization_error(quantize_fns_t & qfns, size_t test_size, const float * test_data) {
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> tmp_q(2*test_size);
|
||||
std::vector<float> tmp_out(test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(test_data, tmp_q.data(), test_size);
|
||||
qfns.dequantize_row_q(tmp_q.data(), tmp_out.data(), test_size);
|
||||
return array_rmse(test_data, tmp_out.data(), test_size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Total quantization error on test data
|
||||
float reference_quantization_error(quantize_fns_t & qfns, size_t test_size, const float * test_data) {
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> tmp_q(2*test_size);
|
||||
std::vector<float> tmp_out(test_size);
|
||||
std::vector<float> tmp_out_ref(test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(test_data, tmp_q.data(), test_size);
|
||||
qfns.dequantize_row_q(tmp_q.data(), tmp_out.data(), test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q_reference(test_data, tmp_q.data(), test_size);
|
||||
qfns.dequantize_row_q(tmp_q.data(), tmp_out_ref.data(), test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
return array_rmse(tmp_out.data(), tmp_out_ref.data(), test_size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
float dot_product(const float * a1, const float * a2, size_t test_size) {
|
||||
double sum = 0;
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < test_size; i++) {
|
||||
sum += a1[i] * a2[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Total dot product error
|
||||
float dot_product_error(quantize_fns_t & qfns, size_t test_size, const float * test_data1, const float *test_data2) {
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> tmp_q1(2*test_size);
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> tmp_q2(2*test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q (test_data1, tmp_q1.data(), test_size);
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q_dot(test_data2, tmp_q2.data(), test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
float result = INFINITY;
|
||||
qfns.vec_dot_q(test_size, &result, tmp_q1.data(), tmp_q2.data());
|
||||
|
||||
const float dot_ref = dot_product(test_data1, test_data2, test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
return fabsf(result - dot_ref) / test_size;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
|
||||
bool verbose = false;
|
||||
const size_t test_size = 32 * 128;
|
||||
|
||||
std::string arg;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
|
||||
arg = argv[i];
|
||||
|
||||
if (arg == "-v") {
|
||||
verbose = true;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "error: unknown argument: %s\n", arg.c_str());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<float> test_data(test_size);
|
||||
std::vector<float> test_data2(test_size);
|
||||
|
||||
generate_data(0.0, test_data.size(), test_data.data());
|
||||
generate_data(1.0, test_data2.size(), test_data2.data());
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize GGML, ensures float conversion tables are initialized
|
||||
struct ggml_init_params ggml_params = {
|
||||
/* .mem_size = */ 1*1024,
|
||||
/* .mem_buffer = */ NULL,
|
||||
/* .no_alloc = */ true,
|
||||
};
|
||||
struct ggml_context * ctx = ggml_init(ggml_params);
|
||||
|
||||
int num_failed = 0;
|
||||
bool failed = false;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < GGML_TYPE_COUNT; i++) {
|
||||
ggml_type type = (ggml_type) i;
|
||||
quantize_fns_t qfns = ggml_internal_get_quantize_fn(i);
|
||||
|
||||
if (qfns.quantize_row_q && qfns.dequantize_row_q) {
|
||||
const float total_error = total_quantization_error(qfns, test_size, test_data.data());
|
||||
failed = !(total_error < MAX_QUANTIZATION_TOTAL_ERROR);
|
||||
num_failed += failed;
|
||||
if (failed || verbose) {
|
||||
printf("%5s absolute quantization error: %s (%f)\n", ggml_type_name(type), RESULT_STR[failed], total_error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const float reference_error = reference_quantization_error(qfns, test_size, test_data.data());
|
||||
failed = !(reference_error < MAX_QUANTIZATION_REFERENCE_ERROR);
|
||||
num_failed += failed;
|
||||
if (failed || verbose) {
|
||||
printf("%5s reference implementation error: %s (%f)\n", ggml_type_name(type), RESULT_STR[failed], reference_error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const float vec_dot_error = dot_product_error(qfns, test_size, test_data.data(), test_data2.data());
|
||||
failed = !(vec_dot_error < MAX_DOT_PRODUCT_ERROR);
|
||||
num_failed += failed;
|
||||
if (failed || verbose) {
|
||||
printf("%5s dot product error: %s (%f)\n", ggml_type_name(type), RESULT_STR[failed], vec_dot_error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (num_failed || verbose) {
|
||||
printf("%d tests failed\n", num_failed);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_free(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
return num_failed > 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
310
tests/test-quantize-perf.cpp
Normal file
310
tests/test-quantize-perf.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,310 @@
|
|||
// Benchmark quantization specific functions on synthetic data
|
||||
|
||||
#include "ggml.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#undef NDEBUG
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
#include <functional>
|
||||
#include <inttypes.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include <memory>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_ALIGNMENT 64
|
||||
#define QK 32
|
||||
#define WARMUP 5
|
||||
#define ITERATIONS 10
|
||||
|
||||
#define L1_SIZE 32*128
|
||||
#define L2_SIZE 32*2048
|
||||
#define L3_SIZE 32*20480
|
||||
#define MEM_SIZE 32*2048000
|
||||
|
||||
struct quantize_perf_params {
|
||||
std::vector<std::string> include_types;
|
||||
std::vector<size_t> test_sizes;
|
||||
size_t alignment_offset = 0;
|
||||
bool op_quantize_row_q_reference = false;
|
||||
bool op_quantize_row_q = false;
|
||||
bool op_dequantize_row_q = false;
|
||||
bool op_quantize_row_q_dot = false;
|
||||
bool op_vec_dot_q = false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__x86_64__) || defined(__i386__)
|
||||
|
||||
#include <x86intrin.h>
|
||||
inline int64_t cpu_cycles() {
|
||||
// Rough way to detect new-ish CPUs
|
||||
#ifdef __POPCNT__
|
||||
unsigned int dummy;
|
||||
return __rdtscp(&dummy);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
return __rdtsc();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
#define cpu_cycles() 0
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate synthetic data
|
||||
void generate_data(float offset, size_t n, float * dst) {
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||||
dst[i] = 0.1 + 2*cosf(i + offset);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
float gigabytes_per_second(size_t bytes, int64_t usecs) {
|
||||
return bytes / (float) usecs * 1000000 / (1024*1024*1024);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void * align_with_offset(void * ptr, int offset) {
|
||||
size_t dummy_size = MAX_ALIGNMENT * 4;
|
||||
return (char *) std::align(MAX_ALIGNMENT, MAX_ALIGNMENT, ptr, dummy_size) + offset;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void benchmark_function(size_t size, size_t q_size, std::function<size_t(void)> function) {
|
||||
int64_t min_time_us = INT64_MAX;
|
||||
int64_t total_time_us = 0;
|
||||
int64_t min_time_cycles = INT64_MAX;
|
||||
int64_t total_time_cycles = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < WARMUP; i++) {
|
||||
function();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
|
||||
const int64_t start_time = ggml_time_us();
|
||||
const int64_t start_cycles = cpu_cycles();
|
||||
|
||||
function();
|
||||
|
||||
const int64_t end_cycles = cpu_cycles();
|
||||
const int64_t end_time = ggml_time_us();
|
||||
|
||||
total_time_cycles += end_cycles - start_cycles;
|
||||
min_time_cycles = std::min(min_time_cycles, end_cycles - start_cycles);
|
||||
total_time_us += end_time - start_time;
|
||||
min_time_us = std::min(min_time_us, end_time - start_time);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
printf(" min cycles/%d vals : %9.2f\n", QK, QK * min_time_cycles / (float) size);
|
||||
printf(" avg cycles/%d vals : %9.2f\n", QK, QK * total_time_cycles / (float) (size * ITERATIONS));
|
||||
printf(" float32 throughput : %9.2f GB/s\n", gigabytes_per_second(4 * size * ITERATIONS, total_time_us));
|
||||
printf(" quantized throughput : %9.2f GB/s\n", gigabytes_per_second(q_size * ITERATIONS, total_time_us));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
|
||||
quantize_perf_params params {};
|
||||
|
||||
// read command line
|
||||
|
||||
bool invalid_param = false;
|
||||
std::string arg;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
|
||||
arg = argv[i];
|
||||
|
||||
if (arg == "--size") {
|
||||
if (++i >= argc) {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
size_t size = std::stoi(argv[i]);
|
||||
if (size % 32 != 0) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "error: size %zu not divisible by 32\n", size);
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(size);
|
||||
} else if (arg == "-3") {
|
||||
// quick select sizes that probably fit in CPU caches
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(L1_SIZE);
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(L2_SIZE);
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(L3_SIZE);
|
||||
} else if (arg == "-4") {
|
||||
// quick select cache sizes + memory
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(L1_SIZE);
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(L2_SIZE);
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(L3_SIZE);
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(MEM_SIZE);
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--op") {
|
||||
if (++i >= argc) {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::string op {argv[i]};
|
||||
if (op == "quantize_row_q_reference") {
|
||||
params.op_quantize_row_q_reference = true;
|
||||
} else if (op == "quantize_row_q") {
|
||||
params.op_quantize_row_q = true;
|
||||
} else if (op == "dequantize_row_q") {
|
||||
params.op_dequantize_row_q = true;
|
||||
} else if (op == "quantize_row_q_dot") {
|
||||
params.op_quantize_row_q_dot = true;
|
||||
} else if (op == "vec_dot_q") {
|
||||
params.op_vec_dot_q = true;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--type") {
|
||||
if (++i >= argc) {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params.include_types.push_back(argv[i]);
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--alignment-offset") {
|
||||
if (++i >= argc) {
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int alignment = std::stoi(argv[i]);
|
||||
if (alignment < 0 || alignment > MAX_ALIGNMENT) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "error: aligment-offset must be less than %d\n", MAX_ALIGNMENT);
|
||||
invalid_param = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params.alignment_offset = alignment;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "error: unknown argument: %s\n", arg.c_str());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (invalid_param) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "error: invalid parameter for argument: %s\n", arg.c_str());
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (params.test_sizes.empty()) {
|
||||
params.test_sizes.push_back(L1_SIZE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!(params.op_quantize_row_q_reference || params.op_quantize_row_q || params.op_dequantize_row_q || params.op_quantize_row_q_dot || params.op_vec_dot_q)) {
|
||||
params.op_quantize_row_q_reference = params.op_quantize_row_q = params.op_dequantize_row_q = params.op_quantize_row_q_dot = params.op_vec_dot_q = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::sort(params.test_sizes.begin(), params.test_sizes.end());
|
||||
size_t largest = params.test_sizes.back();
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> test_data1_v(largest*4 + MAX_ALIGNMENT*2);
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> test_data2_v(largest*4 + MAX_ALIGNMENT*2);
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> test_q1_v(largest*4 + MAX_ALIGNMENT*2);
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> test_q2_v(largest*4 + MAX_ALIGNMENT*2);
|
||||
std::vector<uint8_t> test_out_v(largest*4 + MAX_ALIGNMENT*2);
|
||||
|
||||
float * test_data1 = (float *) align_with_offset(test_data1_v.data(), params.alignment_offset);
|
||||
float * test_data2 = (float *) align_with_offset(test_data2_v.data(), params.alignment_offset);
|
||||
float * test_q1 = (float *) align_with_offset(test_q1_v.data(), params.alignment_offset);
|
||||
float * test_q2 = (float *) align_with_offset(test_q2_v.data(), params.alignment_offset);
|
||||
float * test_out = (float *) align_with_offset(test_out_v.data(), params.alignment_offset);
|
||||
|
||||
generate_data(0, largest, test_data1);
|
||||
generate_data(1, largest, test_data2);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize GGML, ensures float conversion tables are initialized
|
||||
struct ggml_init_params ggml_params = {
|
||||
/* .mem_size = */ 1*1024,
|
||||
/* .mem_buffer = */ NULL,
|
||||
/* .no_alloc = */ true,
|
||||
};
|
||||
struct ggml_context * ctx = ggml_init(ggml_params);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < GGML_TYPE_COUNT; i++) {
|
||||
ggml_type type = (ggml_type) i;
|
||||
quantize_fns_t qfns = ggml_internal_get_quantize_fn(i);
|
||||
if (!params.include_types.empty() && std::find(params.include_types.begin(), params.include_types.end(), ggml_type_name(type)) == params.include_types.end()) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (qfns.quantize_row_q && qfns.dequantize_row_q) {
|
||||
printf("%s\n", ggml_type_name(type));
|
||||
|
||||
if (params.op_quantize_row_q_reference) {
|
||||
printf(" quantize_row_q_reference\n");
|
||||
for (size_t size : params.test_sizes) {
|
||||
printf(" %zu values (%.2f MB)\n", size, 4*size/(float)(1024*1024));
|
||||
auto quantize_fn = [&](void ) {
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q_reference(test_data1, test_q1, size);
|
||||
return test_q1[0];
|
||||
};
|
||||
size_t quantized_size = size / ggml_blck_size(type) * ggml_type_size(type);
|
||||
benchmark_function(size, quantized_size, quantize_fn);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (params.op_quantize_row_q) {
|
||||
printf(" quantize_row_q\n");
|
||||
for (size_t size : params.test_sizes) {
|
||||
printf(" %zu values (%.2f MB)\n", size, 4*size/(float)(1024*1024));
|
||||
auto quantize_fn = [&](void ) {
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(test_data1, test_q1, size);
|
||||
return test_q1[0];
|
||||
};
|
||||
size_t quantized_size = size / ggml_blck_size(type) * ggml_type_size(type);
|
||||
benchmark_function(size, quantized_size, quantize_fn);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (params.op_dequantize_row_q) {
|
||||
printf(" dequantize_row_q\n");
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(test_data1, test_q1, largest);
|
||||
for (size_t size : params.test_sizes) {
|
||||
printf(" %zu values (%.2f MB)\n", size, 4*size/(float)(1024*1024));
|
||||
auto quantize_fn = [&](void ) {
|
||||
qfns.dequantize_row_q(test_q1, test_out, size);
|
||||
return test_out[0];
|
||||
};
|
||||
size_t quantized_size = size / ggml_blck_size(type) * ggml_type_size(type);
|
||||
benchmark_function(size, quantized_size, quantize_fn);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (params.op_quantize_row_q_dot) {
|
||||
printf(" quantize_row_q_dot\n");
|
||||
for (size_t size : params.test_sizes) {
|
||||
printf(" %zu values (%.2f MB)\n", size, 4*size/(float)(1024*1024));
|
||||
auto quantize_fn = [&](void ) {
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q_dot(test_data1, test_q1, size);
|
||||
return test_q1[0];
|
||||
};
|
||||
size_t quantized_size = size / ggml_blck_size(type) * ggml_type_size(type);
|
||||
benchmark_function(size, quantized_size, quantize_fn);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (params.op_vec_dot_q) {
|
||||
printf(" vec_dot_q\n");
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(test_data1, test_q1, largest);
|
||||
qfns.quantize_row_q(test_data2, test_q2, largest);
|
||||
for (size_t size : params.test_sizes) {
|
||||
printf(" %zu values (%.2f MB)\n", size, 4*size/(float)(1024*1024));
|
||||
auto quantize_fn = [&](void ) {
|
||||
float result;
|
||||
qfns.vec_dot_q(size, &result, test_q1, test_q2);
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
};
|
||||
size_t quantized_size = size / ggml_blck_size(type) * ggml_type_size(type);
|
||||
benchmark_function(size, quantized_size, quantize_fn);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_free(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
|
|||
#include "ggml.h"
|
||||
#undef NDEBUG
|
||||
#include <assert.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main(void) {
|
||||
#define QK 32
|
||||
float src[QK];
|
||||
uint8_t dst[24];
|
||||
int64_t hist[16];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < QK; i++) {
|
||||
src[i] = (float)(i + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
size_t size = ggml_quantize_q4_0(src, dst, QK, QK, hist);
|
||||
assert(size == 20);
|
||||
float max_result = ((float *)dst)[0];
|
||||
float max_expected = src[31] / ((1 << 3) - 1);
|
||||
assert(max_result == max_expected);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < QK; i++) {
|
||||
uint8_t q4_result = (i % 2) ? (dst[sizeof(float) + i/2] >> 4) : (dst[sizeof(float) + i/2] & 0xF);
|
||||
uint8_t q4_expected = roundf(src[i] / max_expected) + 8;
|
||||
assert(q4_result == q4_expected);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
size = ggml_quantize_q4_1(src, dst, QK, QK, hist);
|
||||
assert(size == 24);
|
||||
float delta_result = ((float *)dst)[0];
|
||||
float delta_expected = (src[31] - src[0]) / ((1 << 4) - 1);
|
||||
assert(delta_result == delta_expected);
|
||||
float min_result = ((float *)dst)[1];
|
||||
float min_expected = src[0];
|
||||
assert(min_result == min_expected);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < QK; i++) {
|
||||
uint8_t q4_result = (i % 2) ? (dst[sizeof(float)*2 + i/2] >> 4) : (dst[sizeof(float)*2 + i/2] & 0xF);
|
||||
uint8_t q4_expected = roundf((src[i] - min_expected) / delta_expected);
|
||||
assert(q4_result == q4_expected);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,13 +5,17 @@
|
|||
#include <map>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
static const std::map<std::string, std::vector<llama_token>> k_tests = {
|
||||
{ "Hello World", { 1, 10994, 2787, }, },
|
||||
{ " Hello World", { 1, 15043, 2787, }, },
|
||||
{ " Hello World!", { 1, 15043, 2787, 29991, }, },
|
||||
{ " this is 🦙.cpp", { 1, 445, 338, 29871, 243, 162, 169, 156, 29889, 8223, }, },
|
||||
{ "w048 7tuijk dsdfhu", { 1, 29893, 29900, 29946, 29947, 29871, 29955, 9161, 13535, 18031, 2176, 6905, }, },
|
||||
{ "нещо на Български", { 1, 821, 4851, 665, 1386, 29713, 1305, }, },
|
||||
static const std::map<std::string, std::vector<llama_token>> & k_tests()
|
||||
{
|
||||
static std::map<std::string, std::vector<llama_token>> _k_tests = {
|
||||
{ "Hello World", { 1, 10994, 2787, }, },
|
||||
{ " Hello World", { 1, 15043, 2787, }, },
|
||||
{ " Hello World!", { 1, 15043, 2787, 29991, }, },
|
||||
{ " this is 🦙.cpp", { 1, 445, 338, 29871, 243, 162, 169, 156, 29889, 8223, }, },
|
||||
{ "w048 7tuijk dsdfhu", { 1, 29893, 29900, 29946, 29947, 29871, 29955, 9161, 13535, 18031, 2176, 6905, }, },
|
||||
{ "нещо на Български", { 1, 821, 4851, 665, 1386, 29713, 1305, }, },
|
||||
};
|
||||
return _k_tests;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,7 +51,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv) {
|
|||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (const auto & test_kv : k_tests) {
|
||||
for (const auto & test_kv : k_tests()) {
|
||||
std::vector<llama_token> res(test_kv.first.size());
|
||||
const int n = llama_tokenize(ctx, test_kv.first.c_str(), res.data(), res.size(), true);
|
||||
res.resize(n);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue