Merge 'origin/master' into hipblas
This commit is contained in:
commit
d571d1629f
14 changed files with 1141 additions and 893 deletions
10
.github/workflows/build.yml
vendored
10
.github/workflows/build.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -19,8 +19,8 @@ env:
|
|||
BRANCH_NAME: ${{ github.head_ref || github.ref_name }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
ubuntu-latest-make:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
ubuntu-focal-make:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-20.04
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Clone
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,12 +31,12 @@ jobs:
|
|||
id: depends
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install build-essential
|
||||
sudo apt-get install build-essential gcc-8
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build
|
||||
id: make_build
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
make
|
||||
CC=gcc-8 make
|
||||
|
||||
ubuntu-latest-cmake:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
|
@ -216,7 +216,7 @@ jobs:
|
|||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
needs:
|
||||
- ubuntu-latest-make
|
||||
- ubuntu-focal-make
|
||||
- ubuntu-latest-cmake
|
||||
- macOS-latest-make
|
||||
- macOS-latest-cmake
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
4
Makefile
4
Makefile
|
|
@ -109,9 +109,9 @@ ifdef LLAMA_CUBLAS
|
|||
LDFLAGS += -lcublas -lculibos -lcudart -lcublasLt -lpthread -ldl -lrt -L/usr/local/cuda/lib64
|
||||
OBJS += ggml-cuda.o
|
||||
NVCC = nvcc
|
||||
NVCCFLAGS = --forward-unknown-to-host-linker -arch=native
|
||||
NVCCFLAGS = --forward-unknown-to-host-compiler -arch=native
|
||||
ggml-cuda.o: ggml-cuda.cu ggml-cuda.h
|
||||
$(NVCC) $(NVCCFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) -c $< -o $@
|
||||
$(NVCC) $(NVCCFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) -Wno-pedantic -c $< -o $@
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifdef LLAMA_HIPBLAS
|
||||
ROCM_PATH ?= /opt/rocm
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
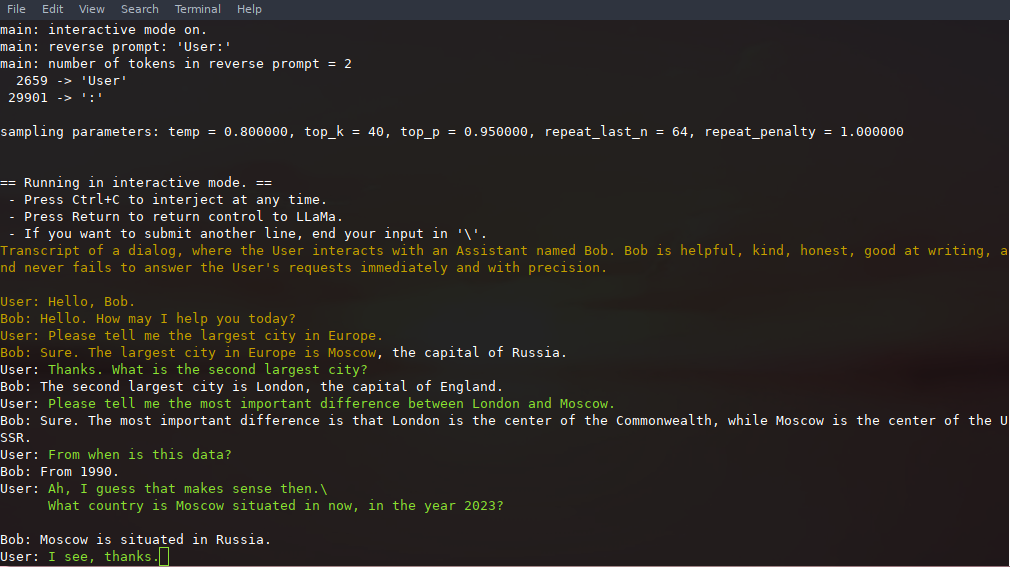
@ -241,7 +241,7 @@ Here is an example of a few-shot interaction, invoked with the command
|
|||
./main -m ./models/13B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -n 256 --repeat_penalty 1.0 --color -i -r "User:" -f prompts/chat-with-bob.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note the use of `--color` to distinguish between user input and generated text.
|
||||
Note the use of `--color` to distinguish between user input and generated text. Other parameters are explained in more detail in the [README](examples/main/README.md) for the `main` example program.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -34,4 +34,5 @@ else()
|
|||
add_subdirectory(quantize-stats)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(perplexity)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(embedding)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(save-load-state)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -156,10 +156,8 @@ bool gpt_params_parse(int argc, char ** argv, gpt_params & params) {
|
|||
params.interactive = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--embedding") {
|
||||
params.embedding = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--interactive-start") {
|
||||
params.interactive = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--interactive-first") {
|
||||
params.interactive_start = true;
|
||||
params.interactive_first = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "-ins" || arg == "--instruct") {
|
||||
params.instruct = true;
|
||||
} else if (arg == "--color") {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ struct gpt_params {
|
|||
bool interactive = false; // interactive mode
|
||||
|
||||
bool embedding = false; // get only sentence embedding
|
||||
bool interactive_start = false; // wait for user input immediately
|
||||
bool interactive_first = false; // wait for user input immediately
|
||||
|
||||
bool instruct = false; // instruction mode (used for Alpaca models)
|
||||
bool ignore_eos = false; // do not stop generating after eos
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,12 +21,20 @@ To get started right away, run the following command, making sure to use the cor
|
|||
./main -m models/7B/ggml-model.bin --prompt "Once upon a time"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following command generates "infinite" text from a starting prompt (you can use `Ctrl-C` to stop it):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./main -m models/7B/ggml-model.bin --ignore-eos --n_predict -1 --keep -1 --prompt "Once upon a time"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For an interactive experience, try this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./main -m models/7B/ggml-model.bin -n -1 --color -r "User:" --in-prefix " " --prompt $'User: Hi\nAI: Hello. I am an AI chatbot. Would you like to talk?\nUser: Sure!\nAI: What would you like to talk about?\nUser:'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the newline characters in the prompt string above only work on Linux. On Windows, you will have to use the ``--file`` option (see below) to load a multi-line prompt from file instead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Options
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we cover the most commonly used options for running the `main` program with the LLaMA models:
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,6 +92,8 @@ Instruction mode is particularly useful when working with Alpaca models, which a
|
|||
|
||||
- `-ins, --instruct`: Enable instruction mode to leverage the capabilities of Alpaca models in completing tasks based on user-provided instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
Technical detail: the user's input is internally prefixed with the reverse prompt (or ``### Instruction:`` as the default), and followed by ``### Response:`` (except if you just press Return without any input, to keep generating a longer response).
|
||||
|
||||
By understanding and utilizing these interaction options, you can create engaging and dynamic experiences with the LLaMA models, tailoring the text generation process to your specific needs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Context Management
|
||||
|
|
@ -114,7 +124,7 @@ The following options are related to controlling the text generation process, in
|
|||
|
||||
The `--n_predict` option controls the number of tokens the model generates in response to the input prompt. By adjusting this value, you can influence the length of the generated text. A higher value will result in longer text, while a lower value will produce shorter text. A value of -1 will cause text to be generated without limit.
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to note that the generated text may be shorter than the specified number of tokens if an End-of-Sequence (EOS) token or a reverse prompt is encountered. In interactive mode text generation will pause and control will be returned to the user. In non-interactive mode, the program will end. In both cases, the text generation may stop before reaching the specified `n_predict` value.
|
||||
It is important to note that the generated text may be shorter than the specified number of tokens if an End-of-Sequence (EOS) token or a reverse prompt is encountered. In interactive mode text generation will pause and control will be returned to the user. In non-interactive mode, the program will end. In both cases, the text generation may stop before reaching the specified `n_predict` value. If you want the model to keep going without ever producing End-of-Sequence on its own, you can use the ``--ignore-eos`` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
### RNG Seed
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -126,7 +136,7 @@ The RNG seed is used to initialize the random number generator that influences t
|
|||
|
||||
- `--temp N`: Adjust the randomness of the generated text (default: 0.8).
|
||||
|
||||
Temperature is a hyperparameter that controls the randomness of the generated text. It affects the probability distribution of the model's output tokens. A higher temperature (e.g., 1.5) makes the output more random and creative, while a lower temperature (e.g., 0.5) makes the output more focused, deterministic, and conservative. The default value is 0.8, which provides a balance between randomness and determinism.
|
||||
Temperature is a hyperparameter that controls the randomness of the generated text. It affects the probability distribution of the model's output tokens. A higher temperature (e.g., 1.5) makes the output more random and creative, while a lower temperature (e.g., 0.5) makes the output more focused, deterministic, and conservative. The default value is 0.8, which provides a balance between randomness and determinism. At the extreme, a temperature of 0 will always pick the most likely next token, leading to identical outputs in each run.
|
||||
|
||||
Example usage: `--temp 0.8`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -177,5 +187,5 @@ These options provide extra functionality and customization when running the LLa
|
|||
- `-h, --help`: Display a help message showing all available options and their default values. This is particularly useful for checking the latest options and default values, as they can change frequently, and the information in this document may become outdated.
|
||||
- `--verbose-prompt`: Print the prompt before generating text.
|
||||
- `--mtest`: Test the model's functionality by running a series of tests to ensure it's working properly.
|
||||
- `--lora FNAME`: Apply a LoRA (Layer-wise Relevance Approximation) adapter to the model (implies --no-mmap). This allows you to adapt the pretrained model to specific tasks or domains.
|
||||
- `--lora FNAME`: Apply a LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) adapter to the model (implies --no-mmap). This allows you to adapt the pretrained model to specific tasks or domains.
|
||||
- `--lora-base FNAME`: Optional model to use as a base for the layers modified by the LoRA adapter. This flag is used in conjunction with the `--lora` flag, and specifies the base model for the adaptation.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -178,12 +178,12 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
|
||||
// in instruct mode, we inject a prefix and a suffix to each input by the user
|
||||
if (params.instruct) {
|
||||
params.interactive_start = true;
|
||||
params.interactive_first = true;
|
||||
params.antiprompt.push_back("### Instruction:\n\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// enable interactive mode if reverse prompt or interactive start is specified
|
||||
if (params.antiprompt.size() != 0 || params.interactive_start) {
|
||||
if (params.antiprompt.size() != 0 || params.interactive_first) {
|
||||
params.interactive = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -246,7 +246,7 @@ int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
|||
#endif
|
||||
" - Press Return to return control to LLaMa.\n"
|
||||
" - If you want to submit another line, end your input in '\\'.\n\n");
|
||||
is_interacting = params.interactive_start;
|
||||
is_interacting = params.interactive_first;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool is_antiprompt = false;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
4
examples/save-load-state/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
4
examples/save-load-state/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
|||
set(TARGET save-load-state)
|
||||
add_executable(${TARGET} save-load-state.cpp)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(${TARGET} PRIVATE common llama ${CMAKE_THREAD_LIBS_INIT})
|
||||
target_compile_features(${TARGET} PRIVATE cxx_std_11)
|
||||
128
examples/save-load-state/save-load-state.cpp
Normal file
128
examples/save-load-state/save-load-state.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
|
|||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#include <chrono>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "common.h"
|
||||
#include "llama.h"
|
||||
#include "llama.cpp"
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std;
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
|
||||
gpt_params params;
|
||||
params.model = "models/llama-7B/ggml-model.bin";
|
||||
params.seed = 42;
|
||||
params.n_threads = 4;
|
||||
params.repeat_last_n = 64;
|
||||
params.prompt = "The quick brown fox";
|
||||
|
||||
if (gpt_params_parse(argc, argv, params) == false) {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto lparams = llama_context_default_params();
|
||||
|
||||
lparams.n_ctx = params.n_ctx;
|
||||
lparams.n_parts = params.n_parts;
|
||||
lparams.seed = params.seed;
|
||||
lparams.f16_kv = params.memory_f16;
|
||||
lparams.use_mmap = params.use_mmap;
|
||||
lparams.use_mlock = params.use_mlock;
|
||||
|
||||
auto n_past = 0;
|
||||
auto last_n_tokens_data = vector<llama_token>(params.repeat_last_n, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
// init
|
||||
auto ctx = llama_init_from_file(params.model.c_str(), lparams);
|
||||
auto tokens = vector<llama_token>(params.n_ctx);
|
||||
auto n_prompt_tokens = llama_tokenize(ctx, params.prompt.c_str(), tokens.data(), tokens.size(), true);
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_prompt_tokens < 1) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s : failed to tokenize prompt\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// evaluate prompt
|
||||
|
||||
llama_eval(ctx, tokens.data(), n_prompt_tokens, n_past, params.n_threads);
|
||||
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data.insert(last_n_tokens_data.end(), tokens.data(), tokens.data() + n_prompt_tokens);
|
||||
n_past += n_prompt_tokens;
|
||||
|
||||
// Save state (rng, logits, embedding and kv_cache) to file
|
||||
FILE *fp_write = fopen("dump_state.bin", "wb");
|
||||
auto state_size = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
auto state_mem = new uint8_t[state_size];
|
||||
llama_copy_state_data(ctx, state_mem); // could also copy directly to memory mapped file
|
||||
fwrite(state_mem, 1, state_size, fp_write);
|
||||
fclose(fp_write);
|
||||
|
||||
// save state (last tokens)
|
||||
auto last_n_tokens_data_saved = vector<llama_token>(last_n_tokens_data);
|
||||
auto n_past_saved = n_past;
|
||||
|
||||
// first run
|
||||
printf("\n%s", params.prompt.c_str());
|
||||
for (auto i = 0; i < params.n_predict; i++) {
|
||||
auto next_token = llama_sample_top_p_top_k(
|
||||
ctx,
|
||||
&last_n_tokens_data.back() - params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
40,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.1);
|
||||
auto next_token_str = llama_token_to_str(ctx, next_token);
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data.push_back(next_token);
|
||||
printf("%s", next_token_str);
|
||||
if (llama_eval(ctx, &next_token, 1, n_past, params.n_threads)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s : failed to evaluate\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
n_past += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n\n");
|
||||
|
||||
// free old model
|
||||
llama_free(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// load new model
|
||||
|
||||
auto ctx2 = llama_init_from_file(params.model.c_str(), lparams);
|
||||
|
||||
// Load state (rng, logits, embedding and kv_cache) from file
|
||||
FILE *fp_read = fopen("dump_state.bin", "rb");
|
||||
auto state_size2 = llama_get_state_size(ctx2);
|
||||
if (state_size != state_size2) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s : failed to validate state size\n", __func__);
|
||||
}
|
||||
fread(state_mem, 1, state_size, fp_read);
|
||||
llama_set_state_data(ctx2, state_mem); // could also read directly from memory mapped file
|
||||
fclose(fp_read);
|
||||
|
||||
// restore state (last tokens)
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data = last_n_tokens_data_saved;
|
||||
n_past = n_past_saved;
|
||||
|
||||
// second run
|
||||
for (auto i = 0; i < params.n_predict; i++) {
|
||||
auto next_token = llama_sample_top_p_top_k(
|
||||
ctx2,
|
||||
&last_n_tokens_data.back() - params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
params.repeat_last_n,
|
||||
40,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
1.1);
|
||||
auto next_token_str = llama_token_to_str(ctx2, next_token);
|
||||
last_n_tokens_data.push_back(next_token);
|
||||
printf("%s", next_token_str);
|
||||
if (llama_eval(ctx2, &next_token, 1, n_past, params.n_threads)) {
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s : failed to evaluate\n", __func__);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
n_past += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("\n\n");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
215
ggml.c
215
ggml.c
|
|
@ -436,7 +436,7 @@ static const size_t CACHE_LINE_SIZE_F32 = CACHE_LINE_SIZE/sizeof(float);
|
|||
static inline __m128i bytes_from_nibbles_16(const uint8_t * rsi)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Load 8 bytes from memory
|
||||
__m128i tmp = _mm_loadu_si64( ( const __m128i* )rsi );
|
||||
__m128i tmp = _mm_loadl_epi64( ( const __m128i* )rsi );
|
||||
|
||||
// Expand bytes into uint16_t values
|
||||
__m128i bytes = _mm_cvtepu8_epi16( tmp );
|
||||
|
|
@ -692,13 +692,17 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0_reference(const float * restrict x, block_q4_0 * r
|
|||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
float amax = 0.0f; // absolute max
|
||||
float max = 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK4_0; l++) {
|
||||
const float v = x[i*QK4_0 + l];
|
||||
amax = MAX(amax, fabsf(v));
|
||||
if (amax < fabsf(v)) {
|
||||
amax = fabsf(v);
|
||||
max = v;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = amax / ((1 << 3) - 1);
|
||||
const float d = max / -8;
|
||||
const float id = d ? 1.0f/d : 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i].d = d;
|
||||
|
|
@ -707,8 +711,8 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0_reference(const float * restrict x, block_q4_0 * r
|
|||
const float v0 = x[i*QK4_0 + l + 0]*id;
|
||||
const float v1 = x[i*QK4_0 + l + 1]*id;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t vi0 = (int8_t)roundf(v0) + 8;
|
||||
const uint8_t vi1 = (int8_t)roundf(v1) + 8;
|
||||
const uint8_t vi0 = MIN(15, (int8_t)roundf(v0) + 8);
|
||||
const uint8_t vi1 = MIN(15, (int8_t)roundf(v1) + 8);
|
||||
|
||||
assert(vi0 < 16);
|
||||
assert(vi1 < 16);
|
||||
|
|
@ -728,28 +732,42 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
|
||||
#if defined(__POWER9_VECTOR__)
|
||||
const vector float v85 = vec_splats(8.5f);
|
||||
const vector signed int v15 = vec_splats(15);
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
float amax = 0.0f; // absolute max
|
||||
float max = 0.0f;
|
||||
float min = 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
vector float srcv [8];
|
||||
vector float asrcv[8];
|
||||
vector float amaxv[8];
|
||||
vector float maxv[8];
|
||||
vector float minv[8];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) srcv[l] = *(vector float *)(x + i*32 + 4*l);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) asrcv[l] = vec_abs(srcv[l]);
|
||||
//for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) asrcv[l] = vec_abs(srcv[l]);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) amaxv[2*l] = vec_max(asrcv[2*l], asrcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
//for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) amaxv[4*l] = vec_max(amaxv[4*l], amaxv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
amaxv[0] = vec_max(amaxv[0], amaxv[2]);
|
||||
amaxv[4] = vec_max(amaxv[4], amaxv[6]);
|
||||
//for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) amaxv[8*l] = vec_max(amaxv[8*l], amaxv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
amaxv[0] = vec_max(amaxv[0], amaxv[4]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) maxv[2*l] = vec_max(asrcv[2*l], asrcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
//for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) maxv[4*l] = vec_max(maxv[4*l], maxv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
maxv[0] = vec_max(maxv[0], maxv[2]);
|
||||
maxv[4] = vec_max(maxv[4], maxv[6]);
|
||||
//for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) maxv[8*l] = vec_max(maxv[8*l], maxv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
maxv[0] = vec_max(maxv[0], maxv[4]);
|
||||
|
||||
amax = MAX(
|
||||
MAX(vec_extract(amaxv[0], 0), vec_extract(amaxv[0], 1)),
|
||||
MAX(vec_extract(amaxv[0], 2), vec_extract(amaxv[0], 3)));
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) minv[2*l] = vec_min(asrcv[2*l], asrcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
//for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) minv[4*l] = vec_min(minv[4*l], minv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
minv[0] = vec_min(minv[0], minv[2]);
|
||||
minv[4] = vec_min(minv[4], minv[6]);
|
||||
//for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) minv[8*l] = vec_min(minv[8*l], minv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
minv[0] = vec_min(minv[0], minv[4]);
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = amax / ((1 << 3) - 1);
|
||||
|
||||
max = MAX(
|
||||
MAX(vec_extract(maxv[0], 0), vec_extract(maxv[0], 1)),
|
||||
MAX(vec_extract(maxv[0], 2), vec_extract(maxv[0], 3)));
|
||||
min = MIN(
|
||||
MIN(vec_extract(minv[0], 0), vec_extract(minv[0], 1)),
|
||||
MIN(vec_extract(minv[0], 2), vec_extract(minv[0], 3)));
|
||||
|
||||
const float magnitude = max >= fabsf(min) ? max : min;
|
||||
const float d = magnitude / -8;
|
||||
const float id = d ? 1.0/d : 0.0;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i].d = d;
|
||||
|
|
@ -759,27 +777,33 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) {
|
||||
const vector float vf = vec_madd(srcv[l], vid, v85);
|
||||
const vector signed int vi = vec_signed(vf);
|
||||
const vector signed int vc = vec_min(vi, v15);
|
||||
|
||||
pb[2*l + 0] = vec_extract(vi, 0) | (vec_extract(vi, 1) << 4);
|
||||
pb[2*l + 1] = vec_extract(vi, 2) | (vec_extract(vi, 3) << 4);
|
||||
pb[2*l + 0] = vec_extract(vc, 0) | (vec_extract(vc, 1) << 4);
|
||||
pb[2*l + 1] = vec_extract(vc, 2) | (vec_extract(vc, 3) << 4);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#elif __ARM_NEON
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
float32x4_t srcv [8];
|
||||
float32x4_t asrcv[8];
|
||||
float32x4_t amaxv[8];
|
||||
float32x4_t maxv[8];
|
||||
float32x4_t minv[8];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) srcv[l] = vld1q_f32(x + i*32 + 4*l);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) asrcv[l] = vabsq_f32(srcv[l]);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) amaxv[2*l] = vmaxq_f32(asrcv[2*l], asrcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) amaxv[4*l] = vmaxq_f32(amaxv[4*l], amaxv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) amaxv[8*l] = vmaxq_f32(amaxv[8*l], amaxv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) maxv[2*l] = vmaxq_f32(srcv[2*l], srcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) maxv[4*l] = vmaxq_f32(maxv[4*l], maxv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) maxv[8*l] = vmaxq_f32(maxv[8*l], maxv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
|
||||
const float amax = vmaxvq_f32(amaxv[0]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) minv[2*l] = vminq_f32(srcv[2*l], srcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) minv[4*l] = vminq_f32(minv[4*l], minv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) minv[8*l] = vminq_f32(minv[8*l], minv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = amax / ((1 << 3) - 1);
|
||||
const float max = vmaxvq_f32(maxv[0]);
|
||||
const float min = vminvq_f32(minv[0]);
|
||||
|
||||
const float magnitude = max >= fabsf(min) ? max : min;
|
||||
const float d = magnitude / -8;
|
||||
const float id = d ? 1.0f/d : 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i].d = d;
|
||||
|
|
@ -788,9 +812,10 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
const float32x4_t v = vmulq_n_f32(srcv[l], id);
|
||||
const float32x4_t vf = vaddq_f32(v, vdupq_n_f32(8.5f));
|
||||
const int32x4_t vi = vcvtq_s32_f32(vf);
|
||||
const int32x4_t vc = vminq_s32(vi, vdupq_n_s32(15));
|
||||
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 0] = vgetq_lane_s32(vi, 0) | (vgetq_lane_s32(vi, 1) << 4);
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 1] = vgetq_lane_s32(vi, 2) | (vgetq_lane_s32(vi, 3) << 4);
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 0] = vgetq_lane_s32(vc, 0) | (vgetq_lane_s32(vc, 1) << 4);
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 1] = vgetq_lane_s32(vc, 2) | (vgetq_lane_s32(vc, 3) << 4);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVX2__)
|
||||
|
|
@ -802,22 +827,31 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
__m256 v3 = _mm256_loadu_ps( x + 24 );
|
||||
x += 32;
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute max(abs(e)) for the block
|
||||
const __m256 signBit = _mm256_set1_ps( -0.0f );
|
||||
__m256 maxAbs = _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v0 );
|
||||
maxAbs = _mm256_max_ps( maxAbs, _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v1 ) );
|
||||
maxAbs = _mm256_max_ps( maxAbs, _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v2 ) );
|
||||
maxAbs = _mm256_max_ps( maxAbs, _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v3 ) );
|
||||
// Compute max for the block
|
||||
__m256 max = _mm256_max_ps( v0, v1 );
|
||||
__m256 maxTmp = _mm256_max_ps( v2, v3 );
|
||||
max = _mm256_max_ps( max, maxTmp );
|
||||
|
||||
__m128 max4 = _mm_max_ps( _mm256_extractf128_ps( maxAbs, 1 ), _mm256_castps256_ps128( maxAbs ) );
|
||||
__m128 max4 = _mm_max_ps( _mm256_extractf128_ps( max, 1 ), _mm256_castps256_ps128( max ) );
|
||||
max4 = _mm_max_ps( max4, _mm_movehl_ps( max4, max4 ) );
|
||||
max4 = _mm_max_ss( max4, _mm_movehdup_ps( max4 ) );
|
||||
const float maxScalar = _mm_cvtss_f32( max4 );
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute min for the block
|
||||
__m256 min = _mm256_min_ps( v0, v1 );
|
||||
__m256 minTmp = _mm256_min_ps( v2, v3 );
|
||||
min = _mm256_min_ps( min, minTmp );
|
||||
|
||||
__m128 min4 = _mm_min_ps( _mm256_extractf128_ps( min, 1 ), _mm256_castps256_ps128( min ) );
|
||||
min4 = _mm_min_ps( min4, _mm_movehl_ps( min4, min4 ) );
|
||||
min4 = _mm_min_ss( min4, _mm_movehdup_ps( min4 ) );
|
||||
const float minScalar = _mm_cvtss_f32( min4 );
|
||||
|
||||
// Quantize these floats
|
||||
const float d = maxScalar / 7.0f;
|
||||
const float magnitude = maxScalar >= fabsf(minScalar) ? maxScalar : minScalar;
|
||||
const float d = magnitude / -8.0f;
|
||||
y[i].d = d;
|
||||
const float id = ( maxScalar != 0.0f ) ? 7.0f / maxScalar : 0.0f;
|
||||
const float id = ( magnitude != 0.0f ) ? -8.0f / magnitude : 0.0f;
|
||||
const __m256 mul = _mm256_set1_ps( id );
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply the multiplier
|
||||
|
|
@ -850,9 +884,11 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
const __m256i perm = _mm256_setr_epi32( 0, 4, 1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7 );
|
||||
i0 = _mm256_permutevar8x32_epi32( i0, perm );
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply offset to translate the range from [ -7 .. +7 ] into [ +1 .. +15 ]
|
||||
// Apply offset and clamp to translate the range from [ -8 .. +8 ] into [ +0 .. +15 ]
|
||||
const __m256i off = _mm256_set1_epi8( 8 );
|
||||
i0 = _mm256_add_epi8( i0, off );
|
||||
const __m256i maxNibble = _mm256_set1_epi8( 15 );
|
||||
i0 = _mm256_min_epi8( i0, maxNibble );
|
||||
|
||||
// Compress the vector into 4 bit/value, and store
|
||||
__m128i res = packNibbles( i0 );
|
||||
|
|
@ -867,22 +903,31 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
__m256 v3 = _mm256_loadu_ps( x + 24 );
|
||||
x += 32;
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute max(abs(e)) for the block
|
||||
const __m256 signBit = _mm256_set1_ps( -0.0f );
|
||||
__m256 maxAbs = _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v0 );
|
||||
maxAbs = _mm256_max_ps( maxAbs, _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v1 ) );
|
||||
maxAbs = _mm256_max_ps( maxAbs, _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v2 ) );
|
||||
maxAbs = _mm256_max_ps( maxAbs, _mm256_andnot_ps( signBit, v3 ) );
|
||||
// Compute max for the block
|
||||
__m256 max = _mm256_max_ps( v0, v1 );
|
||||
__m256 maxTmp = _mm256_max_ps( v2, v3 );
|
||||
max = _mm256_max_ps( max, maxTmp );
|
||||
|
||||
__m128 max4 = _mm_max_ps( _mm256_extractf128_ps( maxAbs, 1 ), _mm256_castps256_ps128( maxAbs ) );
|
||||
__m128 max4 = _mm_max_ps( _mm256_extractf128_ps( max, 1 ), _mm256_castps256_ps128( max ) );
|
||||
max4 = _mm_max_ps( max4, _mm_movehl_ps( max4, max4 ) );
|
||||
max4 = _mm_max_ss( max4, _mm_movehdup_ps( max4 ) );
|
||||
const float maxScalar = _mm_cvtss_f32( max4 );
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute min for the block
|
||||
__m256 min = _mm256_min_ps( v0, v1 );
|
||||
__m256 minTmp = _mm256_min_ps( v2, v3 );
|
||||
min = _mm256_min_ps( min, minTmp );
|
||||
|
||||
__m128 min4 = _mm_min_ps( _mm256_extractf128_ps( min, 1 ), _mm256_castps256_ps128( min ) );
|
||||
min4 = _mm_min_ps( min4, _mm_movehl_ps( min4, min4 ) );
|
||||
min4 = _mm_min_ss( min4, _mm_movehdup_ps( min4 ) );
|
||||
const float minScalar = _mm_cvtss_f32( min4 );
|
||||
|
||||
// Quantize these floats
|
||||
const float d = maxScalar / 7.0f;
|
||||
const float magnitude = maxScalar >= fabsf(minScalar) ? maxScalar : minScalar;
|
||||
const float d = magnitude / -8.0f;
|
||||
y[i].d = d;
|
||||
const float id = ( maxScalar != 0.0f ) ? 7.0f / maxScalar : 0.0f;
|
||||
const float id = ( magnitude != 0.0f ) ? -8.0f / magnitude : 0.0f;
|
||||
const __m256 mul = _mm256_set1_ps( id );
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply the multiplier
|
||||
|
|
@ -923,10 +968,13 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
ni0 = _mm_packs_epi16( ni0, ni2 );
|
||||
ni4 = _mm_packs_epi16( ni4, ni6 );
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply offset to translate the range from [ -7 .. +7 ] into [ +1 .. +15 ]
|
||||
const __m128i off = _mm_set1_epi8( 8);
|
||||
// Apply offset and clamp to translate the range from [ -8 .. +8 ] into [ +0 .. +15 ]
|
||||
const __m128i off = _mm_set1_epi8( 8 );
|
||||
ni0 = _mm_add_epi8( ni0, off );
|
||||
ni4 = _mm_add_epi8( ni4, off );
|
||||
const __m128i maxNibble = _mm_set1_epi8( 15 );
|
||||
ni0 = _mm_min_epi8( ni0, maxNibble );
|
||||
ni4 = _mm_min_epi8( ni4, maxNibble );
|
||||
|
||||
// Compress the vector into 4 bit/value, and store
|
||||
__m128i res = packNibbles( ni0, ni4 );
|
||||
|
|
@ -934,24 +982,32 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
}
|
||||
#elif defined(__wasm_simd128__)
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
float amax = 0.0f; // absolute max
|
||||
float max = 0.0f;
|
||||
float min = 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
v128_t srcv [8];
|
||||
v128_t asrcv[8];
|
||||
v128_t amaxv[8];
|
||||
v128_t maxv[8];
|
||||
v128_t minv[8];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) srcv[l] = wasm_v128_load(x + i*32 + 4*l);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 8; l++) asrcv[l] = wasm_f32x4_abs(srcv[l]);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) amaxv[2*l] = wasm_f32x4_max(asrcv[2*l], asrcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) amaxv[4*l] = wasm_f32x4_max(amaxv[4*l], amaxv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) amaxv[8*l] = wasm_f32x4_max(amaxv[8*l], amaxv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) maxv[2*l] = wasm_f32x4_max(srcv[2*l], srcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) maxv[4*l] = wasm_f32x4_max(maxv[4*l], maxv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) maxv[8*l] = wasm_f32x4_max(maxv[8*l], maxv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
|
||||
amax = MAX(
|
||||
MAX(wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(amaxv[0], 0), wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(amaxv[0], 1)),
|
||||
MAX(wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(amaxv[0], 2), wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(amaxv[0], 3)));
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) minv[2*l] = wasm_f32x4_min(srcv[2*l], srcv[2*l+1]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 2; l++) minv[4*l] = wasm_f32x4_min(minv[4*l], minv[4*l+2]);
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < 1; l++) minv[8*l] = wasm_f32x4_min(minv[8*l], minv[8*l+4]);
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = amax / ((1 << 3) - 1);
|
||||
max = MAX(
|
||||
MAX(wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(maxv[0], 0), wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(maxv[0], 1)),
|
||||
MAX(wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(maxv[0], 2), wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(maxv[0], 3)));
|
||||
min = MIN(
|
||||
MIN(wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(minv[0], 0), wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(minv[0], 1)),
|
||||
MIN(wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(minv[0], 2), wasm_f32x4_extract_lane(minv[0], 3)));
|
||||
|
||||
const float magnitude = max >= fabsf(min) ? max : min;
|
||||
const float d = magnitude / -8;
|
||||
const float id = d ? 1.0/d : 0.0;
|
||||
|
||||
y[i].d = d;
|
||||
|
|
@ -960,9 +1016,10 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_0(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
const v128_t v = wasm_f32x4_mul(srcv[l], wasm_f32x4_splat(id));
|
||||
const v128_t vf = wasm_f32x4_add(v, wasm_f32x4_splat(8.5f));
|
||||
const v128_t vi = wasm_i32x4_trunc_sat_f32x4(vf);
|
||||
const v128_t vc = wasm_i32x4_min_u(vi, wasm_i32x4_splat(15));
|
||||
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 0] = wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vi, 0) | (wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vi, 1) << 4);
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 1] = wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vi, 2) | (wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vi, 3) << 4);
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 0] = wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vc, 0) | (wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vc, 1) << 4);
|
||||
y[i].qs[2*l + 1] = wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vc, 2) | (wasm_i32x4_extract_lane(vc, 3) << 4);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
|
@ -1143,13 +1200,17 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_2_reference(const float * restrict x, block_q4_2 * r
|
|||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
float amax = 0.0f; // absolute max
|
||||
float max = 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK4_2; l++) {
|
||||
const float v = x[i*QK4_2 + l];
|
||||
amax = MAX(amax, fabsf(v));
|
||||
if (amax < fabsf(v)) {
|
||||
amax = fabsf(v);
|
||||
max = v;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const float d = amax / ((1 << 3) - 1);
|
||||
const float d = max / -8;
|
||||
|
||||
const float id = d ? 1.0f/d : 0.0f;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1159,8 +1220,8 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_2_reference(const float * restrict x, block_q4_2 * r
|
|||
const float v0 = x[i*QK4_2 + l + 0]*id;
|
||||
const float v1 = x[i*QK4_2 + l + 1]*id;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t vi0 = (uint8_t)(v0 + 8.5f);
|
||||
const uint8_t vi1 = (uint8_t)(v1 + 8.5f);
|
||||
const uint8_t vi0 = MIN(15, (uint8_t)(v0 + 8.5f));
|
||||
const uint8_t vi1 = MIN(15, (uint8_t)(v1 + 8.5f));
|
||||
|
||||
assert(vi0 < 16);
|
||||
assert(vi1 < 16);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1254,9 +1315,7 @@ static void quantize_row_q4_2(const float * restrict x, void * restrict vy, int
|
|||
|
||||
block_q4_2 * restrict y = vy;
|
||||
|
||||
//quantize_row_q4_2_reference(x, y, k);
|
||||
// This produces the exact same format, just better match to the input floats ("better" as measured by RMSE)
|
||||
quantize_row_q4_2_rmse(x, y, k);
|
||||
quantize_row_q4_2_reference(x, y, k);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void quantize_row_q4_3_reference(const float * restrict x, block_q4_3 * restrict y, int k) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1807,7 +1866,7 @@ static const quantize_fns_t quantize_fns[GGML_TYPE_COUNT] = {
|
|||
[GGML_TYPE_Q4_2] = {
|
||||
.dequantize_row_q = dequantize_row_q4_2,
|
||||
.quantize_row_q = quantize_row_q4_2,
|
||||
.quantize_row_q_reference = (quantize_row_q_t) quantize_row_q4_2_rmse, //quantize_row_q4_2_reference,
|
||||
.quantize_row_q_reference = (quantize_row_q_t) quantize_row_q4_2_reference,
|
||||
.quantize_row_q_dot = quantize_row_q8_0,
|
||||
.vec_dot_q = ggml_vec_dot_q4_2_q8_0,
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
|
@ -6779,15 +6838,20 @@ static void ggml_compute_forward_sum_f32(
|
|||
const size_t nb02 = src0->nb[2];
|
||||
const size_t nb03 = src0->nb[3];
|
||||
|
||||
ggml_float sum = 0;
|
||||
float row_sum = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int64_t i03 = 0; i03 < ne03; i03++) {
|
||||
for (int64_t i02 = 0; i02 < ne02; i02++) {
|
||||
for (int64_t i01 = 0; i01 < ne01; i01++) {
|
||||
ggml_vec_sum_f32(ne00,
|
||||
(float *) (dst->data),
|
||||
&row_sum,
|
||||
(float *) ((char *) src0->data + i01*nb01 + i02*nb02 + i03*nb03));
|
||||
sum += row_sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
((float *) dst->data)[0] = sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void ggml_compute_forward_sum(
|
||||
|
|
@ -12138,8 +12202,7 @@ size_t ggml_quantize_q4_2(const float * src, void * dst, int n, int k, int64_t *
|
|||
for (int j = 0; j < n; j += k) {
|
||||
block_q4_2 * restrict y = (block_q4_2 *)dst + j/QK4_2;
|
||||
|
||||
//quantize_row_q4_2_reference(src + j, y, k);
|
||||
quantize_row_q4_2_rmse(src + j, y, k);
|
||||
quantize_row_q4_2_reference(src + j, y, k);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < QK4_2; l += 2) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
327
llama.cpp
327
llama.cpp
|
|
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ static const std::map<e_model, size_t> & MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0()
|
|||
{ MODEL_7B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 1024ull * MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
return _MEM_REQ_SCRATCH0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ static const std::map<e_model, size_t> & MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1()
|
|||
{ MODEL_7B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_13B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_30B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 512ull * MB },
|
||||
{ MODEL_65B, 1024ull * MB },
|
||||
};
|
||||
return _MEM_REQ_SCRATCH1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -2072,35 +2072,191 @@ int llama_apply_lora_from_file(struct llama_context * ctx, const char * path_lor
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the KV cache that will contain the context for the
|
||||
// ongoing prediction with the model.
|
||||
const uint8_t * llama_get_kv_cache(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size of the KV cache
|
||||
size_t llama_get_kv_cache_size(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int llama_get_kv_cache_token_count(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx->model.kv_self.n;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sets the KV cache containing the current context for the model
|
||||
void llama_set_kv_cache(
|
||||
struct llama_context * ctx,
|
||||
const uint8_t * kv_cache,
|
||||
size_t n_size,
|
||||
int n_token_count) {
|
||||
// Make sure we have the same kv cache setup
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size == n_size);
|
||||
void * k_data = ctx->model.kv_self.k->data; // remember data pointers
|
||||
void * v_data = ctx->model.kv_self.v->data; // because their value is stored in buf and overwritten by memcpy
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr, kv_cache, n_size);
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.k->data = k_data; // restore correct data pointers
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.v->data = v_data;
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.n = n_token_count;
|
||||
#define LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE 64*1024
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size of the state
|
||||
size_t llama_get_state_size(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
// we don't know size of rng until we actually serialize it. so reserve more than enough memory for its serialized state.
|
||||
// for reference, std::mt19937(1337) serializes to 6701 bytes.
|
||||
const size_t s_rng_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_rng = LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE;
|
||||
const size_t s_logits_capacity = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_logits_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_logits = ctx->logits.capacity() * sizeof(float);
|
||||
const size_t s_embedding_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_embedding = ctx->embedding.size() * sizeof(float);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv_ntok = sizeof(int);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv = ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size;
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t s_total = (
|
||||
+ s_rng_size
|
||||
+ s_rng
|
||||
+ s_logits_capacity
|
||||
+ s_logits_size
|
||||
+ s_logits
|
||||
+ s_embedding_size
|
||||
+ s_embedding
|
||||
+ s_kv_size
|
||||
+ s_kv_ntok
|
||||
+ s_kv
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
return s_total;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copies the state to the specified destination address
|
||||
size_t llama_copy_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, uint8_t * dest) {
|
||||
uint8_t * out = dest;
|
||||
|
||||
// copy rng
|
||||
{
|
||||
std::stringstream rng_ss;
|
||||
rng_ss << ctx->rng;
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t rng_size = rng_ss.str().size();
|
||||
char rng_buf[LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE];
|
||||
|
||||
memset(&rng_buf[0], 0, LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE);
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_buf[0], rng_ss.str().data(), rng_ss.str().size());
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &rng_size, sizeof(rng_size)); out += sizeof(rng_size);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &rng_buf[0], LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE); out += LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy logits
|
||||
{
|
||||
const size_t logits_cap = ctx->logits.capacity();
|
||||
const size_t logits_size = ctx->logits.size();
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &logits_cap, sizeof(logits_cap)); out += sizeof(logits_cap);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &logits_size, sizeof(logits_size)); out += sizeof(logits_size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (logits_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->logits.data(), logits_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
out += logits_cap * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy embeddings
|
||||
{
|
||||
const size_t embedding_size = ctx->embedding.size();
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &embedding_size, sizeof(embedding_size)); out += sizeof(embedding_size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (embedding_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->embedding.data(), embedding_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
out += embedding_size * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy kv cache
|
||||
{
|
||||
const size_t kv_size = ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size;
|
||||
const int kv_ntok = llama_get_kv_cache_token_count(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(out, &kv_size, sizeof(kv_size)); out += sizeof(kv_size);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &kv_ntok, sizeof(kv_ntok)); out += sizeof(kv_ntok);
|
||||
|
||||
if (kv_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr, kv_size); out += kv_size;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t written = out - dest;
|
||||
const size_t expected = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(written == expected);
|
||||
|
||||
return written;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sets the state reading from the specified source address
|
||||
size_t llama_set_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, const uint8_t * src) {
|
||||
const uint8_t * in = src;
|
||||
|
||||
// set rng
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t rng_size;
|
||||
char rng_buf[LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE];
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_size, in, sizeof(rng_size)); in += sizeof(rng_size);
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_buf[0], in, LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE); in += LLAMA_MAX_RNG_STATE;
|
||||
|
||||
std::stringstream rng_ss;
|
||||
rng_ss.str(std::string(&rng_buf[0], rng_size));
|
||||
rng_ss >> ctx->rng;
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(rng_ss.fail() == false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set logits
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t logits_cap;
|
||||
size_t logits_size;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&logits_cap, in, sizeof(logits_cap)); in += sizeof(logits_cap);
|
||||
memcpy(&logits_size, in, sizeof(logits_size)); in += sizeof(logits_size);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->logits.capacity() == logits_cap);
|
||||
|
||||
if (logits_size) {
|
||||
ctx->logits.resize(logits_size);
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->logits.data(), in, logits_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
in += logits_cap * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set embeddings
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t embedding_size;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&embedding_size, in, sizeof(embedding_size)); in += sizeof(embedding_size);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->embedding.capacity() == embedding_size);
|
||||
|
||||
if (embedding_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->embedding.data(), in, embedding_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
in += embedding_size * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set kv cache
|
||||
{
|
||||
size_t kv_size;
|
||||
int kv_ntok;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&kv_size, in, sizeof(kv_size)); in += sizeof(kv_size);
|
||||
memcpy(&kv_ntok, in, sizeof(kv_ntok)); in += sizeof(kv_ntok);
|
||||
|
||||
if (kv_size) {
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size == kv_size);
|
||||
|
||||
void * k_data = ctx->model.kv_self.k->data; // remember data pointers
|
||||
void * v_data = ctx->model.kv_self.v->data; // because their value is stored in buf and overwritten by memcpy
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr, in, kv_size); in += kv_size;
|
||||
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.k->data = k_data; // restore correct data pointers
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.v->data = v_data;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.n = kv_ntok;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const size_t nread = in - src;
|
||||
const size_t expected = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(nread == expected);
|
||||
|
||||
return nread;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int llama_eval(
|
||||
|
|
@ -2256,120 +2412,3 @@ std::vector<std::pair<std::string, struct ggml_tensor *>>& llama_internal_get_te
|
|||
return ctx->model.tensors_by_name;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size of the state
|
||||
size_t llama_get_state_size(struct llama_context * ctx) {
|
||||
// we don't know size of rng until we actually serialize it. so reserve more than enough memory for its serialized state.
|
||||
// for reference, std::mt19937(1337) serializes to 6701 bytes.
|
||||
const size_t s_rng_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_rng = 64*1024;
|
||||
const size_t s_logits_capacity = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_logits_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_logits = ctx->logits.capacity() * sizeof(float);
|
||||
const size_t s_embedding_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_embedding = ctx->embedding.size() * sizeof(float);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv_size = sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv_ntok = sizeof(int);
|
||||
const size_t s_kv = llama_get_kv_cache_size(ctx);
|
||||
const size_t s_total = (
|
||||
+ s_rng_size
|
||||
+ s_rng
|
||||
+ s_logits_capacity
|
||||
+ s_logits_size
|
||||
+ s_logits
|
||||
+ s_embedding_size
|
||||
+ s_embedding
|
||||
+ s_kv_size
|
||||
+ s_kv_ntok
|
||||
+ s_kv
|
||||
);
|
||||
return s_total;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copies the state to the specified destination address
|
||||
size_t llama_copy_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, uint8_t * dest) {
|
||||
std::stringstream rng_ss;
|
||||
rng_ss << ctx->rng;
|
||||
const size_t rng_size = rng_ss.str().size();
|
||||
char rng_buf[64*1024];
|
||||
memset(&rng_buf[0], 0, 64*1024);
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_buf[0], rng_ss.str().data(), rng_ss.str().size());
|
||||
const size_t logits_capacity = ctx->logits.capacity();
|
||||
const size_t logits_size = ctx->logits.size();
|
||||
const size_t embedding_size = ctx->embedding.size();
|
||||
const size_t kv_size = llama_get_kv_cache_size(ctx);
|
||||
const int kv_ntok = llama_get_kv_cache_token_count(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t * out = dest;
|
||||
memcpy(out, &rng_size, sizeof(size_t)); out += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &rng_buf[0], 64*1024); out += 64*1024;
|
||||
memcpy(out, &logits_capacity, sizeof(size_t)); out += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &logits_size, sizeof(size_t)); out += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
if (logits_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->logits.data(), logits_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
}
|
||||
out += logits_capacity * sizeof(float);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &embedding_size, sizeof(size_t)); out += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
if (embedding_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, ctx->embedding.data(), embedding_size * sizeof(float)); out += embedding_size * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
memcpy(out, &kv_size, sizeof(size_t)); out += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
memcpy(out, &kv_ntok, sizeof(int)); out += sizeof(int);
|
||||
if (kv_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(out, llama_get_kv_cache(ctx), kv_size); out += kv_size;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const size_t written = out - dest;
|
||||
const size_t expected = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(written == expected);
|
||||
return written;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sets the state reading from the specified source address
|
||||
size_t llama_set_state_data(struct llama_context * ctx, const uint8_t * src) {
|
||||
size_t rng_size;
|
||||
char rng_buf[64*1024];
|
||||
std::stringstream rng_ss;
|
||||
|
||||
const uint8_t * in = src;
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_size, in, sizeof(size_t)); in += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
memcpy(&rng_buf[0], in, 64*1024); in += 64*1024;
|
||||
rng_ss.str(std::string(&rng_buf[0], rng_size));
|
||||
rng_ss >> ctx->rng;
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(rng_ss.fail() == false);
|
||||
|
||||
size_t logits_capacity;
|
||||
size_t logits_size;
|
||||
size_t embedding_size;
|
||||
size_t kv_size;
|
||||
int kv_ntok;
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(&logits_capacity, in, sizeof(size_t)); in += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
memcpy(&logits_size, in, sizeof(size_t)); in += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->logits.capacity() == logits_capacity);
|
||||
if (logits_size) {
|
||||
ctx->logits.resize(logits_size);
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->logits.data(), in, logits_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
}
|
||||
in += logits_capacity * sizeof(float);
|
||||
memcpy(&embedding_size, in, sizeof(size_t)); in += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->embedding.capacity() == embedding_size);
|
||||
if (embedding_size) {
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->embedding.data(), in, embedding_size * sizeof(float));
|
||||
in += embedding_size * sizeof(float);
|
||||
}
|
||||
memcpy(&kv_size, in, sizeof(size_t)); in += sizeof(size_t);
|
||||
memcpy(&kv_ntok, in, sizeof(int)); in += sizeof(int);
|
||||
if (kv_size) {
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.size == kv_size);
|
||||
void * k_data = ctx->model.kv_self.k->data; // remember data pointers
|
||||
void * v_data = ctx->model.kv_self.v->data; // because their value is stored in buf and overwritten by memcpy
|
||||
memcpy(ctx->model.kv_self.buf.addr, in, kv_size);
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.k->data = k_data; // restore correct data pointers
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.v->data = v_data;
|
||||
in += kv_size;
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx->model.kv_self.n = kv_ntok;
|
||||
const size_t nread = in - src;
|
||||
const size_t expected = llama_get_state_size(ctx);
|
||||
LLAMA_ASSERT(nread == expected);
|
||||
return nread;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
14
llama.h
14
llama.h
|
|
@ -112,23 +112,9 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
const char * path_base_model,
|
||||
int n_threads);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the KV cache that will contain the context for the
|
||||
// ongoing prediction with the model.
|
||||
LLAMA_API const uint8_t * llama_get_kv_cache(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size of the KV cache
|
||||
LLAMA_API size_t llama_get_kv_cache_size(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the number of tokens in the KV cache
|
||||
LLAMA_API int llama_get_kv_cache_token_count(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
// Sets the KV cache containing the current context for the model
|
||||
LLAMA_API void llama_set_kv_cache(
|
||||
struct llama_context * ctx,
|
||||
const uint8_t * kv_cache,
|
||||
size_t n_size,
|
||||
int n_token_count);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the size in bytes of the state (rng, logits, embedding and kv_cache)
|
||||
LLAMA_API size_t llama_get_state_size(struct llama_context * ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue