|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| docs | ||
| img | ||
| istio-manifests | ||
| kubernetes-manifests | ||
| pb | ||
| src | ||
| tests/cartservice | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| cloudbuild.yaml | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| skaffold.yaml | ||
Hipster Shop: Cloud-Native Microservices Demo Application
This project contains a 10-tier microservices application. The application is a web-based e-commerce app called “Hipster Shop” where users can browse items, add them to the cart, and purchase them.
Google uses this application to demonstrate Kubernetes, GKE, Istio, Stackdriver, gRPC and similar cloud-native technologies nowadays.
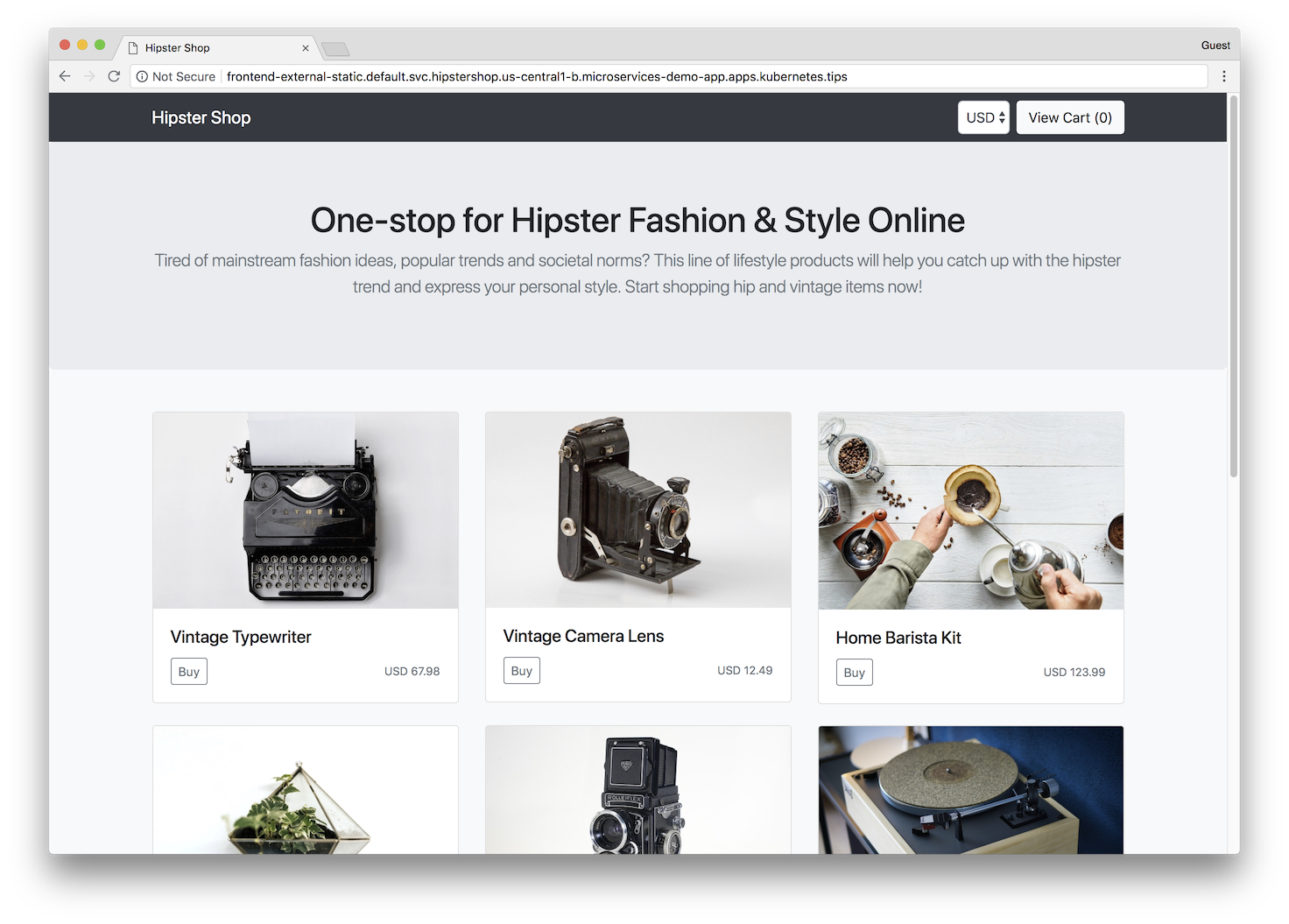
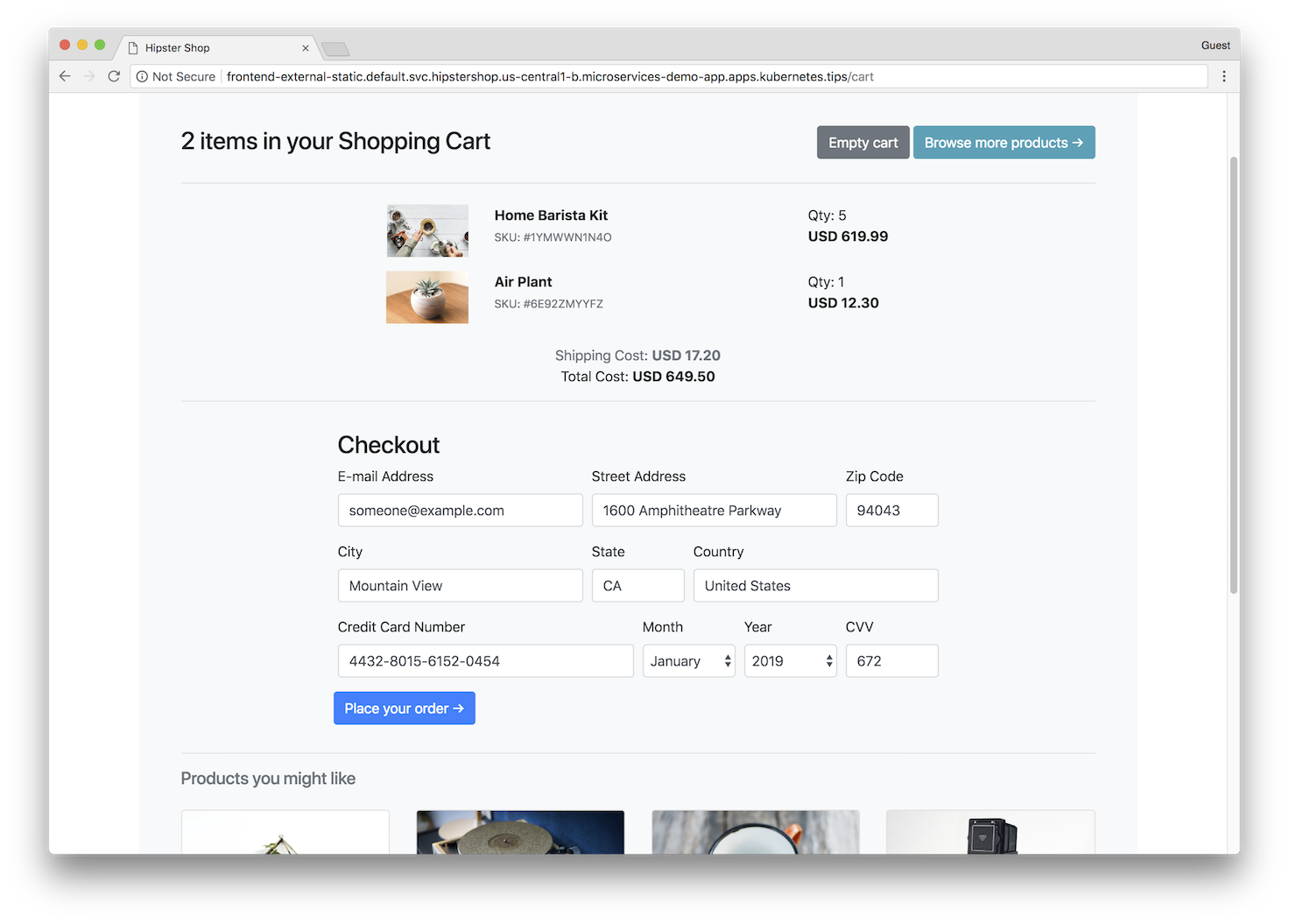
Screenshots
| Home Page | Checkout Screen |
|---|---|
 |
 |
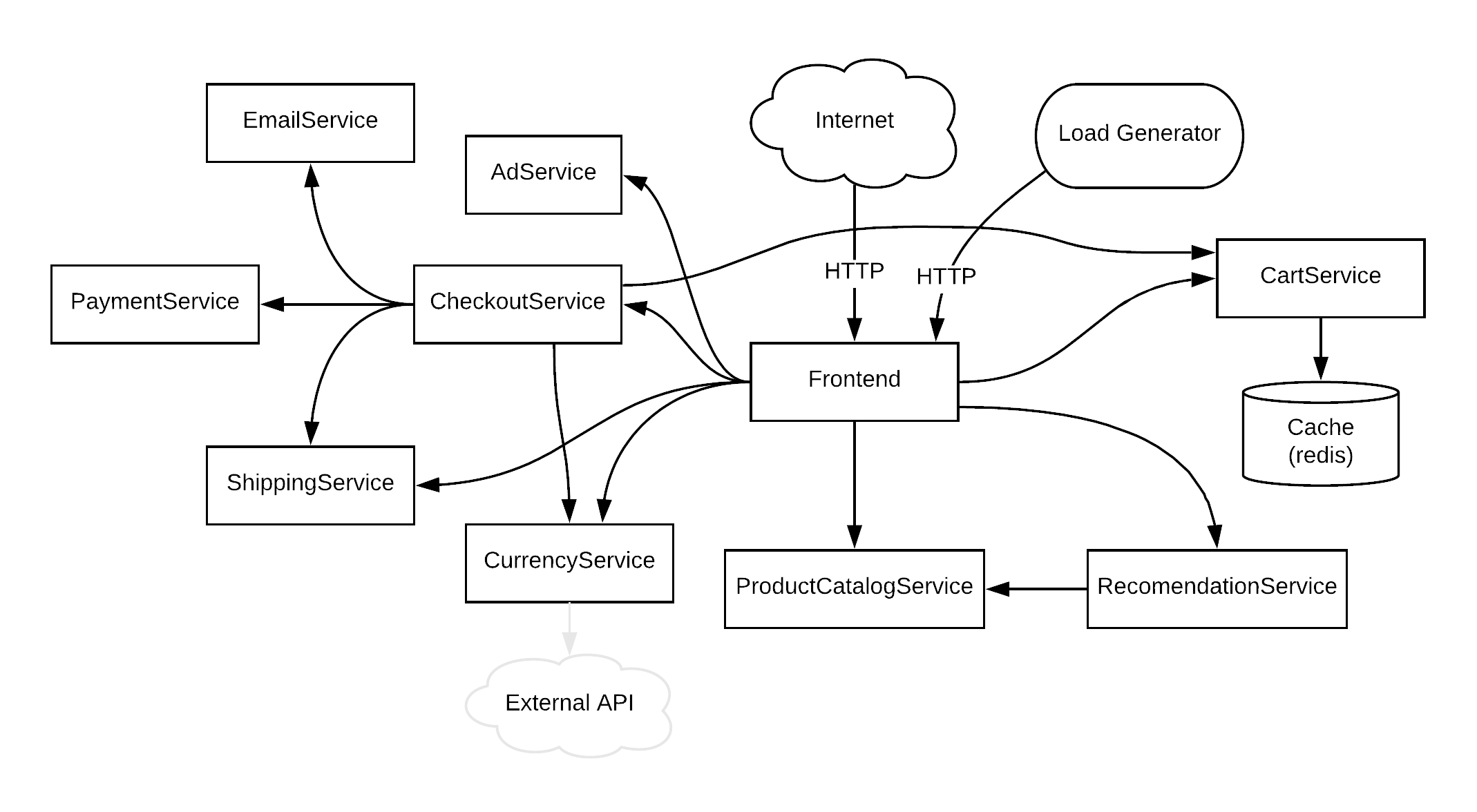
Service Architecture
Hipster Shop is composed of many microservices written in different languages that talk to each other over gRPC.
Find Protocol Buffers Descriptions at the ./pb directory.
| Service | Language | Description |
|---|---|---|
| frontend | Go | Exposes an HTTP server to serve the website. Does not require signup/login and generates session IDs for all users automatically. |
| cartservice | C# | Stores the items in the user's shipping cart in Redis and retrieves it. |
| productcatalogservice | Go | Provides the list of products from a JSON file and ability to search products and get individual products. |
| currencyservice | Node.js | Converts one money amount to another currency. Uses real values fetched from European Central Bank. It's the highest QPS service. |
| paymentservice | Node.js | Charges the given credit card info (hypothetically😇) with the given amount and returns a transaction ID. |
| shippingservice | Go | Gives shipping cost estimates based on the shopping cart. Ships items to the given address (hypothetically😇) |
| emailservice | Python | Sends users an order confirmation email (hypothetically😇). |
| checkoutservice | Go | Retrieves user cart, prepares order and orchestrates the payment, shipping and the email notification. |
| recommendationservice | Python | Recommends other products based on what's given in the cart. |
| adservice | Java | Provides text ads based on given context words. |
| loadgenerator | Python/Locust | Continuously sends requests imitating realistic user shopping flows to the frontend. |
Features
- Kubernetes/GKE: The app is designed to run on Kubernetes (both locally on "Docker for Desktop", as well as on the cloud with GKE).
- gRPC: Microservices use a high volume of gRPC calls to communicate to each other.
- Istio: Application works on Istio service mesh.
- OpenCensus Tracing: Most services are instrumented using OpenCensus trace interceptors for gRPC/HTTP.
- Stackdriver APM: Many services are instrumented with Profiling, Tracing and Debugging. In addition to these, using Istio enables features like Request/Response Metrics and Context Graph out of the box. When it is running out of Google Cloud, this code path remains inactive.
- Skaffold: Application is deployed to Kubernetes with a single command using Skaffold.
- Synthetic Load Generation: The application demo comes with a background job that creates realistic usage patterns on the website using Locust load generator.
Installation
Note: that the first build can take up to 20-30 minutes. Consequent builds will be faster.
Option 1: Running locally with “Docker for Desktop”
💡 Recommended if you're planning to develop the application.
-
Install tools to run a Kubernetes cluster locally:
- kubectl (can be installed via
gcloud components install kubectl) - Docker for Desktop (Mac/Windows): It provides Kubernetes support as noted here.
- skaffold
- kubectl (can be installed via
-
Launch “Docker for Desktop”. Go to Preferences and choose “Enable Kubernetes”.
-
Run
kubectl get nodesto verify you're connected to “Kubernetes on Docker”. -
Run
skaffold run(first time will be slow, it can take ~20-30 minutes). This will build and deploy the application. If you need to rebuild the images automatically as you refactor he code, runskaffold devcommand. -
Run
kubectl get podsto verify the Pods are ready and running. The application frontend should be available at http://localhost:80 on your machine.
Option 2: Running on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
💡 Recommended for demos and making it available publicly.
-
Install tools specified in the previous section (Docker, kubectl, skaffold)
-
Create a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster and make sure
kubectlis pointing to the cluster.gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com gcloud container clusters create demo --enable-autoupgrade \ --enable-autoscaling --min-nodes=3 --max-nodes=10 --num-nodes=5 kubectl get nodes -
Enable Google Container Registry (GCR) on your GCP project and configure the
dockerCLI to authenticate to GCR:gcloud services enable containerregistry.googleapis.com gcloud auth configure-docker -q -
Set your project ID on image names:
-
Edit
skaffold.yaml, update theimageName:fields that look likegcr.io/[PROJECT_ID]with your own GCP project ID. -
Similarly, edit all Kubernetes Deployment manifests in the
./kubernetes-manifestsdirectory. Find theimage:fields withgcr.io/[...]and change them to your own GCP project ID.
-
-
Run
skaffold runfrom the root of this repository. This command:- builds the container images
- pushes them to GCR
- applies the
./kubernetes-manifestsdeploying the application to Kubernetes.
Troubleshooting: If you get "No space left on device" error on Google Cloud Shell, you can build the images on Google Cloud Build: Enable the Cloud Build API, then run
skaffold run -p gcbinstead. -
Find the IP address of your application, then visit the application on your browser to confirm installation.
kubectl get service frontend-externalTroubleshooting: A Kubernetes bug (will be fixed in 1.12) combined with a Skaffold bug causes load balancer to not to work even after getting an IP address. If you are seeing this, run
kubectl get service frontend-external -o=yaml | kubectl apply -f-to trigger load balancer reconfiguration.
(Optional) Deploying on a Istio-installed cluster
Note: you followed GKE deployment steps above, run
skaffold deletefirst to delete what's deployed.
-
Create a GKE cluster.
-
Install Istio without mutual TLS authentication option.
(Optional) If you'd like to enable mTLS in the demo app, you need to make a few changes to the deployment manifests:
kubernetes-manifests/frontend.yaml: delete "livenessProbe" and "readinessProbe" fields.kubernetes-manifests/loadgenerator.yaml: delete "initContainers" field.
-
Install the automatic sidecar injection (annotate the
defaultnamespace with the label):kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled -
Apply the manifests in
./istio-manifestsdirectory.kubectl apply -f ./istio-manifestsThis is required only once.
-
Deploy the application with
skaffold run. -
Run
kubectl get podsto see pods are in a healthy and ready state. -
Find the IP address of your istio gateway Ingress or Service, and visit the application.
INGRESS_HOST="$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')" echo "$INGRESS_HOST" curl -v "http://$INGRESS_HOST"
Note to fellow Googlers: Please fill out the form at go/microservices-demo if you are using this application.
This is not an official Google project.