| openshift/templates | ||
| views | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
| server.js | ||
Node.js sample app on OpenShift!
This example will serve a welcome page and the current hit count as stored in a database to http://host:8080.
OpenShift setup
One option is to use the Docker all-in-one launch as described in the origins project.
The project
If you don't have a project setup all ready, go ahead and take care of that
$ oc new-project nodejs-echo --display-name="nodejs" --description="Sample Node.js app"
That's it, project has been created. Though it would probably be good to set your current project to this (thought new-project does it automatically as well), such as:
$ oc project nodejs
The app
Now let's pull in the app source code from GitHub repo (fork if you like)
create
$ oc new-app https://github.com/openshift/nodejs-ex -l name=myapp
That should be it, new-app will take care of creating the right build configuration, deployment configuration and service definition. Next you'll be able to kick off the build. The -l flag will apply a label of "name=myapp" to all the resources created by new-app, for easy management later.
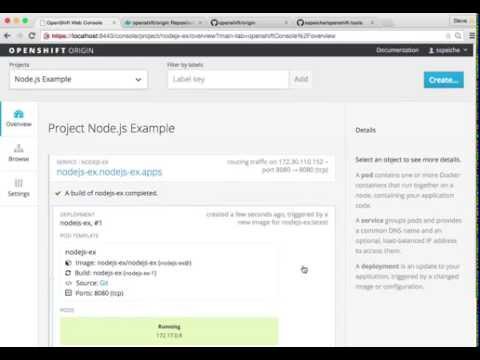
Note, you can follow along with the web console (located at https://ip-address:8443/console) to see what new resources have been created and watch the progress of the build and deployment.
build
$ oc start-build nodejs --follow
You can alternatively leave off --follow and use oc build-logs nodejs-n where n is the number of the build (output of start-build).
deploy
happens automatically, to monitor its status either watch the web console or oc get pods to see when the pod is up. Another helpful command is
$ oc status
This will help indicate what IP address the service is running, the default port for it to deploy at is 8080.
enjoy
Determine the service ip for the application by running
$ oc svc
Run/test your app by browsing to
$ curl service-ip-address:8080
update
Assuming you used the URL of your own forked report, we can easily push changes to that hosted repo and simply repeat the steps above to build which will trigger the new built image to be deployed.
delete
$ oc delete all -l name=myapp
To remove all the resources with the label "name=myapp".
Web UI
To run this example from the Web UI, you can same steps following done on the CLI as defined above by The project. Here's a video showing it in motion: